|
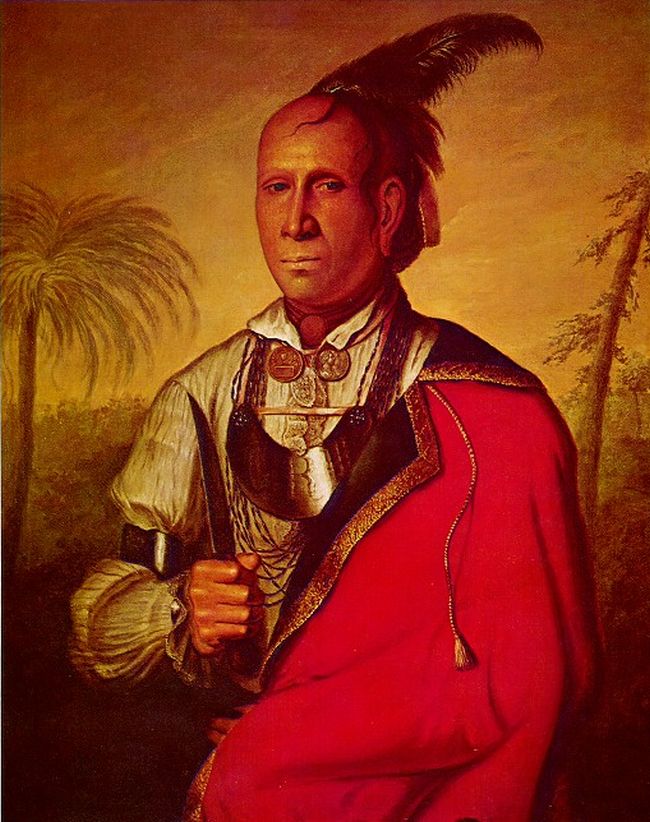
John Watts (Cherokee Chief)
John Watts (or'' Kunokeski ''), also known as Young Tassel, was one of the leaders of the Chickamauga Cherokee (or "Lower Cherokee") during the Cherokee-American wars. Watts became particularly active in the fighting after frontiersmen murdered his uncle, Old Tassel Carpenter 1708-1788, in 1788, while he traveled with Cherokee delegates to a peace conference. Family life John Watts 1746-1808 was the "mixed-blood", or mixed-race son of British trader John Watts 1704-1779 and a Cherokee mother, Oousta White Owl Carpenter 1722-1768. The senior Watts, father of Young Tassell, served as the official British government Indian interpreter for the area until his death in 1779. Watts's mother, Oousta, was a sister of Cherokee chiefs Attakullkulla Carpenter 1702-1777 and Old Tassel - Great Eagle Carpenter 1702-1777, father to Chief DoubleHead, Hanging Maw and Pumpkin Boy, . The young Watts was raised in Cherokee culture. Watts' parents resided in the Overhill Towns along the Little Tennes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chickamauga Cherokee
The Chickamauga Cherokee refers to a group that separated from the greater body of the Cherokee during the American Revolutionary War. The majority of the Cherokee people wished to make peace with the Americans near the end of 1776, following several military setbacks and American reprisals. The followers of the skiagusta (or red chief), Dragging Canoe, moved with him in the winter of 1776–77 down the Tennessee River away from their historic Overhill Cherokee towns. Relocated in a more isolated area, they established 11 new towns in order to gain distance from colonists' encroachments. The frontier Americans associated Dragging Canoe and his band with their new town on Chickamauga Creek and began to refer to them as the ''Chickamaugas.'' Five years later, the Chickamauga moved further west and southwest into present-day Alabama, establishing five larger settlements. They were then more commonly known as the ''Lower Cherokee''. This term was closely associated with the peop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Major Ridge
Major Ridge, The Ridge (and sometimes Pathkiller II) (c. 1771 – 22 June 1839) (also known as ''Nunnehidihi'', and later ''Ganundalegi'') was a Cherokee leader, a member of the tribal council, and a lawmaker. As a warrior, he fought in the Cherokee–American wars against American frontiersmen. Later, Major Ridge led the Cherokee in alliances with General Andrew Jackson and the United States in the Creek and Seminole wars of the early 19th century. Along with Charles R. Hicks and James Vann, Ridge was part of the "Cherokee triumvirate," a group of rising younger chiefs in the early nineteenth-century Cherokee Nation who supported acculturation and other changes in how the people dealt with the United States. All identified as Cherokee; they were of mixed race and had some exposure to European-American culture. Ridge became a wealthy planter, slave owner, and ferryman in Georgia. Under increasing pressure for removal from the federal government, Ridge and others of the Tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clinch River
The Clinch River is a river that flows southwest for more than through the Great Appalachian Valley in the U.S. states of Virginia and Tennessee, gathering various tributaries, including the Powell River, before joining the Tennessee River in Kingston, Tennessee. Course The Clinch River is dammed twice: by Norris Dam, the first dam built by the Tennessee Valley Authority (TVA); and by the Melton Hill Dam, the only TVA dam with a navigation lock that is not located on the main channel of the Tennessee River. An important tributary of the Clinch River is the Powell River. The Clinch and Powell River drainage basins are separated by Powell Mountain. Tributaries entering the Clinch River below Norris Dam but above Melton Hill Dam include Coal Creek, Hinds Creek, Bull Run Creek, and Beaver Creek. Poplar Creek enters the river below the Melton Hill Dam. History A peninsula located at the mouth of the Clinch River, called Southwest Point, was the site of an early frontier fort ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muscle Shoals, Alabama
Muscle Shoals is the largest city in Colbert County, Alabama, Colbert County, Alabama, United States. It is located along the Tennessee River in the northern part of the state and, as of the 2010 United States Census, 2010 census, the population of Muscle Shoals was 13,146. The estimated population in 2019 was 14,575. Both the city and the Florence-Muscle Shoals Metropolitan Area (including four cities in Colbert and Lauderdale County, Alabama, Lauderdale counties) are commonly called "the Shoals". Northwest Alabama Regional Airport serves the Shoals region, located in the northwest section of the state. Due to its strategic location along the Tennessee River, Muscle Shoals had long been territory of Native American tribes. In the late 18th and early 19th centuries, as Europeans entered the area in greater number, it became a center of historic land disputes. The new state of Georgia had ambitions to anchor its western claims (to the Mississippi River) by encouraging European- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skiagusta
A skiagusta (ᎠᏍᎦᏯᎬᏍᏔ, also ''asgayagvsta'', also ''skyagunsta'', also ''skayagusta''), (ᎠᏍᎦᏯᎬᏍᏔ, ''asgayagvsta''), also spelled ''skyagusta'', ''skiagunsta'', ''skyagunsta'', ''skayagunsta'', ''skygusta'', ''askayagusta'', ''asgayagusta'', ''skyacust'', or ''syacust''.Cherokee has 17 verb tenses, 10 persons, and six tones. See is a Cherokee title for a war chief, known as the '' 'red chief' '' in times of turmoil. The skiagusta was the highest possible rank for a red chief; however, he remained subordinate to the council of the 'white', or peace, chief in non-tactical matters, even during wartime. Cherokee leaders Before the 1794 establishment of the Cherokee Nation, the Cherokee people had no standing government. The citizens were all considered equal, although those with the ability to speak well were highly regarded and held more power in council. The Cherokee people as a whole were historically connected by a decentralized and loose confederacy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cherokee Nation (19th Century)
The Cherokee Nation (Cherokee: ᏣᎳᎩᎯ ᎠᏰᎵ ''Tsalagihi Ayeli'' or ᏣᎳᎩᏰᎵ ''Tsalagiyehli''), also known as the Cherokee Nation of Oklahoma, is the largest of three Cherokee federally recognized tribes in the United States. It was established in the 20th century and includes people descended from members of the Old Cherokee Nation who relocated, due to increasing pressure, from the Southeast to Indian Territory and Cherokee who were forced to relocate on the Trail of Tears. The tribe also includes descendants of Cherokee Freedmen, Absentee Shawnee, and Natchez Nation. As of 2021, over 400,000 people were enrolled in the Cherokee Nation. Headquartered in Tahlequah, Oklahoma, the Cherokee Nation has a reservation spanning 14 counties in the northeastern corner of Oklahoma. These are Adair, Cherokee, Craig, Delaware, Mayes, McIntosh, Muskogee, Nowata, Ottawa, Rogers, Sequoyah, Tulsa, Wagoner, and Washington counties. History Late 18th century through 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Principal Chiefs Of The Cherokee
Principal Chief is today the title of the chief executives of the Cherokee Nation, of the Eastern Band of Cherokee Indians, and of the United Keetoowah Band of Cherokee Indians, the three federally recognized tribes of Cherokee. In the eighteenth century, when the people were primarily organized by clans and towns, they would appoint a leader for negotiations with the Europeans. They called him ''Uku'', or "First Beloved Man". The title of "Principal Chief" was created in 1794, when the Cherokee began to formalize a more centralized political structure. They founded the original Cherokee Nation. The Cherokee Nation–East adopted a written constitution in 1827, creating a government with three branches: legislative, executive, and judicial. The Principal Chief was elected by the National Council, which was the legislature of the Nation. The Cherokee Nation–West adopted a similar constitution in 1833. In 1839 most of the reunited nation was reunited in Indian Territory, after f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
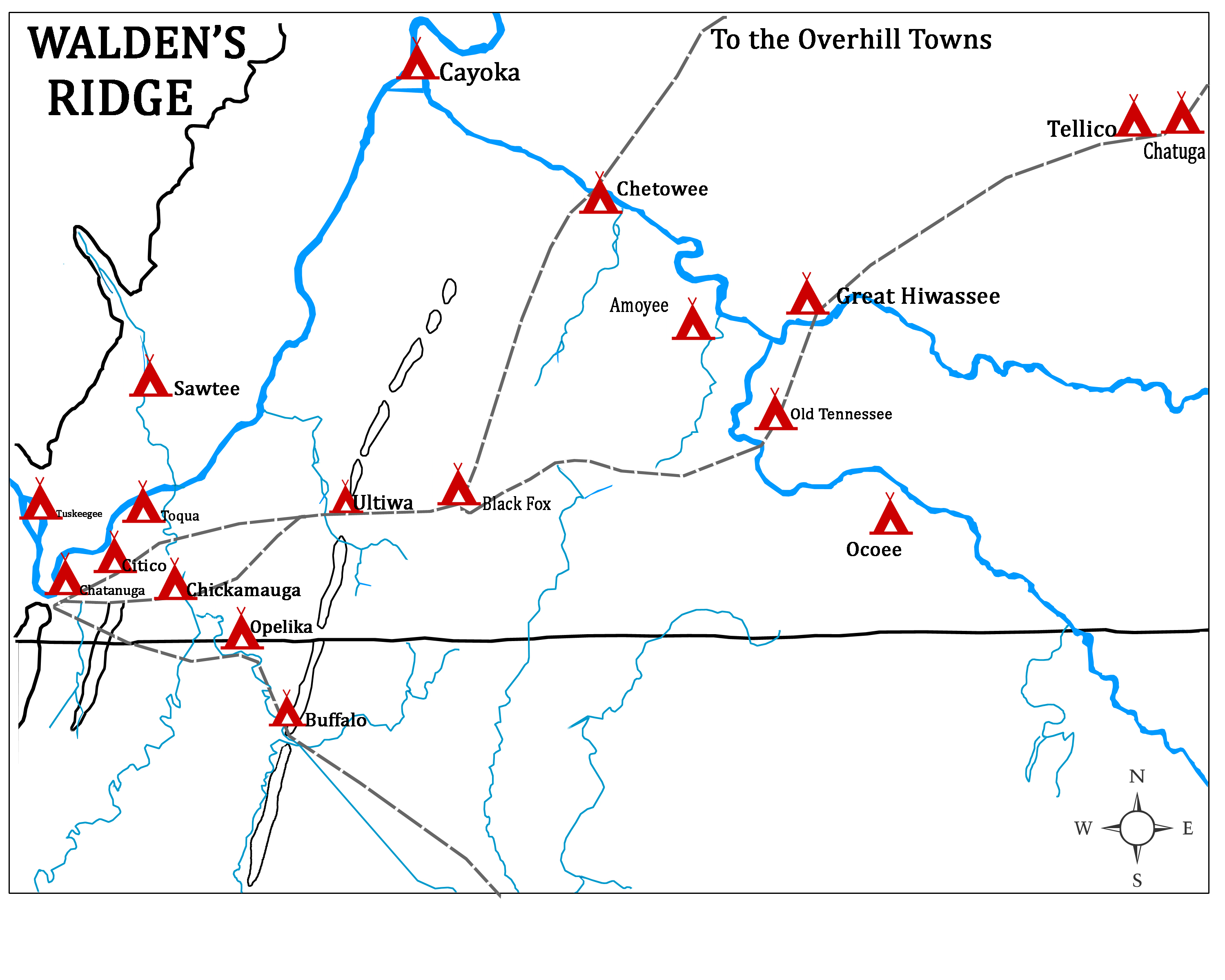
Black Fox (Cherokee Chief)
Black Fox (c. 1746-1811), also called Enola, was a Cherokee leader during the Cherokee–American wars. He was a signatory of the Holston Treaty, and later became a Principal Chief of the Cherokee Nation. Early leadership Named at birth Enola (also rendered Inali or Enoli), Black Fox was born about 1746.O'Dell, Larry''Encyclopedia of Oklahoma History and Culture''; "Inola;" retrieved February 28, 2013 He was a brother-in-law of Chickamauga Cherokee leader, Dragging Canoe, and accompanied him on his migrations south to the Lower Towns during the Cherokee–American wars. Black Fox was the "Beloved Man" (headman) of Ustanali, an important Native American settlement site which is located in what is today New Town in northwestern Georgia. As the fight with the frontier Americans drew to a close, he was one of the signers of the Treaty of Holston (July 2, 1791), an attempt at ending hostilities in the Holston River region. Principal chief In 1801 Black Fox was named by the co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doublehead
Doublehead (1744–1807) or Incalatanga (''Tal-tsu'tsa'', ᏔᎵᏧᏍᎦ in Cherokee), was one of the most feared warriors of the Cherokee during the Cherokee–American wars. Following the peace treaty at the Tellico Blockhouse in 1794, he served as one of the leaders of the Chickamauga Cherokee (or "Lower Cherokee"), and he was chosen as the leader of Chickamauga (taking on the title ''Chuqualataque'') in 1802. Personal life It is thought that Doublehead's father was Great Eagle (or ''Willenewa''), a nephew of Chief Old Hop and a cousin of Chief ''Attakullakulla'' (or Little Carpenter). He was a brother of Old Tassel, "First Beloved Man" of the Overhill Cherokee. Two of his relatives, '' Tahlonteeskee'' and John Jolly, were also leaders among the Chickamauga and both later became Principal Chiefs of the Cherokee Nation. Doublehead's last wife was Nancy Drumgoole. Their youngest son, Bird Doublehead, was only twelve years old at the time of Doublehead's assassination. Livin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Holston
The Treaty of Holston (or Treaty of the Holston) was a treaty between the United States government and the Cherokee signed on July 2, 1791, and proclaimed on February 7, 1792. It was negotiated and signed by William Blount, governor of the Southwest Territory and superintendent of Native Americans in the United States, Indian affairs for the southern district for the United States, and various representatives of the Cherokee peoples, most notably John Watts (Cherokee chief), John Watts. The treaty established terms of relations between the United States and the Cherokee, and established that the Cherokee tribes were to fall under the protectorate, protection of the United States, with the United States managing all future foreign affairs for all the loosely affiliated Cherokee tribes. A monument to the treaty, erected in 1997, is located on the banks of the Tennessee River in downtown Knoxville, Tennessee, where the treaty was negotiated. Terms This treaty mentions the following ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unicoi County, Tennessee
Unicoi County () is a county located in the U.S. state of Tennessee. As of the 2010 census, the population was 18,313. Its county seat is Erwin. ''Unicoi'' is a Cherokee word meaning "white," "hazy," "fog-like," or "fog draped," and refers to the mist often seen in the foothills and mountains of this far northeast county. Unicoi County is part of the Johnson City Metropolitan Statistical Area, which is a component of the Johnson City– Kingsport–Bristol, TN- VA Combined Statistical Area, commonly known as the " Tri-Cities" region. History This area was long inhabited by indigenous peoples, including the historic Cherokee who encountered European and English traders and settlers. The mountainous terrain made it less attractive to subsistence farmers. Unicoi County was created in 1875 from portions of Washington and Carter counties. Its first European-American settlers had arrived more than a century earlier but the population had been small. The county remained pred ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flint Creek (Tennessee)
Flint Creek may refer to: Watercourses * Flint Creek (Alabama) * Flint Creek (Arkansas/Oklahoma) *Flint Creek (New York) Towns * Flint Creek, Oklahoma Other uses * Flint Creek Range The Flint Creek Range, el. , is a mountain range northeast of Philipsburg, Montana in Granite County, Montana. The highest point in the range is Mount Powell, at 10,168 ft. in elevation. About 60,000 acres of the Flints are roadless. From D ..., mountain range in Montana * Flint Creek Water Park, a waterpark in Mississippi * Flint Creek Farm, an historic farm in Minnesota {{Geodis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |