|
Jevstatije Mihajlović
Jevstatije Mihajlovic-Eta ( Veliki Beckerek, 1802 - Budapest, 18 October 1888) was a Serbian writer, lawyer, senator and judge. Biography He was born in 1802 in Veliki Bečkerek (today Zrenjanin). In his youth, he worked as a teacher for some time. He studied philosophy in Petrovaradin, and law in Sárospatak. After completing his studies, he returned in 1827 back to Veliki Bečkerek, where he lived until 1849 and held important positions in the city government, as well as in Torontál County. As an educated man and an official of the county and the city, he was registered as a subscriber of several Serbian periodicals many times, and he was also engaged in literary work. According to subscriptions and published works, it is possible to monitor his career progress. He published his first romantic story in 1827 in Buda, as a "lawyer". The following year in 1828, Mihajlović became a subscriber of a book as a "jurat and writer" in Bečkerek. Then his long public activity bega ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Veliki Beckerek
Zrenjanin ( sr-Cyrl, Зрењанин, ; hu, Nagybecskerek; ro, Becicherecu Mare; sk, Zreňanin; german: Großbetschkerek) is a city and the administrative center of the Central Banat District in the autonomous province of Vojvodina, Serbia. The city urban area has a population of 76,511 inhabitants, while the city administrative area has 123,362 inhabitants (2011 census data). The old name for Zrenjanin is Veliki Bečkerek or ''Nagybecskerek'' as it was known under Austria-Hungary up until 1918. Zrenjanin is the largest city in the Serbian part of the Banat geographical region, and the third largest city in Vojvodina (after Novi Sad and Subotica). The city was designated European city of sport. Name The city was named after Žarko Zrenjanin (1902–1942) in 1946 in honour and remembrance of his name. One of the leaders of the Vojvodina communist Partisans during World War II, he was imprisoned and released after being tortured by the Nazis for months, and later killed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vojvodina
Vojvodina ( sr-Cyrl, Војводина}), officially the Autonomous Province of Vojvodina, is an autonomous province that occupies the northernmost part of Serbia. It lies within the Pannonian Basin, bordered to the south by the national capital Belgrade and the Sava and Danube Rivers. The administrative center, Novi Sad, is the second-largest city in Serbia. The historic regions of Banat, Bačka, and Syrmia overlap the province. Modern Vojvodina is multi-ethnic and multi-cultural, with some 26 ethnic groups and six official languages. About two million people, nearly 27% of Serbia's population, live in the province. Naming ''Vojvodina'' is also the Serbian word for voivodeship, a type of duchy overseen by a voivode. The Serbian Voivodeship, a precursor to modern Vojvodina, was an Austrian province from 1849 to 1860. Its official name is the Autonomous Province of Vojvodina. Its name in the province's six official languages is: * Croatian: ''Autonomna Pokrajina Vojvodina'' * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
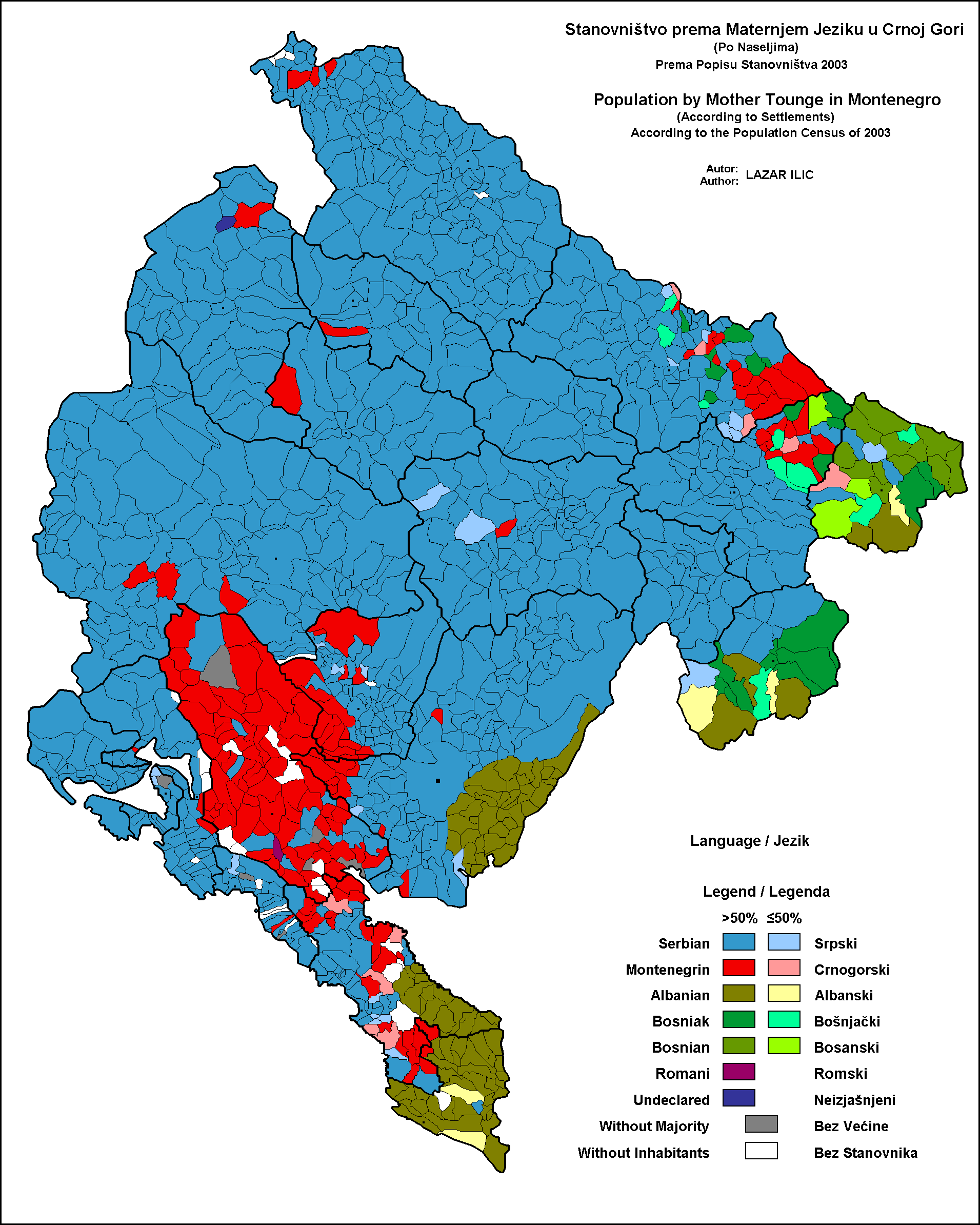
Serbian Language
Serbian (, ) is the standardized variety of the Serbo-Croatian language mainly used by Serbs. It is the official and national language of Serbia, one of the three official languages of Bosnia and Herzegovina and co-official in Montenegro and Kosovo. It is a recognized minority language in Croatia, North Macedonia, Romania, Hungary, Slovakia, and the Czech Republic. Standard Serbian is based on the most widespread dialect of Serbo-Croatian, Shtokavian (more specifically on the dialects of Šumadija-Vojvodina and Eastern Herzegovina), which is also the basis of standard Croatian, Bosnian, and Montenegrin varieties and therefore the Declaration on the Common Language of Croats, Bosniaks, Serbs, and Montenegrins was issued in 2017. The other dialect spoken by Serbs is Torlakian in southeastern Serbia, which is transitional to Macedonian and Bulgarian. Serbian is practically the only European standard language whose speakers are fully functionally digraphic, using both Cyril ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Srem
Syrmia ( sh, Srem/Срем or sh, Srijem/Сријем, label=none) is a region of the southern Pannonian Plain, which lies between the Danube and Sava rivers. It is divided between Serbia and Croatia. Most of the region is flat, with the exception of the low Fruška gora mountain stretching along the Danube in its northern part. Etymology The word "Syrmia" is derived from the ancient city of Sirmium (now Sremska Mitrovica). Sirmium was a Celtic or Illyrian town founded in the third century BC. ''Srem'' ( sr-cyr, Срем) and ''Srijem'' are used to designate the region in Serbia and Croatia respectively. Other names for the region include: * Latin: ''Syrmia'' or ''Sirmium'' * Hungarian: ''Szerémség'', ''Szerém'', or ''Szerémország'' * German: ''Syrmien'' * Slovak: ''Sriem'' * Rusyn: Срим * Romanian: ''Sirmia'' History Prehistory Between 3000 BC and 2400 BC, Syrmia was at the centre of Indo-European Vučedol culture. Roman era Sirmium was conquer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slavonian Dialect
Shtokavian or Štokavian (; sh-Latn, štokavski / sh-Cyrl, italics=no, штокавски, ) is the prestige dialect of the pluricentric Serbo-Croatian language and the basis of its Serbian, Croatian, Bosnian and Montenegrin standards. It is a part of the South Slavic dialect continuum. Its name comes from the form for the interrogatory pronoun for "what" in Western Shtokavian, (it is in Eastern Shtokavian). This is in contrast to Kajkavian and Chakavian ( and also meaning "what"). Shtokavian is spoken in Serbia, Montenegro, Bosnia and Herzegovina, much of Croatia, as well as the southern part of Austria's Burgenland. The primary subdivisions of Shtokavian are based on two principles: one is whether the subdialect is Old-Shtokavian or Neo-Shtokavian, and different accents according to the way the old Slavic phoneme ''jat'' has changed. Modern dialectology generally recognises seven Shtokavian subdialects. Early history of Shtokavian The Proto-Shtokavian idiom app ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dalmatian (language)
Dalmatian () or Dalmatic (; dlm, langa dalmata, link=no or simply ; it, lingua dalmatica, dalmatico; sh, dalmatski) was a Romance languages, Romance language that was spoken in the Dalmatia region of present-day Croatia, and as far south as Kotor in Montenegro. The name refers to a tribe of the Illyrian languages, Illyrian linguistic group, Dalmatae. The Ragusan dialect of Dalmatian, the most studied prestige dialect, was the official language of the Republic of Ragusa for much of its medieval history until it was gradually supplanted by other local languages. Dalmatian speakers lived in the coastal towns of Zadar ('), Trogir ('), Spalato (Split, Croatia, Split; '), Ragusa (Dubrovnik; '), and Kotor ('), each of these cities having a local dialect, and on the islands of Krk ('), Cres ('), and Rab ('). Dialects Almost every city developed its own dialect. Most of these became extinct before they were recorded, so the only trace of these ancient dialects is some words borrowed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Herzegovinian Dialect
The Eastern Herzegovinian dialect (, Serbo-Croatian: ''istočnohercegovački'' / источнохерцеговачки) is the most widespread subdialect of the Shtokavian dialect of Serbo-Croatian, both by territory and the number of speakers. It is the dialectal basis for all modern literary Serbo-Croatian standards: Bosnian, Croatian, Serbian, and Montenegrin (the latter only partially codified). Distribution It covers large areas of Croatia, Bosnia-Herzegovina, Serbia and Montenegro. It is also spoken in four villages in White Carniola, Slovenia ( Miliči, Bojanci, Marindol and Paunoviči), the inhabitants of which are descendants of Uskoks. It is composed of two larger zones that are territorially separated: * Southeastern zone, where it originated from (eastern Herzegovina, western Montenegro, western Serbia, eastern Bosnia, Posavinan Podrinje) * Northwestern zone (western and northwestern Bosnia, northern Dalmatia with Gorski Kotar, narrower strips of Croatia, parts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Montenegrin Language
Montenegrin ( ; cnr, label=none, / ) is a normative variety of the Serbo-Croatian language mainly used by Montenegrins and is the official language of Montenegro. Montenegrin is based on the most widespread dialect of Serbo-Croatian, Shtokavian, more specifically on Eastern Herzegovinian, which is also the basis of Standard Croatian, Serbian, and Bosnian. Montenegro's language has historically and traditionally been called either Serbian or Montenegrin. The idea of a standardized Montenegrin standard language separate from Serbian appeared in the 1990s during the breakup of Yugoslavia, through proponents of Montenegrin independence from the State Union of Serbia and Montenegro. Montenegrin became the official language of Montenegro with the ratification of a new constitution on 22 October 2007. Language standardization In January 2008, the government of Montenegro formed the Board (Council) for Standardization of the Montenegrin Language, which aims to standardize the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Illyrian Movement
The Illyrian movement ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, Ilirski pokret, Илирски покрет; sl, Ilirsko gibanje) was a pan-South-Slavic cultural and political campaign with roots in the early modern period, and revived by a group of young Croatian intellectuals during the first half of the 19th century, around the years of 1835–1863 (there is some disagreement regarding the official dates from 1835 to 1870). This movement aimed to create a Croatian national establishment in Austria-Hungary through linguistic and ethnic unity, and through it lay the foundation for cultural and linguistic unification of all South Slavs under the revived umbrella term '' Illyrian''. Aspects of the movement pertaining to the development of Croatian culture are considered in Croatian historiography to be part of the Croatian national revival ( hr, Hrvatski narodni preporod). Name In the 19th century, the name ''Illyrian'' was chosen by the members of the movement as a reference to the theory according t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trebinje
Trebinje ( sr-Cyrl, Требиње, ) is a city and municipality located in the Republika Srpska entity of Bosnia and Herzegovina. It is the southernmost city in Bosnia and Herzegovina and is situated on the banks of Trebišnjica river in the region of East Herzegovina. As of 2013, it has a population of 31,433 inhabitants. The city's old town quarter dates to the 18th-century Ottoman period, and includes the Arslanagić Bridge, also known as Perovića Bridge. Geography Physical geography The city lies in the Trebišnjica river valley, at the foot of Leotar, in southeastern Herzegovina, some by road from Dubrovnik, Croatia, on the Adriatic coast. There are several mills along the river, as well as several bridges, including three in the city of Trebinje itself, as well as a historic Ottoman Arslanagić Bridge nearby. The river is heavily exploited for hydro-electric energy. After it passes through the Popovo Polje area southwest of the city, the river – which always floo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vuk Karadžić
Vuk Stefanović Karadžić ( sr-Cyrl, Вук Стефановић Караџић, ; 6 November 1787 (26 October OS)7 February 1864) was a Serbian philologist, anthropologist and linguist. He was one of the most important reformers of the modern Serbian language. For his collection and preservation of Serbian folktales, ''Encyclopædia Britannica'' labelled him "the father of Serbian folk-literature scholarship." He was also the author of the first Serbian dictionary in the new reformed language. In addition, he translated the New Testament into the reformed form of the Serbian spelling and language. He was well known abroad and familiar to Jacob Grimm, Johann Wolfgang von Goethe and historian Leopold von Ranke. Karadžić was the primary source for Ranke's ''Die serbische Revolution'' (" The Serbian Revolution"), written in 1829. Biography Early life Vuk Karadžić was born to a Serbian family of Stefan and Jegda (née ''Zrnić'') in the village of Tršić, near Loznica, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romanticism
Romanticism (also known as the Romantic movement or Romantic era) was an artistic, literary, musical, and intellectual movement that originated in Europe towards the end of the 18th century, and in most areas was at its peak in the approximate period from 1800 to 1850. Romanticism was characterized by its emphasis on emotion and individualism, clandestine literature, paganism, idealization of nature, suspicion of science and industrialization, and glorification of the past with a strong preference for the medieval rather than the classical. It was partly a reaction to the Industrial Revolution, the social and political norms of the Age of Enlightenment, and the scientific rationalization of nature. It was embodied most strongly in the visual arts, music, and literature, but had a major impact on historiography, education, chess, social sciences, and the natural sciences. It had a significant and complex effect on politics, with romantic thinkers influencing conservatism, libe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |