|
José Celestino Mutis
José Celestino Bruno Mutis y Bosio (6 April 1732 – 11 September 1808) was a Spanish priest, botanist and mathematician. He was a significant figure in the Spanish American Enlightenment, whom Alexander von Humboldt met with on his expedition to Spanish America. He is one of the most important authors of the Spanish Universalist School of the 18th century, together with Juan Andrés or Antonio Eximeno. Life He was born in Cádiz and baptized with the name ''José Celestino Bruno Mutis y Bosio''. He began his medical studies at the College of Surgery in Cádiz, where he also studied physics, chemistry and botany. He graduated in medicine from the University of Seville on 2 May 1755. On 5 July 1757 he received his doctorate in medicine. From 1757 to 1760 he was interim professor of anatomy in Madrid. During those same years he continued to study botany at the Migas Calientes Botanical Gardens (now the Real Jardín Botánico de Madrid), and also astronomy and philosopher mat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spanish American Enlightenment
The ideas of the Spanish Enlightenment, which emphasized reason, science, practicality, clarity rather than obscurantism, and secularism, were transmitted from France to the New World in the eighteenth century, following the establishment of the Bourbon monarchy in Spain. In Spanish America, the ideas of the Enlightenment affected educated elites in major urban centers, especially Mexico City, Lima, and Guatemala, where there were universities founded in the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries. In these centers of learning, American-born Spanish intellectuals were already participants in intellectual and scientific discourse, with Spanish American universities increasingly anti-scholastic and opposed to “untested authority” even before the Spanish Bourbons came to power. The best studied is the University of San Carlos Guatemala, founded in 1676. In Spanish America just as in Spain, the Enlightenment had some aspects of anticlericalism, but many priests were in favor of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cádiz
Cádiz (, , ) is a city and port in southwestern Spain. It is the capital of the Province of Cádiz, one of eight that make up the autonomous community of Andalusia. Cádiz, one of the oldest continuously inhabited cities in Western Europe, was founded by the Phoenicians.Strabo, '' Geographica'' 3.5.5 In the 18th century, the Port in the Bay of Cádiz consolidated as the main harbor of mainland Spain, enjoying the virtual monopoly of trade with the Americas until 1778. It is also the site of the University of Cádiz. Situated on a narrow slice of land surrounded by the sea‚ Cádiz is, in most respects, a typically Andalusian city with well-preserved historical landmarks. The older part of Cádiz, within the remnants of the city walls, is commonly referred to as the Old Town (Spanish: ''Casco Antiguo''). It is characterized by the antiquity of its various quarters (''barrios''), among them ''El Pópulo'', ''La Viña'', and ''Santa María'', which present a marked contr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Madrid
Madrid ( , ) is the capital and most populous city of Spain. The city has almost 3.4 million inhabitants and a metropolitan area population of approximately 6.7 million. It is the second-largest city in the European Union (EU), and its monocentric metropolitan area is the third-largest in the EU.United Nations Department of Economic and Social AffairWorld Urbanization Prospects (2007 revision), (United Nations, 2008), Table A.12. Data for 2007. The municipality covers geographical area. Madrid lies on the River Manzanares in the central part of the Iberian Peninsula. Capital city of both Spain (almost without interruption since 1561) and the surrounding autonomous community of Madrid (since 1983), it is also the political, economic and cultural centre of the country. The city is situated on an elevated plain about from the closest seaside location. The climate of Madrid features hot summers and cool winters. The Madrid urban agglomeration has the second-large ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copernican Heliocentrism
Copernican heliocentrism is the astronomical model developed by Nicolaus Copernicus and published in 1543. This model positioned the Sun at the center of the Universe, motionless, with Earth and the other planets orbiting around it in circular paths, modified by epicycles, and at uniform speeds. The Copernican model displaced the geocentric model of Ptolemy that had prevailed for centuries, which had placed Earth at the center of the Universe. Although he had circulated an outline of his own heliocentric theory to colleagues sometime before 1514, he did not decide to publish it until he was urged to do so later by his pupil Rheticus. Copernicus's challenge was to present a practical alternative to the Ptolemaic model by more elegantly and accurately determining the length of a solar year while preserving the metaphysical implications of a mathematically ordered cosmos. Thus, his heliocentric model retained several of the Ptolemaic elements, causing inaccuracies, such as the pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Del Rosario University
Universidad del Rosario (officially in es, Colegio Mayor de Nuestra Señora del Rosario) is a Colombian university founded on Roman Catholic principles, in 1653 by Fray Cristobal de Torres. Located in Bogotá, due to its important place in Colombian history, it is known as "the Cradle of the Republic". Most faculties reside at the Cloister, the main campus located in the historic-geographical centre of Bogotá. It also included a private all-male traditional primary and secondary school until 2008. Nowadays the institution is based on secular ideas and remains very influential in Colombian culture and public life. At least 28 of Colombia's Presidents have been students of this university. It has influenced and participated in very important transitional processes like the revolution for the independence from Spain and the drafting of the Political National Constitution of 1991. One of the most important 1886 Constitution's Supreme Court (1936), the so-called golden court, was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mariquita, Tolima
San Sebastián de Mariquita is a town and municipality in the Tolima department of Colombia, about northwest of Bogotá. This town and municipality contains several important Spanish settlements that were located here due to its vicinity to the Magdalena River. Today, Mariquita is frequented by tourists from the capital visiting attractions like the Medina Waterfalls (''Cataratas de Medina'') and the mint (''Casa de la Moneda''). The Spanish conquistador Gonzalo Jiménez de Quesada died there and is buried in the Primatial Cathedral of Bogotá. Today it is home to large hotels and haciendas, among them Villa de los Caballeros. The population of the municipality was 32,642 as of the 2005 census.http://www.dane.gov.co/files/censo2005/regiones/tolima/mariquita.pdf Notable people * Gilberto Rodríguez Orejuela, drug lord * Miguel Rodríguez Orejuela Miguel Ángel Rodríguez Orejuela (born August 15, 1943) is a convicted Colombian drug lord, formerly one of the leaders of the Cal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
La Mesa, Cundinamarca
La Mesa () is a municipality and town of Colombia in the Tequendama Province of the department of Cundinamarca. The urban centre is located from Bogotá. Geography Its name ("The Table" in Spanish) comes from its geographical position, located on the top of a plateau with an area of 14 km2 (2.5 sq mi) in the centre of the Eastern Ranges of the Colombian Andes. History Before the Spanish conquest of the Muisca, the area was inhabited by the Panche who were notable warriors and defeated by an alliance of the Spanish conquistadors and the ''zipa'' Sagipa in the Battle of Tocarema on August 20, 1538. This town is famed for the Botanical Expedition on the New Kingdom of Granada which commenced from there in 1783 led by the biologist José Celestino Mutis. The expedition researched local fauna and flora. It was also an important trade centre during the 19th and part of the 20th century. Originally La Mesa was located a short distance from its present location and was know ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Río Magdalena
The Magdalena River ( es, Río Magdalena, ; less commonly ) is the main river of Colombia, flowing northward about through the western half of the country. It takes its name from the biblical figure Mary Magdalene. It is navigable through much of its lower reaches, in spite of the shifting sand bars at the mouth of its river delta, delta, as far as Honda, Tolima, Honda, at the downstream base of its rapids. It flows through the Magdalena River Valley. Its drainage basin covers a surface of , which is 24% of the country's area and where 66% of its population lives. Course The Magdalena River is the largest river system of the northern Andes, with a length of 1,612 km. Its headwaters are in the south of Colombia, where the Andes, Andean subranges Cordillera Central (Colombia), Cordillera Central and Cordillera Oriental, Colombia, Cordillera Oriental separate, in Huila Department. The river runs east then north in a great valley between the two cordilleras. It reaches the coast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (; 23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after his ennoblement in 1761 as Carl von Linné Blunt (2004), p. 171. (), was a Swedish botanist, zoologist, taxonomist, and physician who formalised binomial nomenclature, the modern system of naming organisms. He is known as the "father of modern taxonomy". Many of his writings were in Latin; his name is rendered in Latin as and, after his 1761 ennoblement, as . Linnaeus was born in Råshult, the countryside of Småland, in southern Sweden. He received most of his higher education at Uppsala University and began giving lectures in botany there in 1730. He lived abroad between 1735 and 1738, where he studied and also published the first edition of his ' in the Netherlands. He then returned to Sweden where he became professor of medicine and botany at Uppsala. In the 1740s, he was sent on several journeys through Sweden to find and classify plants and animals. In the 1750s and 1760s, he continued to collect an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
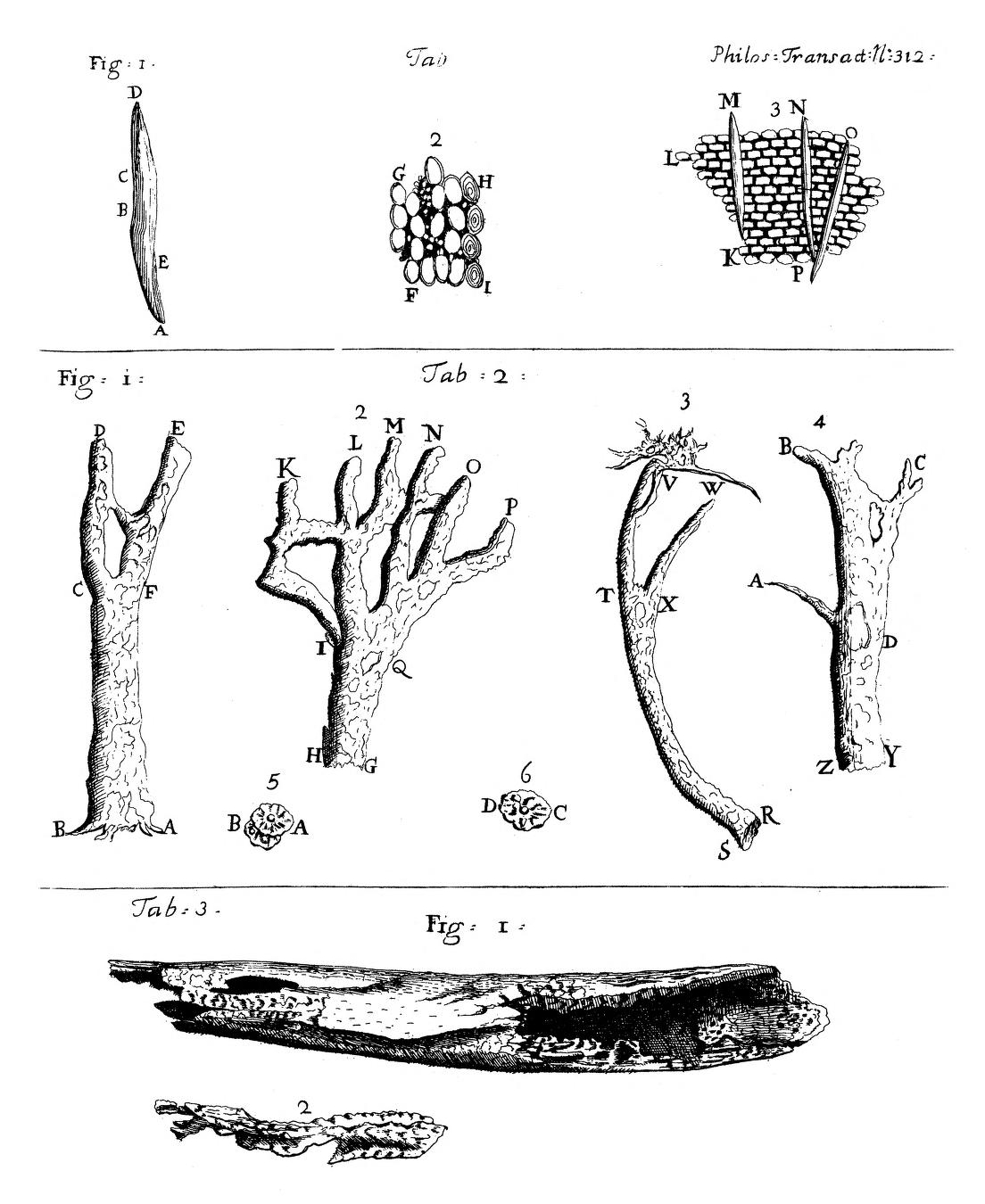
Cinchona
''Cinchona'' (pronounced or ) is a genus of flowering plants in the family Rubiaceae containing at least 23 species of trees and shrubs. All are native to the Tropical Andes, tropical Andean forests of western South America. A few species are reportedly naturalization (biology), naturalized in Central America, Jamaica, French Polynesia, Sulawesi, Saint Helena in the South Atlantic, and São Tomé and Príncipe off the coast of tropical Africa, and others have been cultivated in India and Java, where they have formed hybrids. ''Cinchona'' has been historically sought after for its medicinal value, as the bark of several species yields quinine and other alkaloids. These were the only effective treatments against malaria during the height of European colonialism, which made them of great economic and political importance. Trees in the genus are also known as fever trees because of their anti-malarial properties. The artificial Quinine total synthesis, synthesis of quinine in 1944 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |