|
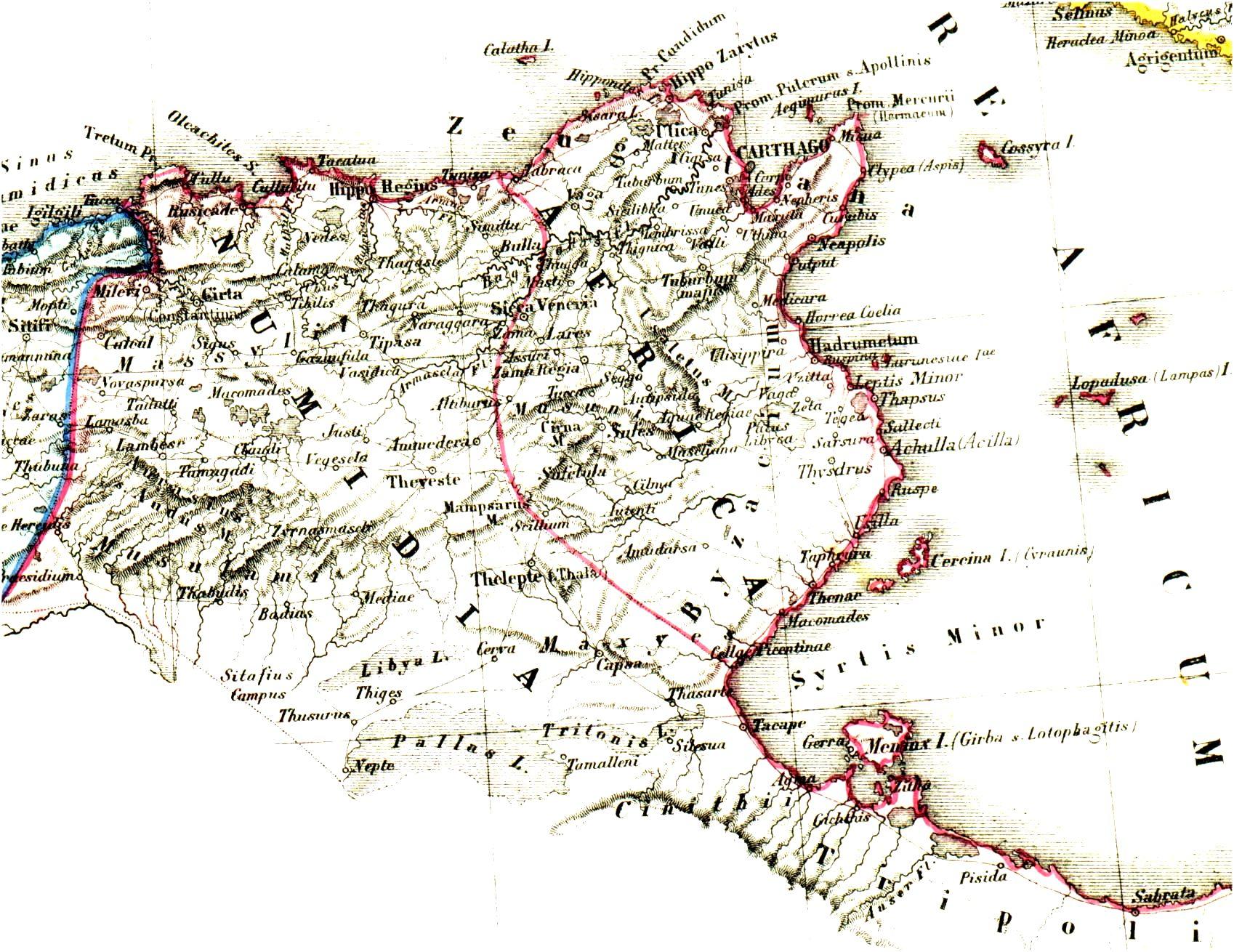
John Troglita
John Troglita ( la, Ioannes Troglita, el, ) was a 6th-century Byzantine general. He participated in the Vandalic War and served in North Africa as a regional military governor during the years 533–538, before being sent east to the wars with the Sassanid Persians. As ''dux Mesopotamiae'', Troglita distinguished himself in several battles, and was noticed by agents of the Byzantine emperor, Justinian I ( r. 527–565). In summer 546, Justinian chose John Troglita to assume overall command of Byzantine forces in Africa, where a succession of revolts by the indigenous Moorish tribes and within the imperial army itself had seriously reduced the Byzantine position. Troglita quickly secured an initial victory in the winter of 546/547 against the Moors of Byzacena, but was defeated in summer 547 by the tribes of Tripolitania, and Africa was once again laid open to destructive raids. Troglita reorganized his army and secured the assistance of some tribal leaders, and confronted and deci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
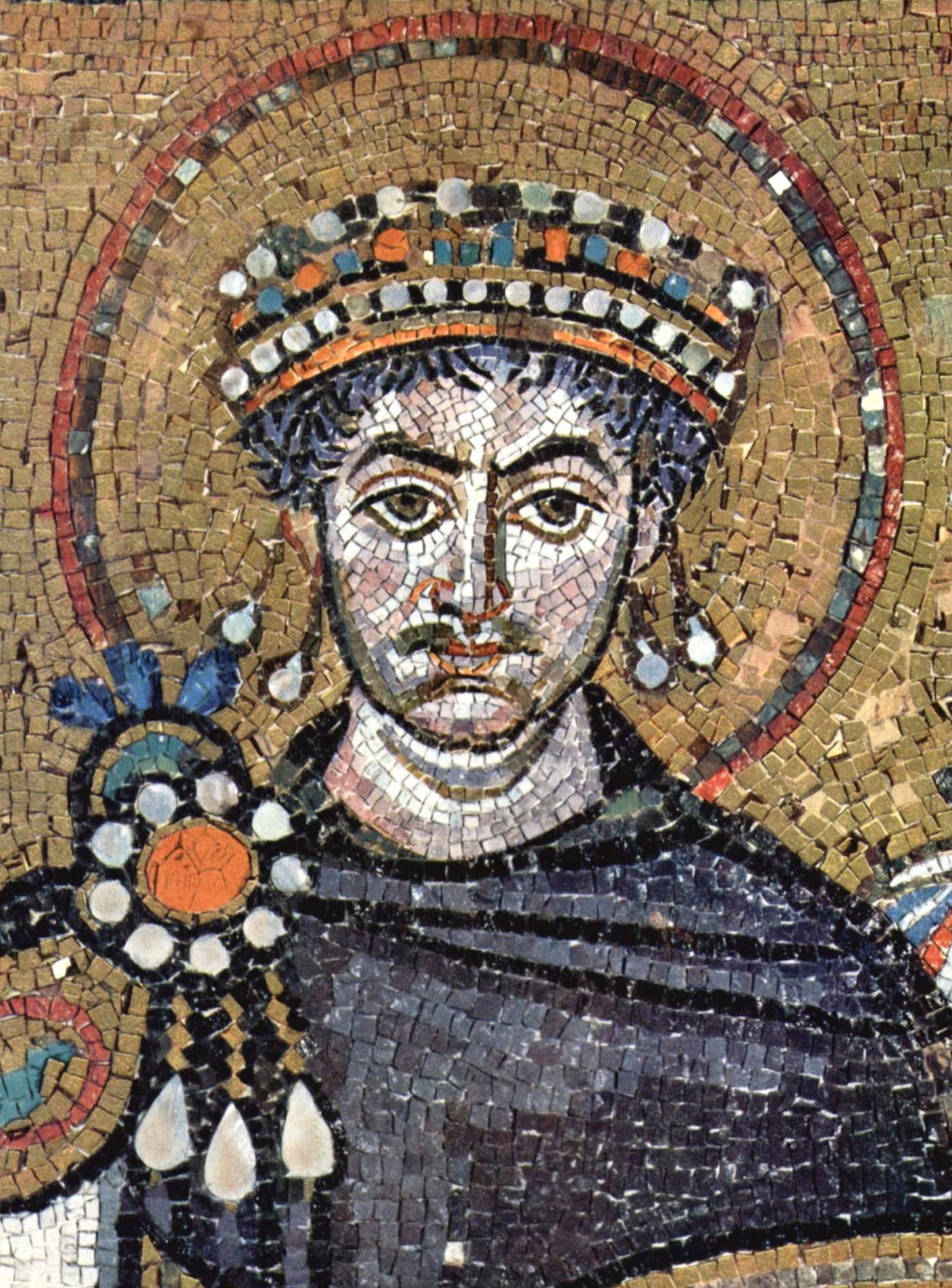
Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinople. It survived the fragmentation and fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD and continued to exist for an additional thousand years until the fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Empire in 1453. During most of its existence, the empire remained the most powerful economic, cultural, and military force in Europe. The terms "Byzantine Empire" and "Eastern Roman Empire" were coined after the end of the realm; its citizens continued to refer to their empire as the Roman Empire, and to themselves as Romans—a term which Greeks continued to use for themselves into Ottoman times. Although the Roman state continued and its traditions were maintained, modern historians prefer to differentiate the Byzantine Empire from Ancient Rome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classical Antiquity
Classical antiquity (also the classical era, classical period or classical age) is the period of cultural history between the 8th century BC and the 5th century AD centred on the Mediterranean Sea, comprising the interlocking civilizations of ancient Greece and ancient Rome known as the Greco-Roman world. It is the period in which both Greek and Roman societies flourished and wielded huge influence throughout much of Europe, North Africa, and Western Asia. Conventionally, it is taken to begin with the earliest-recorded Epic Greek poetry of Homer (8th–7th-century BC), and continues through the emergence of Christianity (1st century AD) and the fall of the Western Roman Empire (5th-century AD). It ends with the decline of classical culture during late antiquity (250–750), a period overlapping with the Early Middle Ages (600–1000). Such a wide span of history and territory covers many disparate cultures and periods. ''Classical antiquity'' may also refer to an idealized v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ostrogoth
The Ostrogoths ( la, Ostrogothi, Austrogothi) were a Roman-era Germanic people. In the 5th century, they followed the Visigoths in creating one of the two great Gothic kingdoms within the Roman Empire, based upon the large Gothic populations who had settled in the Balkans in the 4th century, having crossed the Lower Danube. While the Visigoths had formed under the leadership of Alaric I, the new Ostrogothic political entity which came to rule Italy was formed in the Balkans under the influence of the Amal dynasty, the family of Theodoric the Great. After the death of Attila and collapse of the Hunnic empire represented by the Battle of Nedao in 453, the Amal family began to form their kingdom in Pannonia. Byzantine Emperor Zeno played these Pannonian Goths off against the Thracian Goths, but instead the two groups united after the death of the Thracian leader Theoderic Strabo and his son Recitach. Zeno then backed Theodoric to invade Italy and replace Odoacer there, whom he ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germanus (cousin Of Justinian I)
Germanus ( el, Γερμανός; died 550) was an East Roman (Byzantine) general, one of the leading commanders of Emperor Justinian I (r. 527–565). Germanus was Emperor Justinian's cousin, and a member of the ruling dynasty. He held commands in Thrace, North Africa, and the East against Persia, and was slated to command the final Byzantine expedition against the Ostrogoths. Having married into the Gothic Amal royal line through his second wife Matasuntha and a distinguished service record, at the time of his sudden death, he was considered the probable heir to Emperor Justinian. Biography Origins and early career Germanus was born before 505, the nephew of Emperor Justin I (r. 518–527) and thus cousin of Emperor Justinian I (r. 527–565), and not his nephew, as is often erroneously stated... According to a statement in Jordanes's ''Getica'', Germanus was a descendant of the noble Roman clan of the Anicii. The exact nature of his connection, however, if indeed it is anything ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stotzas
Stotzas (Greek: Στότζας), also Stutias, Theophanes writes him Tzotzas (Τζότζας), was an East Roman (Byzantine) soldier and leader of a military rebellion in the Praetorian prefecture of Africa in the 530s. Stotzas attempted to establish Africa as a separate state and had been chosen by the rebelling soldiers as their leader. Nearly succeeding in taking Carthage, Stotzas was defeated at the Battle of the River Bagradas by Belisarius and fled into Numidia, where he regrouped. After another attempt at taking control of Africa, Stotzas was defeated by Germanus in 537 and fled with some of his followers into Mauretania. In Mauretania, Stotzas would marry the daughter of a local noble, perhaps the daughter of the Mauro-Roman King Masuna or Mastigas, and would allegedly be raised to King in 541 AD, succeeding Mastigas as King of the Moors and Romans. He followed the Berber king Antalas in his rebellion against Eastern Roman rule in 544 AD. In the Battle of Thacia in autu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leuathae
The Laguatan (Lawata, Lawati) was a Zenata Berber clan that inhabited the Cyrenaica area during the Roman period. They have been described as primarily raiders and nomadic, but others consider them a settled group who also raided. The Laguatan emerged in the late 3rd century, when the first groups started a westward migration from their original homes in the Libyan Desert. Under the label of Austuriani (probably reflecting a then-dominant sub-tribe) they are recorded as raiding the Cyrenaica and Tripolitania in the 4th century, and in the 520s, under their leader Cabaon, they scored a major victory over the Vandals, gaining effective independence from them. In the 540s, they played a major role in the tribal wars against the Byzantines, until finally defeated by John Troglita. Procopius of Caesarea (''Vandalic War'' II.21.2 & II.28.47) calls them the Leuathae ( el, Λευάθαι), while Flavius Cresconius Corippus calls them Ilaguas and Laguantan. According to Corippus, they were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solomon (magister Militum)
Solomon ( el, Σολόμων) was an East Roman (Byzantine) general from northern Mesopotamia, who distinguished himself as a commander in the Vandalic War and the reconquest of North Africa in 533–534. He spent most of the next decade in Africa as its governor general, combining the military post of with the civil position of praetorian prefect. Solomon successfully confronted the large-scale rebellion of the native Berbers (), but was forced to flee following an army mutiny in spring of 536. His second tenure in Africa began in 539 and it was marked by victories over the Berbers, which led to the consolidation of the Byzantine position. A few years of prosperity followed, but were cut short by the rekindled Berber revolt and Solomon's defeat and death at the Battle of Cillium in 544. Biography Solomon was born, probably circa 480/490, in the fortress of Idriphthon in the district of Solachon, near Dara in the province of Mesopotamia. He was a eunuch as a result of an accident ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Tricamarum
The Battle of Tricamarum took place on December 15, 533 between the armies of the Byzantine Empire, under Belisarius, and the Vandal Kingdom, commanded by King Gelimer, and his brother Tzazon. It followed the Byzantine victory at the Battle of Ad Decimum, and eliminated the power of the Vandals for good, completing the reconquest of North Africa under the Byzantine Emperor Justinian I. The main contemporary source for the battle is Procopius, ''De Bello Vandalico'', which occupies Books III and IV of his magisterial ''Wars of Justinian''. Prelude After the great Byzantine victory at the Battle of Ad Decimum, Belisarius and his army captured Carthage. Vandal king Gelimer set up at Bulla Regia in Numidia, about to the west of Carthage (at what is now the western border of modern Tunisia). He knew that in his current state he would not be able to face Belisarius's forces, so he sent messengers to his brother Tzazon who was then campaigning in Sardinia. When he received the message ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Ad Decimum
The Battle of Ad Decimum took place on September 13, 533 between the armies of the Vandals, commanded by King Gelimer, and the Byzantine Empire, under the command of General Belisarius. This event and events in the following year are sometimes jointly referred to as the Battle of Carthage, one of several battles to bear that name. The Byzantine victory marked the beginning of the end for the Vandals and began the reconquest of the west under the Emperor Justinian I. Battle Prelude The Vandal Kingdom in North Africa was ruled by King Hilderic. His reign was noteworthy for the kingdom's excellent relations with the Byzantine Empire ruled by Emperor Justinian I. Procopius writes that he was "a very particular friend and guest-friend of Justinian, who had not yet come to the throne", noting that Hilderic and Justinian exchanged large presents of money to each other. Hilderic allowed a new Chalcedonian bishop to take office in the Vandal capital of Carthage, and many Vandals beg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foederati
''Foederati'' (, singular: ''foederatus'' ) were peoples and cities bound by a treaty, known as ''foedus'', with Rome. During the Roman Republic, the term identified the ''socii'', but during the Roman Empire, it was used to describe foreign states, client kingdoms or barbarian tribes to which the empire provided benefits in exchange for military assistance. The term was also used, especially under the empire, for groups of "barbarian" mercenaries of various sizes who were typically allowed to settle within the empire. Roman Republic In the early Roman Republic, ''foederati'' were tribes that were bound by a treaty (''foedus'' ) to come to the defence of Rome but were neither Roman colonies nor beneficiaries of Roman citizenship (''civitas''). Members of the Latini tribe were considered blood allies, but the rest were federates or ''socii''. The friction between the treaty obligations without the corresponding benefits of Romanity led to the Social War between the Romans, with a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belisarius
Belisarius (; el, Βελισάριος; The exact date of his birth is unknown. – 565) was a military commander of the Byzantine Empire under the emperor Justinian I. He was instrumental in the reconquest of much of the Mediterranean territory belonging to the former Western Roman Empire, which had been lost less than a century prior. One of the defining features of Belisarius' career was his success despite varying levels of available resources. His name is frequently given as one of the so-called "Last of the Romans". He conquered the Vandal Kingdom of North Africa in the Vandalic War in nine months and conquered much of Italy during the Gothic War. He also defeated the Vandal armies in the battle of Ad Decimum and played an important role at Tricamarum, compelling the Vandal king, Gelimer, to surrender. During the Gothic War, despite being significantly outnumbered, he and his troops recaptured the city of Rome and then held out against great odds during the siege ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Procopius Of Caesarea
Procopius of Caesarea ( grc-gre, Προκόπιος ὁ Καισαρεύς ''Prokópios ho Kaisareús''; la, Procopius Caesariensis; – after 565) was a prominent late antique Greek scholar from Caesarea Maritima. Accompanying the Roman general Belisarius in Emperor Justinian's wars, Procopius became the principal Roman historian of the 6th century, writing the ''History of the Wars'', the ''Buildings'', and the ''Secret History''. Life Apart from his own writings the main source for Procopius's life was an entry in the ''Suda'',Suda pi.2479. See under 'Procopius' oSuda On Line a Byzantine Greek encyclopaedia written sometime after 975 which discusses his early life. He was a native of Caesarea in the province of ''Palaestina Prima''. He would have received a conventional upper class education in the Greek classics and rhetoric, perhaps at the famous school at Gaza. He may have attended law school, possibly at Berytus (present-day Beirut) or Constantinople (now Istanbul), a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |