|
Jellaz Affair
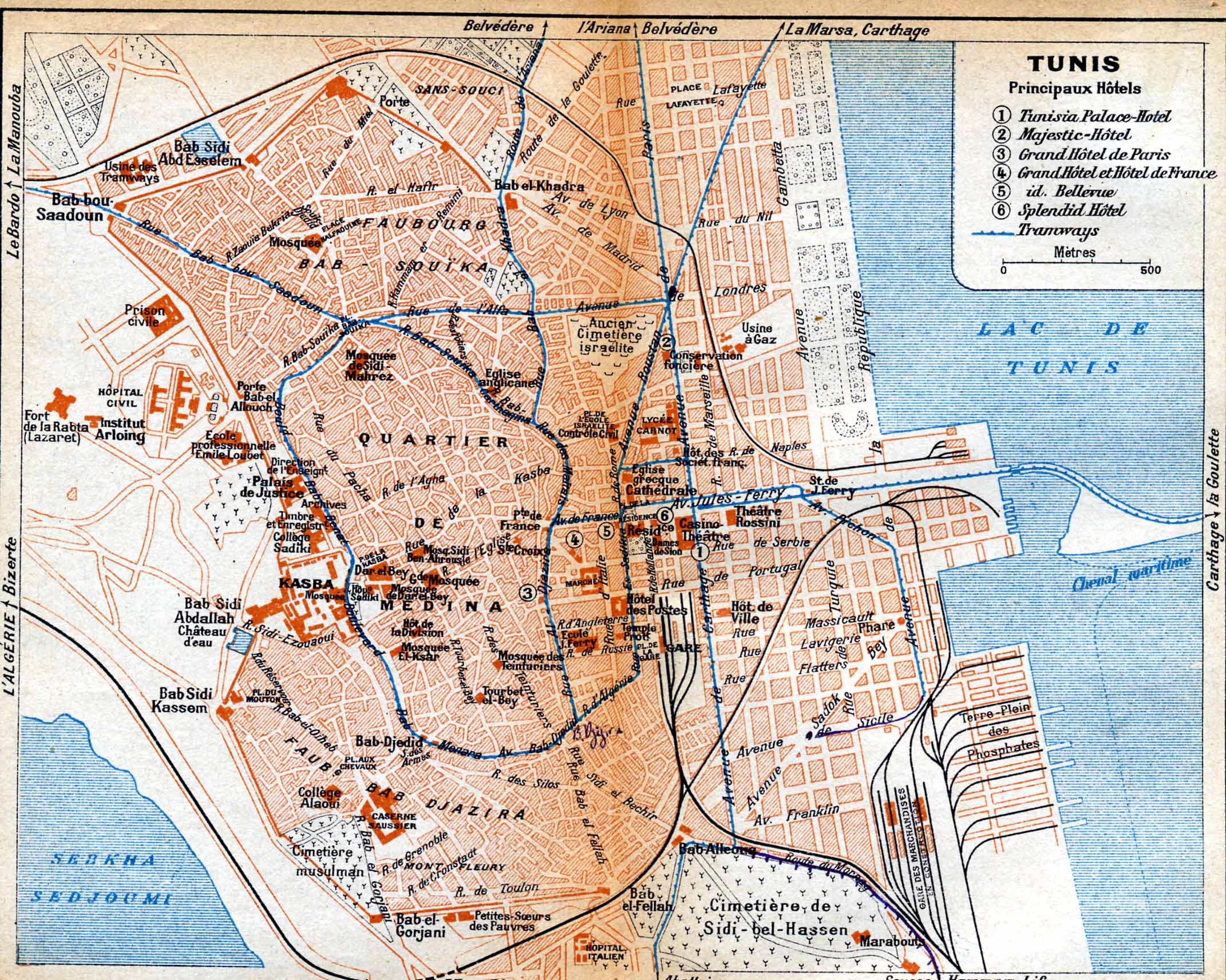
The Jellaz Affair ( ar, أحداث ٱلجلّاز ') (french: Affaire du Djellaz) was a violent confrontation in November 1911 between Tunisian protesters and the authorities of the French Protectorate of Tunisia which began at the Jellaz Cemetery. Over the course of two days, it became a series of fights and attacks in the streets, primarily involving Tunisians and Italian settlers.'Les grands jours de Tunis, ''Gil Blas'', 4 June 1912, pp.1-2 accessed 28/12/2016 It was the most serious outbreak of violence in Tunis, and the first time French soldiers fired on the civilian population, since the establishment of the Protectorate in 1881. It was therefore a critical juncture in the development of the Tunisian nationalism, Tunisian nationalist movement.Mary Dewhurst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tunisia
) , image_map = Tunisia location (orthographic projection).svg , map_caption = Location of Tunisia in northern Africa , image_map2 = , capital = Tunis , largest_city = capital , coordinates = , official_languages = Arabic Translation by the University of Bern: "Tunisia is a free State, independent and sovereign; its religion is the Islam, its language is Arabic, and its form is the Republic." , religion = , languages_type = Spoken languages , languages = Minority Dialects : Jerba Berber (Chelha) Matmata Berber Judeo-Tunisian Arabic (UNESCO CR) , languages2_type = Foreign languages , languages2 = , ethnic_groups = * 98% Arab * 2% Other , demonym = Tunisian , government_type = Unitary presidential republic , leader_title1 = President , leader_name1 = Kais Saied , leader_t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agadir Crisis
The Agadir Crisis, Agadir Incident, or Second Moroccan Crisis was a brief crisis sparked by the deployment of a substantial force of French troops in the interior of Morocco in April 1911 and the deployment of the German gunboat to Agadir, a Moroccan Atlantic port. Germany did not object to France's expansion but wanted territorial compensation for itself. Berlin threatened warfare, sent a gunboat, and stirred up German nationalists. Negotiations between Berlin and Paris resolved the crisis on 4 November 1911: France took over Morocco as a protectorate in exchange for territorial concessions to German Cameroon from the French Congo. In Britain, David Lloyd George, then Chancellor of the Exchequer, made a dramatic " Mansion House" speech on 21 July 1911 – with the consent of the prime minister and Foreign Secretary Sir Edward Grey, bypassing the non-interventionist majority in the Cabinet – that denounced the German move as an intolerable humiliation. There was ta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gabriel Alapetite 2
In Abrahamic religions ( Judaism, Christianity and Islam), Gabriel (); Greek: grc, Γαβριήλ, translit=Gabriḗl, label=none; Latin: ''Gabriel''; Coptic: cop, Ⲅⲁⲃⲣⲓⲏⲗ, translit=Gabriêl, label=none; Amharic: am, ገብርኤል, translit=Gabrəʾel, label=none; arc, ܓ݁ܰܒ݂ܪܺܝܐܝܶܠ, translit=Gaḇrīʾēl; ar, جِبْرِيل, Jibrīl, also ar, جبرائيل, Jibrāʾīl or ''Jabrāʾīl'', group="N" is an archangel with power to announce God's will to men. He is mentioned in the Hebrew Bible, the New Testament, and the Quran. Many Christian traditions — including Anglicanism, Eastern Orthodoxy, and Roman Catholicism — revere Gabriel as a saint. In the Hebrew Bible, Gabriel appears to the prophet Daniel to explain his visions ( Daniel 8:15–26, 9:21–27). The archangel also appears in the Book of Enoch and other ancient Jewish writings not preserved in Hebrew. Alongside the archangel Michael, Gabriel is described as the guar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hammam-Lif
Hammam-Lif ( ar, حمام الأنف, pronounced hammam linf) is a coastal town about 20 km south-east of Tunis, the capital of Tunisia. It has been known since antiquity for its thermal springs originating in Mount Bou Kornine. History Naro, which means fire, was Hammam-Lif's Punic name. In 1883, the French captain Ernest De Prudhomme discovered in his Hammam-lif residence the first archeological ruins of an ancient synagogue that once stood in Hammam-Lif in 3rd-5th century AD. Hammam-Lif was once the home of Italian, Greek and Jewish communities, especially before the end of the French colonial period. Hammam-Lif's most interesting site is probably Dar El Bey, which was the residence of Ali II Bey, the 4th bey of Tunis. Sport The local football team Club Sportif de Hammam-Lif won the Tunisian championship in 1952, 1954, 1955, 1956 and won the Tunisian Cup in 1946, 1947, 1948, 1949, 1950, 1985, 2001 Notable people *Ahmed Achour (1945-2021), conductor and composer *Wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bizerte
Bizerte or Bizerta ( ar, بنزرت, translit=Binzart , it, Biserta, french: link=no, Bizérte) the classical Hippo, is a city of Bizerte Governorate in Tunisia. It is the northernmost city in Africa, located 65 km (40mil) north of the capital Tunis. It is also known as the last town to remain under French control after the rest of the country won its independence from France. The city had 142,966 inhabitants in 2014. Names Hippo is the latinization of a PunicPerseus Digital Library Perseus.tufts.edu name ( xpu, 𐤏𐤐𐤅𐤍, ), probably related to the word ''ûbôn'', meaning "harbor". To distinguish it from (the modern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chasseurs D'Afrique
The ''Chasseurs d'Afrique'' were a light cavalry corps of chasseurs in the French Armée d'Afrique (Army of Africa). First raised in 1831 from regular French cavalry posted to Algeria, they numbered five regiments by World War II. For most of their history they were recruited from either French volunteers or French settlers in North Africa doing their military service. As such they were the mounted equivalent of the French Zouave infantry. The other major cavalry element in the Armee d'Afrique were the Spahis—recruited from the indigenous peoples of Algeria, Tunisia, and Morocco with mostly French officers. History First raised in 1831, shortly after the French occupation of Algiers, the Chasseurs d'Afrique (''Chass. d'Af.'' in common vernacular) were created through transfers from the '' chasseurs à cheval'', other metropolitan cavalry regiments and some infantry units. Initially about 40 members of each squadron were locally recruited indigenous horsemen. Two additional re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zouaves
The Zouaves were a class of light infantry regiments of the French Army serving between 1830 and 1962 and linked to French North Africa; as well as some units of other countries modelled upon them. The zouaves were among the most decorated units of the French Army. It was initially intended that the zouaves would be a regiment of Berber volunteers from the Zwawa group of tribes in Algeria ("Zwawa" being the origin of the French term ''zouave'') who had gained a martial reputation fighting for local rulers under the Ottoman Empire. The regiment was to consist of 1,600 Zwawa Berbers, French non-commissioned officers and French officers. 500 Zwawa were recruited in August and September 1830. However, twelve years later, this idea was dropped. More zouave regiments were raised and the men recruited to serve in them were almost exclusively French or people of French descent born in French Algeria (pied-noirs), a policy which continued until the final dissolution of said regiments a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Casablanca
Casablanca, also known in Arabic as Dar al-Bayda ( ar, الدَّار الْبَيْضَاء, al-Dār al-Bayḍāʾ, ; ber, ⴹⴹⴰⵕⵍⴱⵉⴹⴰ, ḍḍaṛlbiḍa, : "White House") is the largest city in Morocco and the country's economic and business center. Located on the Atlantic coast of the Chaouia plain in the central-western part of Morocco, the city has a population of about 3.71 million in the urban area, and over 4.27 million in the Greater Casablanca, making it the most populous city in the Maghreb region, and the eighth-largest in the Arab world. Casablanca is Morocco's chief port, with the Port of Casablanca being one of the largest artificial ports in the world, and the second largest port in North Africa, after Tanger-Med ( east of Tangier). Casablanca also hosts the primary naval base for the Royal Moroccan Navy. Casablanca is considered a Global Financial Centre, ranking 54th globally in the Global Financial Centres Index rankings for the ye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zaytuna Mosque
Al-Zaytuna Mosque, also known as Ez-Zitouna Mosque, and El-Zituna Mosque ( ar, جامع الزيتونة, literally meaning ''the Mosque of Olive''), is a major mosque at the center of the Medina of Tunis The Medina of Tunis is the medina quarter of Tunis, the capital of Tunisia. It has been a UNESCO World Heritage Site since 1979. The Medina contains some 700 monuments, including palaces, mosques, mausoleums, madrasas and fountains dating fr ... in Tunis, Tunisia. The mosque is the oldest in the city and covers an area of with nine entrances. It was founded at the end of the 7th century or in the early 8th century, but its current architectural form dates from a reconstruction in the 9th century, including many antique columns reused from Carthage, and from later additions and restorations over the centuries. The mosque is known to host one of the first and greatest University of Ez-Zitouna, universities in the history of Islam. Many Muslim scholarly method, scholars were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abdeljelil Zaouche
Abdeljelil Zaouche (; 15 December 1873 – 3 January 1947) was a Tunisian politician, reformer, and campaigner in the Tunisian independence movement. Youth Zaouche was born into a wealthy bourgeois family which had arrived in Tunis from Andalucia via Algeria in the eighteenth century. His father Tahar and his uncle Hassan occupied high-ranking positions under Ali Bey: they were, respectively, General of the royal guard and Brigadier-General in charge of tax-raising. He was born in his family's mansion in La Marsa to an Italian mother. His secondary education was at the Collège Saint-Charles in Tunis and then the lycée Louis-le-Grand in Paris where he took his baccalauréat. In 1894, he matriculated at the law faculty in Paris while also studying at the Institut des sciences politiques and the Collège de France. Strongly influenced by Jean Jaurès, he was also a pupil of Émile Durkheim, Émile Boutroux, Henri Poincaré, Antoine Aulard and Ernest Lavisse. He graduated i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sadok Ghileb
Sadok Ghileb (c. 1840–1912) was a Tunisian politician and mayor of Tunis. Biography Ghileb was born in Tunisia around 1840, into a bourgeois family of Turkish origin. He was the maternal uncle of Mustapha Dinguizli, who succeeded him in office.Mohamed El Aziz Ben Achour, ''Catégories de la société tunisoise dans la deuxième moitié du XIXe siècle'', éd. Institut national d'archéologie et d'art, Tunis, 1989, p. 235 During his studies at the Al-Zaytuna Mosque Ghileb became interested in politics. In 1864 he became an aide to Muhammad III as-Sadiq until he headed to City Council in Tunis as vice president in 1877. Between 1886 and 1902 he became the Governor of El Kef, of Soliman, Bizerte and Nabeul Nabeul (; ar, نابل ,Tamazight: ⵏⴰⴱⴻⵍ), is a coastal town located in northeastern Tunisia, on the south coast of the Cape Bon peninsula and surrounded by the Mediterranean Sea on both sides. It is the first seaside resort in Tunisia .... He succeeded Mohame ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)




