|
Jonas C. Peters
Jonas C. Peters (born 1971 in Chicago, Illinois) is the Bren Professor of Chemistry at the California Institute of Technology and Director of the Resnick Sustainability Institute. He has contributed to the development of catalysts and photocatalysts relevant to small molecule activation. Early life and education Peters was born in 1971 in Chicago, Illinois. He received his Bachelor of Sciences from the University of Chicago in Chemistry in 1993. While an undergraduate student, he worked under Gregory L. Hillhouse on synthetic methods in inorganic chemistry, specifically with regard to the stabilization of reactive species including diazene and nitroxyl. Following his undergraduate, Peters spent a year as a Marshall Scholar at the University of Nottingham working with James J. Turner, . There, he studied physical inorganic chemistry including the photochemical generation and detection of short-lived transient organometallic species by rapid time-resolved infrared spectroscopy. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chicago
(''City in a Garden''); I Will , image_map = , map_caption = Interactive Map of Chicago , coordinates = , coordinates_footnotes = , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = United States , subdivision_type1 = State , subdivision_type2 = Counties , subdivision_name1 = Illinois , subdivision_name2 = Cook and DuPage , established_title = Settled , established_date = , established_title2 = Incorporated (city) , established_date2 = , founder = Jean Baptiste Point du Sable , government_type = Mayor–council , governing_body = Chicago City Council , leader_title = Mayor , leader_name = Lori Lightfoot ( D) , leader_title1 = City Clerk , leader_name1 = Anna Valencia ( D) , unit_pref = Imperial , area_footnotes = , area_tot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marshall Scholarship
The Marshall Scholarship is a postgraduate scholarship for "intellectually distinguished young Americans ndtheir country's future leaders" to study at any university in the United Kingdom. It is widely considered one of the most prestigious scholarships for U.S. citizens, and along with the Fulbright Scholarship, it is the only broadly available scholarship available to Americans to study at any university in the United Kingdom. Created by the Parliament of the United Kingdom in 1953 as a living gift to the United States in recognition of the generosity of Secretary of State George C. Marshall and the Marshall Plan in the wake of World War II, the goal of the scholarship was to strengthen the Special Relationship between the two countries for "the good of mankind in this turbulent world." The scholarships are awarded by the Marshall Aid Commemoration Commission and are largely funded by the British government. The program was also the first major co-educational British gradu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proton-coupled Electron Transfer
A Proton-coupled electron transfer (PCET) is a chemical reaction that involves the transfer of electrons and protons from one atom to another. The term was originally coined for single proton, single electron processes that are concerted, but the definition has relaxed to include many related processes. Reactions that involve the concerted shift of a single electron and a single proton are often called Concerted Proton-Electron Transfer or CPET. In PCET, the proton and the electron (i) start from different orbitals and (ii) are transferred to different atomic orbitals. They transfer in a concerted elementary step. CPET contrast to step-wise mechanisms in which the electron and proton are transferred sequentially. :ET : X+ → Xsup>+ + sup>− :PT : X+ → sup>− + Msup>+ :CPET : X+ → + M Examples PCET is thought to be pervasive. Important examples include water oxidation in photosynthesis, nitrogen fixation, oxygen reduction reaction, and the function of hydrogenas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrocatalyst
An electrocatalyst is a catalyst that participates in electrochemical reactions. Electrocatalysts are a specific form of catalysts that function at electrode surfaces or, most commonly, may be the electrode surface itself. An electrocatalyst can be heterogeneous such as a platinized electrode. Homogeneous electrocatalysts, which are soluble, assist in transferring electrons between the electrode and reactants, and/or facilitate an intermediate chemical transformation described by an overall half reaction. Major challenges in electrocatalysts focus on fuel cells. Practical electrocatalysts Chloralkali process The chloralkali process is a large scale application that uses electrocatalysts. This technology supplies most of the chlorine and sodium hydroxide required by many industries. The cathode is a mixed metal oxide clad titanium anode (also called a dimensionally stable anode). Electrofluorination Many organofluorine compounds are produced by electrofluorination. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Academy Of Arts And Sciences
The American Academy of Arts and Sciences (abbreviation: AAA&S) is one of the oldest learned societies in the United States. It was founded in 1780 during the American Revolution by John Adams, John Hancock, James Bowdoin, Andrew Oliver, and other Founding Fathers of the United States. It is headquartered in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Membership in the academy is achieved through a thorough petition, review, and election process. The academy's quarterly journal, ''Dædalus'', is published by MIT Press on behalf of the academy. The academy also conducts multidisciplinary public policy research. History The Academy was established by the Massachusetts legislature on May 4, 1780, charted in order "to cultivate every art and science which may tend to advance the interest, honor, dignity, and happiness of a free, independent, and virtuous people." The sixty-two incorporating fellows represented varying interests and high standing in the political, professional, and commercial secto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joint Center For Artificial Photosynthesis
The Joint Center for Artificial Photosynthesis (JCAP), founded in 2010, is a (DOE) Energy Innovation Hub whose primary mission is to find a cost-effective method to produce fuels using only sunlight, water, and carbon-dioxide. The program has a budget of $122M over five years, subject to Congressional appropriation. The Director of JCAP is Professor Harry Atwater of Caltech and its two main centers are located at the California Institute of Technology and the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory. In addition, JCAP has partners from Stanford University, the University of California at Berkeley, University of California at Santa Barbara, University of California at Irvine, the University of California at San Diego, and Stanford Linear Accelerator. In addition, JCAP also serves as a hub for other solar fuels research teams across the United States, including 20 DOE Energy Frontier Research Center. In Obama's 2011 State of the Union address, he mentioned the Joint Center for Artifi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrochemical Reduction Of Carbon Dioxide
The electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide, also known as electrolysis of carbon dioxide, is the conversion of carbon dioxide () to more reduced chemical species using electrical energy. It is one possible step in the broad scheme of carbon capture and utilization, nevertheless it is deemed to be one of the most promising approaches. Electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide represents a possible means of producing chemicals or fuels, converting carbon dioxide () to organic feedstocks such as formic acid (HCOOH), carbon monoxide (CO), methane (CH4), ethylene (C2H4) and ethanol (C2H5OH). Among the more selective metallic catalysts in this field are tin for formic acid, silver for carbon monoxide and copper for methane, ethylene or ethanol. Methanol, propanol and 1-butanol have also been produced via CO2 electrochemical reduction, albeit in small quantities. The first examples of electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide are from the 19th century, when carbon dioxide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrogen Fixation
Nitrogen fixation is a chemical process by which molecular nitrogen (), with a strong triple covalent bond, in the air is converted into ammonia () or related nitrogenous compounds, typically in soil or aquatic systems but also in industry. Atmospheric nitrogen is molecular dinitrogen, a relatively nonreactive molecule that is metabolically useless to all but a few microorganisms. Biological nitrogen fixation or ''diazotrophy'' is an important microbials mediated process that converts dinitrogen (N2) gas to ammonia (NH3) using the nitrogenase protein complex (Nif). Nitrogen fixation is essential to life because fixed inorganic nitrogen compounds are required for the biosynthesis of all nitrogen-containing organic compounds, such as amino acids and proteins, nucleoside triphosphates and nucleic acids. As part of the nitrogen cycle, it is essential for agriculture and the manufacture of fertilizer. It is also, indirectly, relevant to the manufacture of all nitrogen chemical c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gregory Fu
Gregory (Greg) C. Fu is a Professor of organic chemistry at the California Institute of Technology and the Norman Chandler Professor of Chemistry. The current research interests of the Fu laboratory include metal-catalyzed coupling reactions and the design of chiral catalysts. In particular, the group is focused on the development of nickel-catalyzed enantioselective cross-couplings of alkyl electrophiles and on photoinduced, copper-catalyzed carbon–heteroatom bond-forming reactions. The group works in collaboration with the laboratory of Professor Jonas C. Peters. In 2014, he was elected as a member of the National Academy of Sciences.. He was awarded an Arthur C. Cope Scholar Award in 1998-1999. He was awarded the Elias J. Corey Award from the American Chemical Society in 2004. Education Gregory Fu received his BS from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology in 1985, where he worked in the laboratory of Professor Karl Barry Sharpless, then completed his PhD at Harvard U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
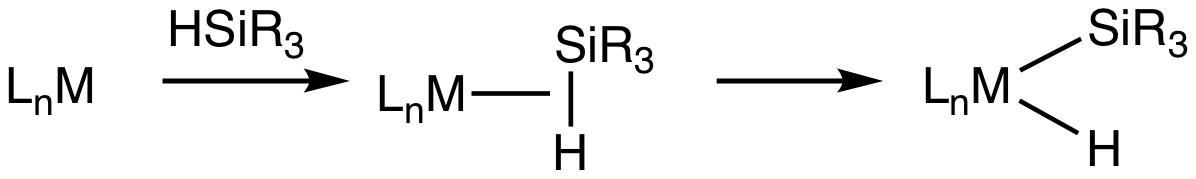
Transition Metal Silane Complexes
Transition metal silane complexes are coordination compounds containing hydrosilane ligands. An early example is (MeC5H4)Mn(CO)2(η2-HSiPh3) (Ph = C6H5). The bonding in silane sigma complexes is similar to that invoked in agostic interactions. The metal center engages the Si-H entity via a 3-center, 2-electron bond. It is widely assumed that these sigma complexes are intermediates in the oxidative addition of hydrosilanes to give metal silyl hydrides. This transformation is invoked in hydrosilylation catalysis. Evidence for sigma-silane complexes is provided by proton NMR spectroscopy. For (MeC5H4)Mn(CO)2(η2-HSiPh3), J(29Si,1H) = 65 Hz compared to 180 Hz in free diphenylsilane. In silyl hydride complexes, the coupling in about 6 Hz. Neutron diffraction Neutron diffraction or elastic neutron scattering is the application of neutron scattering to the determination of the atomic and/or magnetic structure of a material. A sample to be examined is placed in a beam of thermal o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphine Ligand
A metal-phosphine complex is a In coordination complex containing one or more phosphine ligands. Almost always, the phosphine is an organophosphine of the type R3P (R = alkyl, aryl). Metal phosphine complexes are useful in homogeneous catalysis. Prominent examples of metal phosphine complexes include Wilkinson's catalyst (Rh(PPh3)3Cl), Grubbs' catalyst, and tetrakis(triphenylphosphine)palladium(0). Preparation Many metal phosphine complexes are prepared by reactions of metal halides with preformed phosphines. For example, treatment of a suspension of palladium chloride in ethanol with triphenylphosphine yields monomeric bis(triphenylphosphine)palladium(II) chloride units. : dCl2sub>n + 2PPh3 → PdCl2(PPh3)2 The first reported phosphine complexes were ''cis''- and ''trans''-PtCl2(PEt3)2 reported by Cahours and Gal in 1870. Often the phosphine serves both as a ligand and as a reductant. This property is illustrated by the synthesis of many platinum-metal complexes of triphenylph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Don Tilley
T. Don Tilley (born in Norman, Oklahoma, November 22, 1954) is a professor of chemistry at the University of California, Berkeley. __TOC__ Career In 1977, Tilley received his B.S. degree in chemistry from the University of Texas. In 1982, he earned his Ph.D. degree from the University of California, Berkeley for his research on organolanthanide chemistry with Professor Richard A. Andersen. Afterwards, he conducted post-doctoral research with Prof. Robert H. Grubbs and Prof. John E. Bercaw at the California Institute of Technology and with Luigi Venanzi and Piero Pino at ETH in Switzerland, during which he developed the chemistry of the (pentamethylcyclopentadienyl)ruthenium fragment ( p*Ru. He started his independent research career at UC San Diego in 1983, where he was promoted to associate professor in 1988, and to Professor in 1990. In 1994, he accepted appointments as a professor of chemistry at UC Berkeley and Faculty Senior Scientist at the Lawrence Berkeley National L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |