|
John Kidd (chemist)
John Kidd (10 September 1775 – 7 September 1851) was an English physician, chemist and geologist who took a leading role in Oxford's "scientific awakening" in the early years of the nineteenth century. Biography Kidd was born in Westminster, the son of a naval officer, and was educated at Christ Church, Oxford. He became reader in chemistry at Oxford in 1801, and in 1803 was elected the first Aldrichian Professor of Chemistry. He then voluntarily gave courses of lectures on mineralogy and geology. These were delivered in the dark chambers under the Ashmolean Museum, where William Conybeare, William Buckland, Charles Daubeny and others gained their first lessons in geology. Kidd was a popular and instructive lecturer, and through his efforts the geological chair, first held by Buckland, was established. Kidd's two geological publications — his ''Outlines of Mineralogy'' (1809) and ''Geological Essay on the Imperfect Evidence in Support of a Theory of the Earth'' (1815) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Westminster
Westminster is an area of Central London, part of the wider City of Westminster. The area, which extends from the River Thames to Oxford Street, has many visitor attractions and historic landmarks, including the Palace of Westminster, Buckingham Palace, Westminster Abbey, Westminster Cathedral and much of the West End shopping and entertainment district. The name ( ang, Westmynstre) originated from the informal description of the abbey church and royal peculiar of St Peter's (Westminster Abbey), west of the City of London (until the English Reformation there was also an Eastminster, near the Tower of London, in the East End of London). The abbey's origins date from between the 7th and 10th centuries, but it rose to national prominence when rebuilt by Edward the Confessor in the 11th. Westminster has been the home of England's government since about 1200, and from 1707 the Government of the United Kingdom. In 1539, it became a city. Westminster is often used as a m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
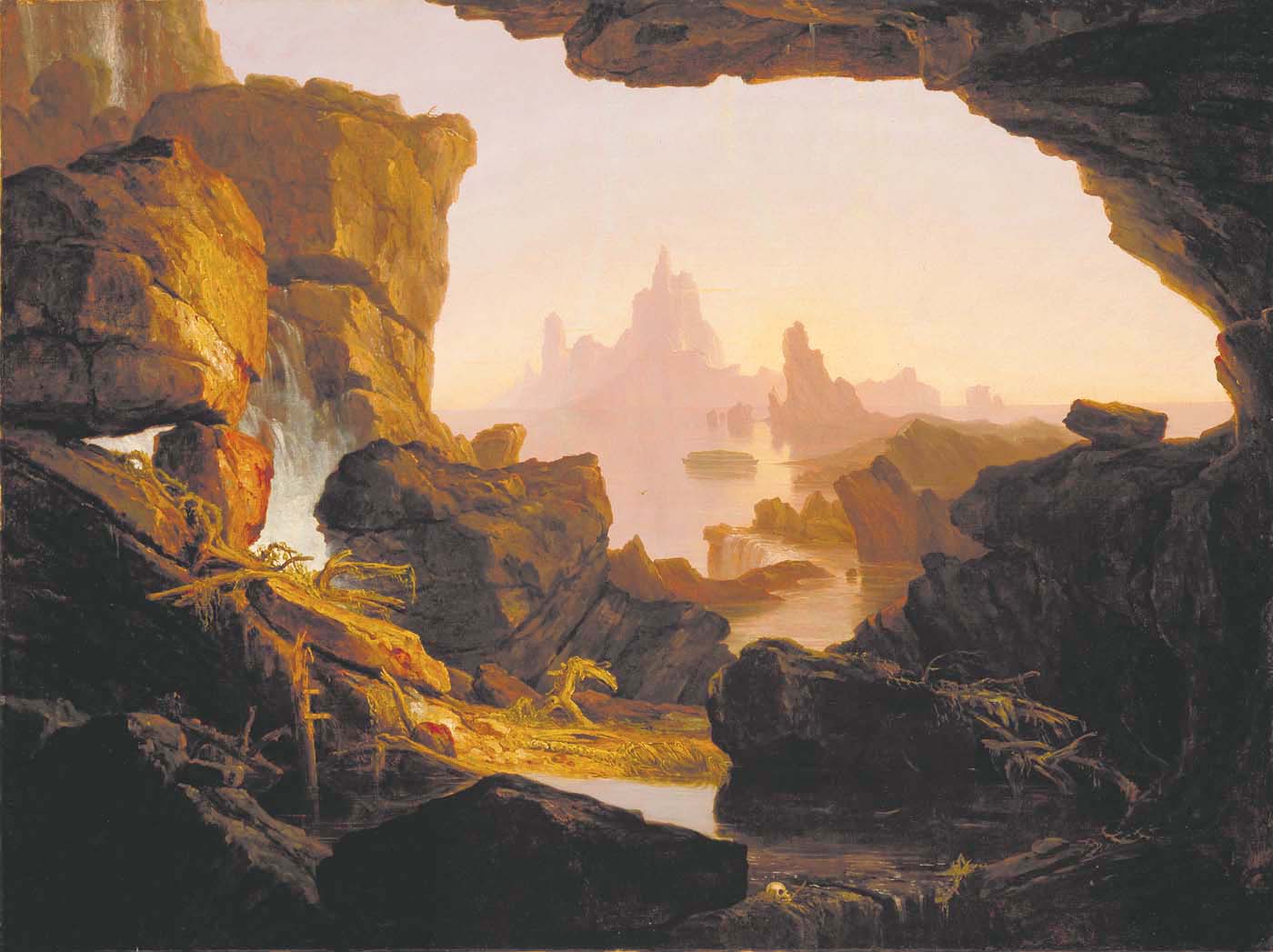
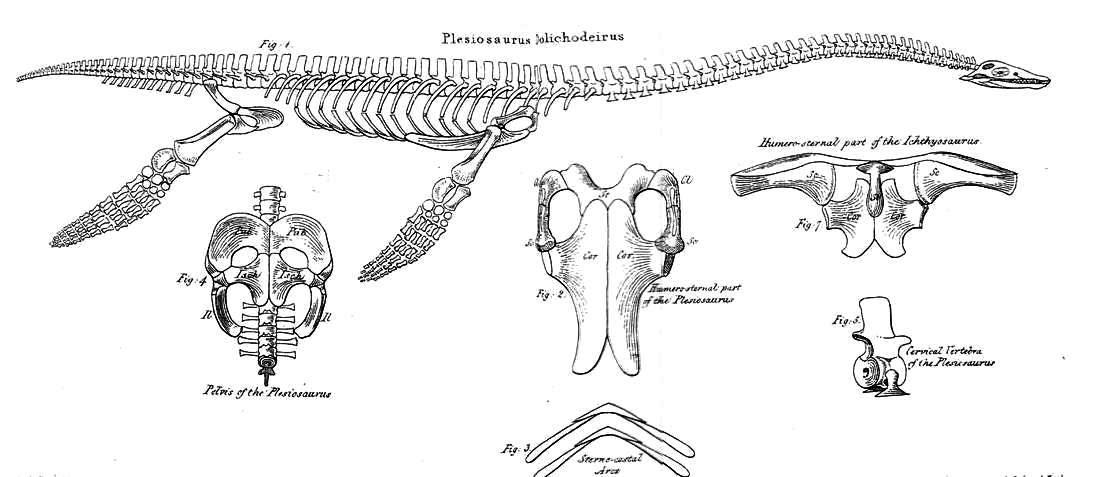
William Conybeare (geologist)
William Daniel Conybeare FRS (7 June 178712 August 1857), dean of Llandaff, was an English geologist, palaeontologist and clergyman. He is probably best known for his ground-breaking work on fossils and excavation in the 1820s, including important papers for the Geological Society of London on ichthyosaur anatomy and the first published scientific description of a plesiosaur. Life and career Childhood and education He was a grandson of John Conybeare, bishop of Bristol (1692–1755), a notable preacher and divine, and son of Dr William Conybeare, rector of St Botolph-without-Bishopsgate. Born in London, he was educated there at Westminster School, then went in 1805 to Christ Church, Oxford, where in 1808 he took his degree of BA, with a first in classics and second in mathematics, and proceeded to MA three years later. Early career Having entered holy orders he became in 1814 curate of Wardington, near Banbury, and he accepted also a lectureship at Brislington near Bristol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transmutation Of Species
Transmutation of species and transformism are unproven 18th and 19th-century evolutionary ideas about the change of one species into another that preceded Charles Darwin's theory of natural selection. The French ''Transformisme'' was a term used by Jean Baptiste Lamarck in 1809 for his theory, and other 18th and 19th century proponents of pre-Darwinian evolutionary ideas included Denis Diderot, Étienne Geoffroy Saint-Hilaire, Erasmus Darwin, Robert Grant, and Robert Chambers, the anonymous author of the book ''Vestiges of the Natural History of Creation''. Opposition in the scientific community to these early theories of evolution, led by influential scientists like the anatomists Georges Cuvier and Richard Owen, and the geologist Charles Lyell, was intense. The debate over them was an important stage in the history of evolutionary thought and influenced the subsequent reaction to Darwin's theory. Terminology Transmutation was one of the names commonly used for evolutionary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Materialism
Materialism is a form of philosophical monism which holds matter to be the fundamental substance in nature, and all things, including mental states and consciousness, are results of material interactions. According to philosophical materialism, mind and consciousness are by-products or epiphenomena of material processes (such as the biochemistry of the human brain and nervous system), without which they cannot exist. This concept directly contrasts with idealism, where mind and consciousness are first-order realities to which matter is dependent while material interactions are secondary. Materialism is closely related to physicalism—the view that all that exists is ultimately physical. Philosophical physicalism has evolved from materialism with the theories of the physical sciences to incorporate more sophisticated notions of physicality than mere ordinary matter (e.g. spacetime, physical energies and forces, and dark matter). Thus, the term ''physicalism'' is preferred ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bridgewater Treatises
The Bridgewater Treatises (1833–36) are a series of eight works that were written by leading scientific figures appointed by the President of the Royal Society in fulfilment of a bequest of £8000, made by Francis Henry Egerton, 8th Earl of Bridgewater, for a work on "the Power, Wisdom, and Goodness of God, as manifested in the Creation." Despite being voluminous and costly, the series was very widely read and discussed, becoming one of the most important contributions to the Victorian literature on the relationship between religion and science. They made such an impact that Charles Darwin began ''On the Origin of Species'' with a quotation from the Bridgewater Treatise of William Whewell. The Bridgewater Bequest Before unexpectedly becoming the 8th Earl of Bridgewater in 1823, Francis Henry Egerton spent most of his life as an absentee parson. He published works of classical scholarship and issued others praising the historical achievements of his family, including those of hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Society
The Royal Society, formally The Royal Society of London for Improving Natural Knowledge, is a learned society and the United Kingdom's national academy of sciences. The society fulfils a number of roles: promoting science and its benefits, recognising excellence in science, supporting outstanding science, providing scientific advice for policy, education and public engagement and fostering international and global co-operation. Founded on 28 November 1660, it was granted a royal charter by King Charles II as The Royal Society and is the oldest continuously existing scientific academy in the world. The society is governed by its Council, which is chaired by the Society's President, according to a set of statutes and standing orders. The members of Council and the President are elected from and by its Fellows, the basic members of the society, who are themselves elected by existing Fellows. , there are about 1,700 fellows, allowed to use the postnominal title FRS (Fellow of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fellow Of The Royal Society
Fellowship of the Royal Society (FRS, ForMemRS and HonFRS) is an award granted by the judges of the Royal Society of London to individuals who have made a "substantial contribution to the improvement of natural science, natural knowledge, including mathematics, engineering science, and medical science". Fellow, Fellowship of the Society, the oldest known scientific academy in continuous existence, is a significant honour. It has been awarded to many eminent scientists throughout history, including Isaac Newton (1672), Michael Faraday (1824), Charles Darwin (1839), Ernest Rutherford (1903), Srinivasa Ramanujan (1918), Albert Einstein (1921), Paul Dirac (1930), Winston Churchill (1941), Subrahmanyan Chandrasekhar (1944), Dorothy Hodgkin (1947), Alan Turing (1951), Lise Meitner (1955) and Francis Crick (1959). More recently, fellowship has been awarded to Stephen Hawking (1974), David Attenborough (1983), Tim Hunt (1991), Elizabeth Blackburn (1992), Tim Berners-Lee (2001), Venki R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bodleian Library
The Bodleian Library () is the main research library of the University of Oxford, and is one of the oldest libraries in Europe. It derives its name from its founder, Sir Thomas Bodley. With over 13 million printed items, it is the second-largest library in Britain after the British Library. Under the Legal Deposit Libraries Act 2003, it is one of six legal deposit libraries for works published in the United Kingdom, and under Irish law it is entitled to request a copy of each book published in the Republic of Ireland. Known to Oxford scholars as "Bodley" or "the Bod", it operates principally as a reference library and, in general, documents may not be removed from the reading rooms. In 2000, a number of libraries within the University of Oxford were brought together for administrative purposes under the aegis of what was initially known as Oxford University Library Services (OULS), and since 2010 as the Bodleian Libraries, of which the Bodleian Library is the largest comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sir Christopher Pegge
Sir Christopher Pegge M.D. (1765–1822) was an English physician. Life The son of Samuel Pegge the younger, by his first wife, he was born in London. He entered Christ Church, Oxford, as a commoner on 18 April 1782, and graduated B.A. on 23 February 1786. He was elected a Fellow of Oriel College in 1788, and graduated M.A. and M.B. there on 10 June and 18 July 1789. He returned to Christ Church, was appointed Lee's reader in anatomy there in 1790, and proceeded M.D. on 27 April 1792. On 9 November 1790 Pegge became physician to the Radcliffe Infirmary, and a Fellow of the Royal Society in 1795. He was knighted on 26 June 1799, and in 1801 was appointed regius professor of physic at Oxford. He was elected a fellow of the Royal College of Physicians on 25 June 1796, delivered the Harveian oration in 1805, and became a censor in 1817. Pegge left Oxford in 1816, and took a house in George Street, Hanover Square, for his health. Soon afterwards he moved on to Hastings. He had resi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regius Professor Of Medicine (Oxford)
The Regius Professor of Medicine is an appointment held at the University of Oxford. The chair was founded by Henry VIII of England by 1546, and until the 20th century the title was Regius Professor of Physic. Henry VIII established five Regius Professorships in the University, the others being the Regius chairs of Divinity, Civil Law, Hebrew and Greek. The Regius Professor of Clinical Medicine is always a member of Christ Church. Holders *1546–1554 John Warner *1554–1561 Thomas Frauncis (or Frances/Francis) (c.1519–1574) *1561–1582 Walter Bayley (1529–1593) *1582–1597 Anthony Aylworth (d.1619) *1597–1612 Bartholomew Warner (1556–1619) *1612–1647 Thomas Clayton the Elder (1575–1647), first Master of Pembroke *1647–1665 Sir Thomas Clayton the Younger (c. 1611–1693), Warden of Merton *1665–1681 James Hyde (1618–1681) *1681–1698 John Luffe (1647–1698) *1698–1718 Thomas Hoy (b.1659, d. in or after 1721) *1718–1729 Joshua Lasher *17 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal College Of Physicians
The Royal College of Physicians (RCP) is a British professional membership body dedicated to improving the practice of medicine, chiefly through the accreditation of physicians by examination. Founded by royal charter from King Henry VIII in 1518, the RCP is the oldest medical college in England. It set the first international standard in the classification of diseases, and its library contains medical texts of great historical interest. The college is sometimes referred to as the Royal College of Physicians of London to differentiate it from other similarly named bodies. The RCP drives improvements in health and healthcare through advocacy, education and research. Its 40,000 members work in hospitals and communities across over 30 medical specialties with around a fifth based in over 80 countries worldwide. The college hosts six training faculties: the Faculty of Forensic and Legal Medicine, the Faculty for Pharmaceutical Medicine, the Faculty of Occupational Medicine the Fac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flood Geology
Flood geology (also creation geology or diluvial geology) is a pseudoscientific attempt to interpret and reconcile geological features of the Earth in accordance with a literal belief in the global flood described in Genesis 6–8. In the early 19th century, diluvial geologists hypothesized that specific surface features provided evidence of a worldwide flood which had followed earlier geological eras; after further investigation they agreed that these features resulted from local floods or from glaciers. In the 20th century, young-Earth creationists revived flood geology as an overarching concept in their opposition to evolution, assuming a recent six-day Creation and cataclysmic geological changes during the biblical flood, and incorporating creationist explanations of the sequences of rock strata. In the early stages of development of the science of geology, fossils were interpreted as evidence of past flooding. The "theories of the Earth" of the 17th century proposed m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |