|
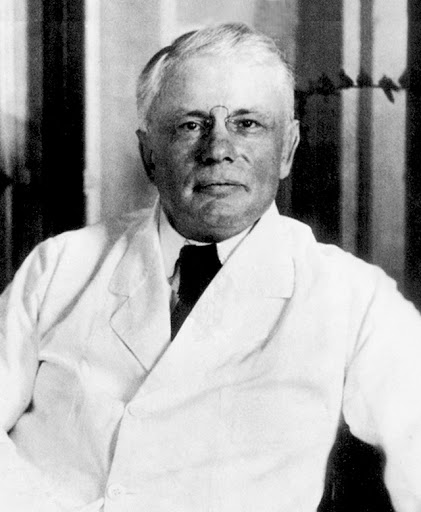
Jules Besson
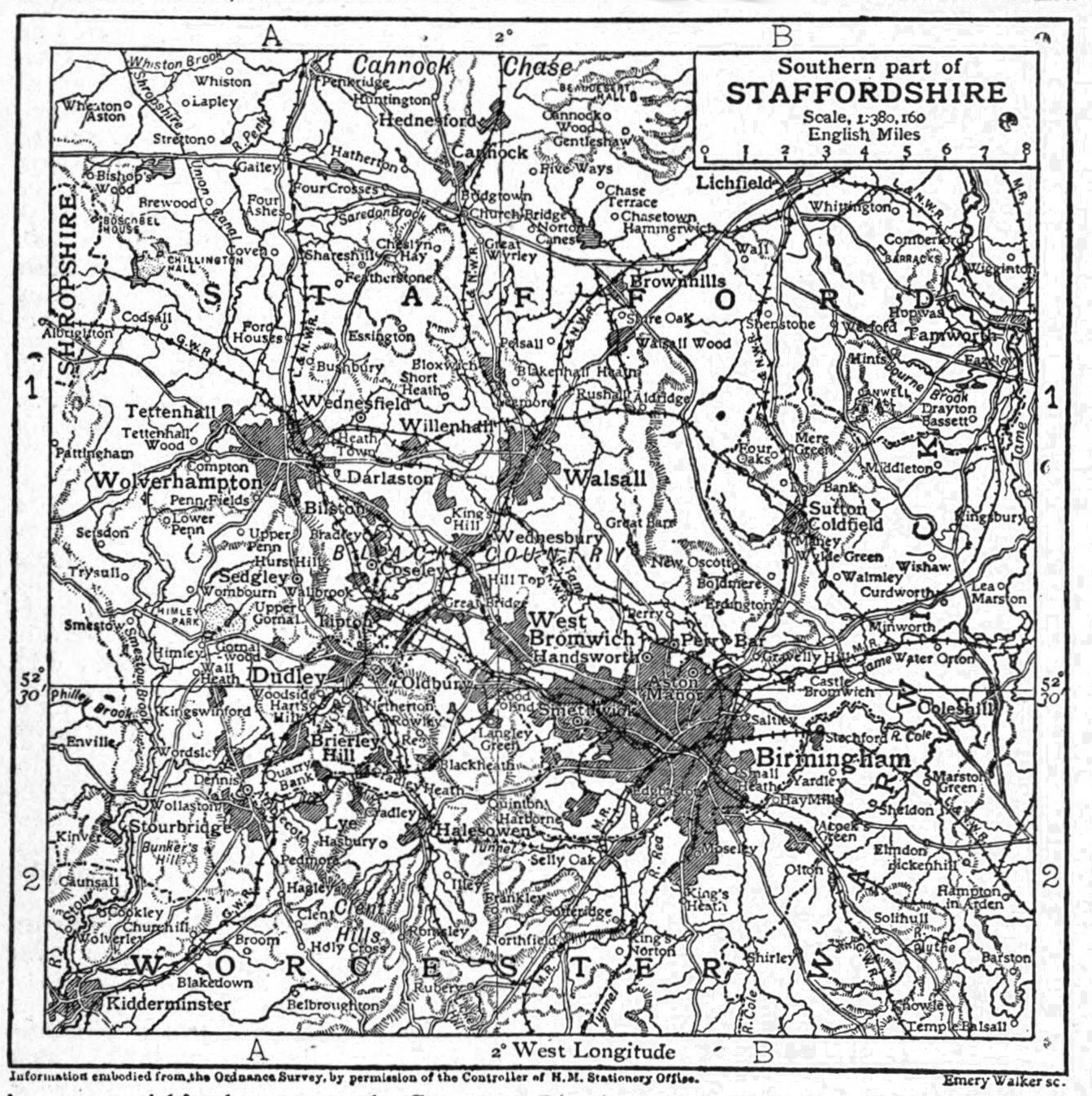
Jules Gustave Besson (1 August 1868 in Paris – ?) was a French painter. He was a pupil of Alexandre Cabanel, Élie Delaunay, and particularly Gustave Moreau at the Beaux-Arts, Paris, but did not follow his teacher's style. In his fifties he moved to Indochina. He won the Prix de l'Indochine in 1925 and in 1926 succeeded André Joyeux as director of the école d'arts appliqués at Gia Dinh. His students in Saigon were not as numerous or as influential as those of his contemporary Victor Tardieu at the EBAI in Hanoi, but their works left a vivid record of life in the south of Vietnam and Cambodia. The school also encouraged the students in the art of photography. He was succeeded at the school by the third director, Stéphane Brecq (1894–1955). Works * Au Pays Noir, 1898 - in the industrial English Black Country The Black Country is an area of the West Midlands county, England covering most of the Metropolitan Boroughs of Dudley, Sandwell and Walsall. Dudley and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paris
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. Since the 17th century, Paris has been one of the world's major centres of finance, diplomacy, commerce, fashion, gastronomy, and science. For its leading role in the arts and sciences, as well as its very early system of street lighting, in the 19th century it became known as "the City of Light". Like London, prior to the Second World War, it was also sometimes called the capital of the world. The City of Paris is the centre of the Île-de-France region, or Paris Region, with an estimated population of 12,262,544 in 2019, or about 19% of the population of France, making the region France's primate city. The Paris Region had a GDP of €739 billion ($743 billion) in 2019, which is the highest in Europe. According to the Economist Intelli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gustave Moreau
Gustave Moreau (; 6 April 1826 – 18 April 1898) was a French artist and an important figure in the Symbolist movement. Jean Cassou called him "the Symbolist painter par excellence".Cassou, Jean. 1979. ''The Concise Encyclopedia of Symbolism.'' Chartwell Books, Inc., Secaucus, New Jersey, 292 pp. He was an influential forerunner of symbolism in the visual arts in the 1860s, and at the height of the symbolist movement in the 1890s, he was among the most significant painters. Art historian Robert Delevoy wrote that Moreau "brought symbolist polyvalence to its highest point in ''Jupiter and Semele''."Delevoy, Robert L. 1978. ''Symbolist and Symbolism.'' Editions D'Art Albert Skira, Geneva//Rizzoli International Publishing, Inc. New York. 247 pp. He was a prolific artist who produced over 15,000 paintings, watercolors, and drawings. Moreau painted allegories and traditional biblical and mythological subjects favored by the fine art academies. J. K. Huysmans wrote, "Gustave Moreau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prix De L'Indochine
The Prix de l'Indochine (1914, 1920–1938) was a French colonial art prize established, originally as a one-off prize in 1910, and awarded 1914, by , Gouverneur général of Indochina. Charles Fouqueray obtained le prix Indochine 1914. From 1925 the prize was associated with the École des Beaux-Arts de l'Indochine. Winners Subsequent winners included Victor Tardieu (1920), Paul Jouve (1921), Antoine Ponchin (1922), Jean Bouchaud (1924), Jules Besson (1925), Paul-Émile Legouez (1926), Raymond Virac (1927), Henri Dabadie (1928), Lucien Lièvre (1929), Louis Rollet (1930), Évariste Jonchère (1932), Jean Despujols (1936) and Louis Bate (1938). In certain years, such as 1935 and 1937, no prize was awarded.Les salons des artistes coloniaux: suivi d'un dictionnaire des sculpteurs Stéphane Richemond Éditions de l'Amateur, 2003 These winners were not required to paint scenes from Asia, which they had usually not visited prior to winning the prize. For example, Henri Dabadie, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
André Joyeux
André Joyeux (1871-?) was a French artist, first teacher and director of the Gia Định art school (Trường Mỹ nghệ thực hành Gia Định) founded in 1913 in a suburb of Saigon, 12 years before Victor Tardieu founded the national EBAI in Hanoi.André-Pallois, Nadine. (1997). ''L'Indochine: un lieu d'échange culturel?: les peintres français.'' École française d'Extrême-Orient. Joyeux studied architecture at the École nationale supérieure des Beaux-Arts in Paris, then, around 1900, went to Saigon, possibly as an architect. In Saigon he started to paint and draw; his pictures were exhibited at the Colonial Exhibition in Marseille in 1906. He then published a first book of caricatures satirising the ''colons'' (his fellow colonial French), as ''Silhouettes Saigonnaises'' (22 plates, Saigon, 1909), then in 1912 a larger book of cartoons and text entitled ''La Vie large des colonies'' (Paris: Maurice Bauche, 1912), since translated into English as "The Colonial Good ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gia Dinh
''Gia'' is a 1998 American biographical drama television film about the life and times of one of the first supermodels, Gia Carangi. The film stars Angelina Jolie as Gia and Faye Dunaway as Wilhelmina Cooper, with Mercedes Ruehl and Elizabeth Mitchell. It was directed by Michael Cristofer and written by Cristofer and Jay McInerney. The original music score was composed by Terence Blanchard. Plot Gia Carangi is a Philadelphia native who moves to New York City to become a fashion model, and immediately catches the attention of powerful agent Wilhelmina Cooper. Gia's attitude and beauty help her rise quickly to the forefront of the modeling industry, but her persistent loneliness, especially after the death of Wilhelmina, drives her to use mood-altering drugs such as cocaine and heroin. She becomes entangled in a passionate affair with Linda, a make-up artist. Their love affair first starts when both pose nude for a photo shoot and make love afterward. Gia tries to get clean and b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Victor Tardieu
Victor François Tardieu (30 April 1870, Orliénas - 12 June 1937, Hanoi) was a French painter; cofounder of what is now known as the Vietnam University of Fine Arts. Biography In 1887, he was admitted to the École nationale des beaux-arts de Lyon. After two years there, he transferred to the Académie Julian in Paris, where he studied for a year. In 1890, he entered the École des beaux-arts de Paris, with the advice and support of Léon Bonnat. He was employed in the workshops of Bonnat and Albert Maignan until 1894. He also collaborated with the stained glass artist; producing a series of glass boxes. In 1902, he married the harpist, Caroline Luigini, daughter of the composer and conductor, Alexandre Luigini. They had one son, the writer Jean Tardieu. Shortly after, at the Salon of the Société des artistes français, he won an award that came with a travel grant, allowing him to visit London, Liverpool and Genoa. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EBAI
The Vietnam University of Fine Arts (formerly ''Hanoi College of Fine Arts'') is an art school in Hanoi, Vietnam originally established under French colonial rule in 1925. The university has trained many of Vietnam’s leading artists and each year it participates in many cultural exchanges with sister institutions overseas. History The history of the Vietnam University of Fine Arts can be traced back to the colonial ''École des Beaux Arts de l’Indochine'' (1925–45) (the ''Indochina College of Fine Arts'') which trained successive generations of Vietnamese students — and a smaller number of students from Cambodia and Laos — in the western art tradition, laying the groundwork for the development of a distinctive Vietnamese style of modern art. The ''École des Beaux-Arts de l’Indochine'' in Hanoi was the predecessor of the Hanoi College of Fine Arts ''( :vi:Trường Đại học Mỹ thuật Việt Nam)''. The ''école'' was established by the French colonia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hanoi
Hanoi or Ha Noi ( or ; vi, Hà Nội ) is the capital and second-largest city of Vietnam. It covers an area of . It consists of 12 urban districts, one district-leveled town and 17 rural districts. Located within the Red River Delta, Hanoi is the cultural and political centre of Vietnam. Hanoi can trace its history back to the third century BCE, when a portion of the modern-day city served as the capital of the historic Vietnamese nation of Âu Lạc. Following the collapse of Âu Lạc, the city was part of Han China. In 1010, Vietnamese emperor Lý Thái Tổ established the capital of the imperial Vietnamese nation Đại Việt in modern-day central Hanoi, naming the city Thăng Long (literally 'Ascending Dragon'). Thăng Long remained Đại Việt's political centre until 1802, when the Nguyễn dynasty, the last imperial Vietnamese dynasty, moved the capital to Huế. The city was renamed Hanoi in 1831, and served as the capital of French Indochina from 1902 to 1945. O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Country
The Black Country is an area of the West Midlands county, England covering most of the Metropolitan Boroughs of Dudley, Sandwell and Walsall. Dudley and Tipton are generally considered to be the centre. It became industrialised during its role as one of the birth places of the Industrial Revolution across the English Midlands with coal mines, coking, iron foundries, glass factories, brickworks and steel mills, producing a high level of air pollution. The name dates from the 1840s, and is believed to come from the soot that the heavy industries covered the area in, although the 30-foot-thick coal seam close to the surface is another possible origin. The road between Wolverhampton and Birmingham was described as "one continuous town" in 1785. Extent The Black Country has no single set of defined boundaries. Some traditionalists define it as "the area where the coal seam comes to the surface – so West Bromwich, Coseley, Oldbury, Blackheath, Cradley Heath, Old Hill, B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
19th-century French Painters
The 19th (nineteenth) century began on 1 January 1801 ( MDCCCI), and ended on 31 December 1900 ( MCM). The 19th century was the ninth century of the 2nd millennium. The 19th century was characterized by vast social upheaval. Slavery was abolished in much of Europe and the Americas. The First Industrial Revolution, though it began in the late 18th century, expanding beyond its British homeland for the first time during this century, particularly remaking the economies and societies of the Low Countries, the Rhineland, Northern Italy, and the Northeastern United States. A few decades later, the Second Industrial Revolution led to ever more massive urbanization and much higher levels of productivity, profit, and prosperity, a pattern that continued into the 20th century. The Islamic gunpowder empires fell into decline and European imperialism brought much of South Asia, Southeast Asia, and almost all of Africa under colonial rule. It was also marked by the collapse of the large S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
19th-century French Male Artists
The 19th (nineteenth) century began on 1 January 1801 ( MDCCCI), and ended on 31 December 1900 ( MCM). The 19th century was the ninth century of the 2nd millennium. The 19th century was characterized by vast social upheaval. Slavery was abolished in much of Europe and the Americas. The First Industrial Revolution, though it began in the late 18th century, expanding beyond its British homeland for the first time during this century, particularly remaking the economies and societies of the Low Countries, the Rhineland, Northern Italy, and the Northeastern United States. A few decades later, the Second Industrial Revolution led to ever more massive urbanization and much higher levels of productivity, profit, and prosperity, a pattern that continued into the 20th century. The Islamic gunpowder empires fell into decline and European imperialism brought much of South Asia, Southeast Asia, and almost all of Africa under colonial rule. It was also marked by the collapse of the large ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Male Painters
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to: * Something of, from, or related to France ** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents ** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with France ** French cuisine, cooking traditions and practices Fortnite French places Arts and media * The French (band), a British rock band * "French" (episode), a live-action episode of ''The Super Mario Bros. Super Show!'' * ''Française'' (film), 2008 * French Stewart (born 1964), American actor Other uses * French (surname), a surname (including a list of people with the name) * French (tunic), a particular type of military jacket or tunic used in the Russian Empire and Soviet Union * French's, an American brand of mustard condiment * French catheter scale, a unit of measurement of diameter * French Defence, a chess opening * French kiss, a type of kiss involving the tongue See also * France (other) * Franch, a surname * French ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |