|
Join In Ant-hole
Join may refer to: * Join (law), to include additional counts or additional defendants on an indictment *In mathematics: ** Join (mathematics), a least upper bound of sets orders in lattice theory ** Join (topology), an operation combining two topological spaces ** Join (sigma algebra), a refinement of sigma algebras ** Join (algebraic geometry), a union of lines between two varieties *In computing: ** Join (relational algebra), a binary operation on tuples corresponding to the relation join of SQL *** Join (SQL), relational join, a binary operation on SQL and relational database tables *** join (Unix), a Unix command similar to relational join ** Join-calculus, a process calculus developed at INRIA for the design of distributed programming languages *** Join-pattern, generalization of Join-calculus *** Joins (concurrency library), a concurrent computing API from Microsoft Research * Join Network Studio of NENU, a non-profit organization of Northeast Normal University * Join ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Join (law)
In law, a joinder is the joining of two or more legal issues together. Procedurally, a joinder allows multiple issues to be heard in one hearing or trial and occurs if the issues or parties involved overlap sufficiently to make the process more efficient or fairer. That helps courts avoid hearing the same facts multiple times or seeing the same parties return to court separately for each of their legal disputes. The term is also used in the realm of contracts to describe the joining of new parties to an existing agreement. Criminal procedure Joinder in criminal law refers to the inclusion of additional counts or additional defendants on an indictment. In English law, charges for any offence may be joined in the same indictment if those charges are founded on the same facts or form or are a part of a series of offences of the same or a similar nature. A number of defendants may be joined in the same indictment even if no single count applies to all of them if the counts are suffic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joins (concurrency Library)
Joins is an asynchronous concurrent computing API (Join-pattern) from Microsoft Research for the .NET Framework. It is based on join calculus and makes the concurrency constructs of the Cω language available as a CLI assembly that any CLI compliant language can use. Overview Joins can be used to express concurrency in an application using the joins pattern, usable both for multi-threaded applications as well as for event based distributed applications. The Joins API emulates declarative type-safe expression of synchronization patterns. The Joins library emulates asynchronous and synchronous methods. An asynchronous method, in Cω and Joins parlance, is one which does not block the caller method, nor does it return any result, whereas a synchronous method blocks the caller method. In the Joins API, synchronous as well as asynchronous methods are implemented as generic delegate Delegate or delegates may refer to: * Delegate, New South Wales, a town in Australia * Delegate (C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joinery (other)
Joinery is a part of woodworking that involves joining pieces of wood, engineered lumber, or synthetic substitutes (such as lamination#Wood, laminate), to produce more complex items. Some woodworking joints employ mechanical fasteners, bindings, or adhesives, while others use only wood elements (such as dowels or plain mortise and tenon fittings). The characteristics of wooden joints - strength, flexibility, toughness, appearance, etc. - derive from the properties of the materials involved and the purpose of the joint. Therefore, different joinery techniques are used to meet differing requirements. For example, the joinery used to construct a house can be different from that used to make cabinetry or furniture, although some concepts overlap. In British English joinery is distinguished from carpentry, which is considered to be a form of structural timber work.; in other locales joinery is considered a form of carpentry. History Many traditional wood joinery techniques use the d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joiner
A joiner is an artisan and tradesperson who builds things by joining pieces of wood, particularly lighter and more ornamental work than that done by a carpenter, including furniture and the "fittings" of a house, ship, etc. Joiners may work in a workshop, because the formation of various joints is made easier by the use of non-portable, powered machinery, or on job site. A joiner usually produces items such as interior and exterior doors, windows, stairs, tables, bookshelves, cabinets, furniture, etc. In shipbuilding a ''marine joiner'' may work with materials other than wood such as linoleum, fibreglass, hardware, and gaskets. The terms ''joinery'' and ''joiner'' are in common use in the UK, Australia, and New Zealand. The term is not in common use in North America, although the main trade union for American carpenters is called the United Brotherhood of Carpenters and Joiners of America. In the UK, an apprentice of wood occupations could choose to study ''bench joinery'' or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joining (metalworking)
Metalworking is the process of shaping and reshaping metals to create useful objects, parts, assemblies, and large scale structures. As a term it covers a wide and diverse range of processes, skills, and tools for producing objects on every scale: from huge ships, buildings, and bridges down to precise engine parts and delicate jewelry. The historical roots of metalworking predate recorded history; its use spans cultures, civilizations and millennia. It has evolved from shaping soft, native metals like gold with simple hand tools, through the smelting of ores and hot forging of harder metals like iron, up to highly technical modern processes such as machining and welding. It has been used as an industry, a driver of trade, individual hobbies, and in the creation of art; it can be regarded as both a science and a craft. Modern metalworking processes, though diverse and specialized, can be categorized into one of three broad areas known as forming, cutting, or joining processes. Mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joining (woodworking)
Join may refer to: * Join (law), to include additional counts or additional defendants on an indictment *In mathematics: ** Join (mathematics), a least upper bound of sets orders in lattice theory ** Join (topology), an operation combining two topological spaces ** Join (sigma algebra), a refinement of sigma algebras ** Join (algebraic geometry), a union of lines between two varieties *In computing: ** Join (relational algebra), a binary operation on tuples corresponding to the relation join of SQL *** Join (SQL), relational join, a binary operation on SQL and relational database tables *** join (Unix), a Unix command similar to relational join ** Join-calculus, a process calculus developed at INRIA for the design of distributed programming languages *** Join-pattern, generalization of Join-calculus *** Joins (concurrency library), a concurrent computing API from Microsoft Research * Join Network Studio of NENU, a non-profit organization of Northeast Normal University * Joi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joins
Join may refer to: * Join (law), to include additional counts or additional defendants on an indictment *In mathematics: ** Join (mathematics), a least upper bound of sets orders in lattice theory ** Join (topology), an operation combining two topological spaces ** Join (sigma algebra), a refinement of sigma algebras ** Join (algebraic geometry), a union of lines between two varieties *In computing: ** Join (relational algebra), a binary operation on tuples corresponding to the relation join of SQL *** Join (SQL), relational join, a binary operation on SQL and relational database tables *** join (Unix), a Unix command similar to relational join ** Join-calculus, a process calculus developed at INRIA for the design of distributed programming languages *** Join-pattern, generalization of Join-calculus *** Joins (concurrency library), a concurrent computing API from Microsoft Research * Join Network Studio of NENU, a non-profit organization of Northeast Normal University * Joins.com, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Join Network Studio Of NENU
Join Network Studio() of Northeast Normal University China is affiliated with Student Career Service Center of NENU. This is a non-profit organization composed by some undergraduate students. All departments except Software Department of the studio are located at the administration building of the main campus of NENU, and Software Department is situated in the Jingyue campus. History At the time of 1999, the informationization of the employment for graduates of China had not started yet, and there is hardly any specialized websites of employment information for graduates. Employment information service was in the stage of low efficiency and high cost, and paper was the medium used most commonly. The reformation on informationization of the employment and the idea of the invisible market on the World Wide Web had not been established on a large scale. The decision makers of the work on employment for students realized that it is necessary to construct a top-ranking employment in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
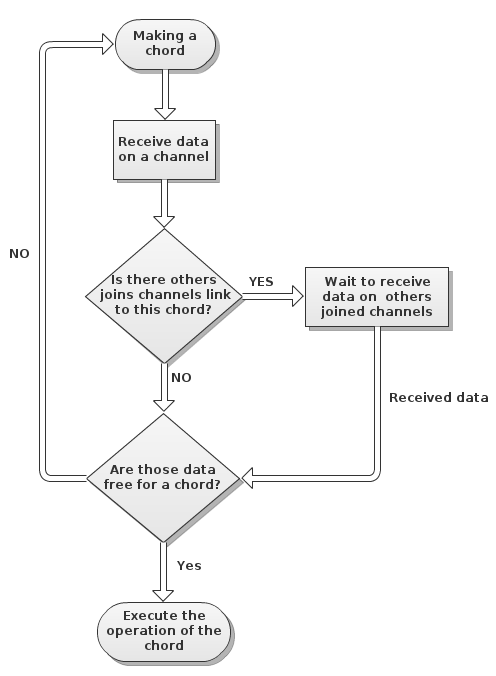
Join-pattern
Join-patterns provides a way to write concurrent, parallel and distributed computer programs by message passing. Compared to the use of threads and locks, this is a high level programming model using communication constructs model to abstract the complexity of concurrent environment and to allow scalability. Its focus is on the execution of a chord between messages atomically consumed from a group of channels. This template is based on join-calculus and uses pattern matching. Concretely, this is done by allowing the join definition of several functions and/or channels by matching concurrent call and messages patterns. It is a type of concurrency pattern because it makes easier and more flexible for these entities to communicate and deal with the multi-threaded programming paradigm. Description The join-pattern (or a chord in Cω) is like a super pipeline with synchronisation and matching. In fact, this concept is summarise by match and join a set of message available from d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Join (mathematics)
In mathematics, specifically order theory, the join of a subset S of a partially ordered set P is the supremum (least upper bound) of S, denoted \bigvee S, and similarly, the meet of S is the infimum (greatest lower bound), denoted \bigwedge S. In general, the join and meet of a subset of a partially ordered set need not exist. Join and meet are dual to one another with respect to order inversion. A partially ordered set in which all pairs have a join is a join-semilattice. Dually, a partially ordered set in which all pairs have a meet is a meet-semilattice. A partially ordered set that is both a join-semilattice and a meet-semilattice is a lattice. A lattice in which every subset, not just every pair, possesses a meet and a join is a complete lattice. It is also possible to define a partial lattice, in which not all pairs have a meet or join but the operations (when defined) satisfy certain axioms. The join/meet of a subset of a totally ordered set is simply the maximal/mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Join-calculus
The join-calculus is a process calculus developed at INRIA. The join-calculus was developed to provide a formal basis for the design of distributed programming languages, and therefore intentionally avoids communications constructs found in other process calculi, such as rendezvous communications, which are difficult to implement in a distributed setting. Despite this limitation, the join-calculus is as expressive as the full π-calculus. Encodings of the π-calculus in the join-calculus, and vice versa, have been demonstrated. The join-calculus is a member of the π-calculus family of process calculi, and can be considered, at its core, an asynchronous π-calculus with several strong restrictions: *Scope restriction, reception, and replicated reception are syntactically merged into a single construct, the ''definition''; *Communication occurs only on defined names; *For every defined name there is exactly one replicated reception. However, as a language for programming, the j ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Join (Unix)
join is a command in Unix and Unix-like operating systems that merges the lines of two sorted text files based on the presence of a common field. It is similar to the join operator used in relational databases but operating on text files. Overview The join command takes as input two text files and a number of options. If no command-line argument is given, this command looks for a pair of lines from the two files having the same first field (a sequence of characters that are different from space), and outputs a line composed of the first field followed by the rest of the two lines. The program arguments specify which character to be used in place of space to separate the fields of the line, which field to use when looking for matching lines, and whether to output lines that do not match. The output can be stored to another file rather than printing using redirection. As an example, the two following files list the known fathers and the mothers of some people. Both files have been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |