|
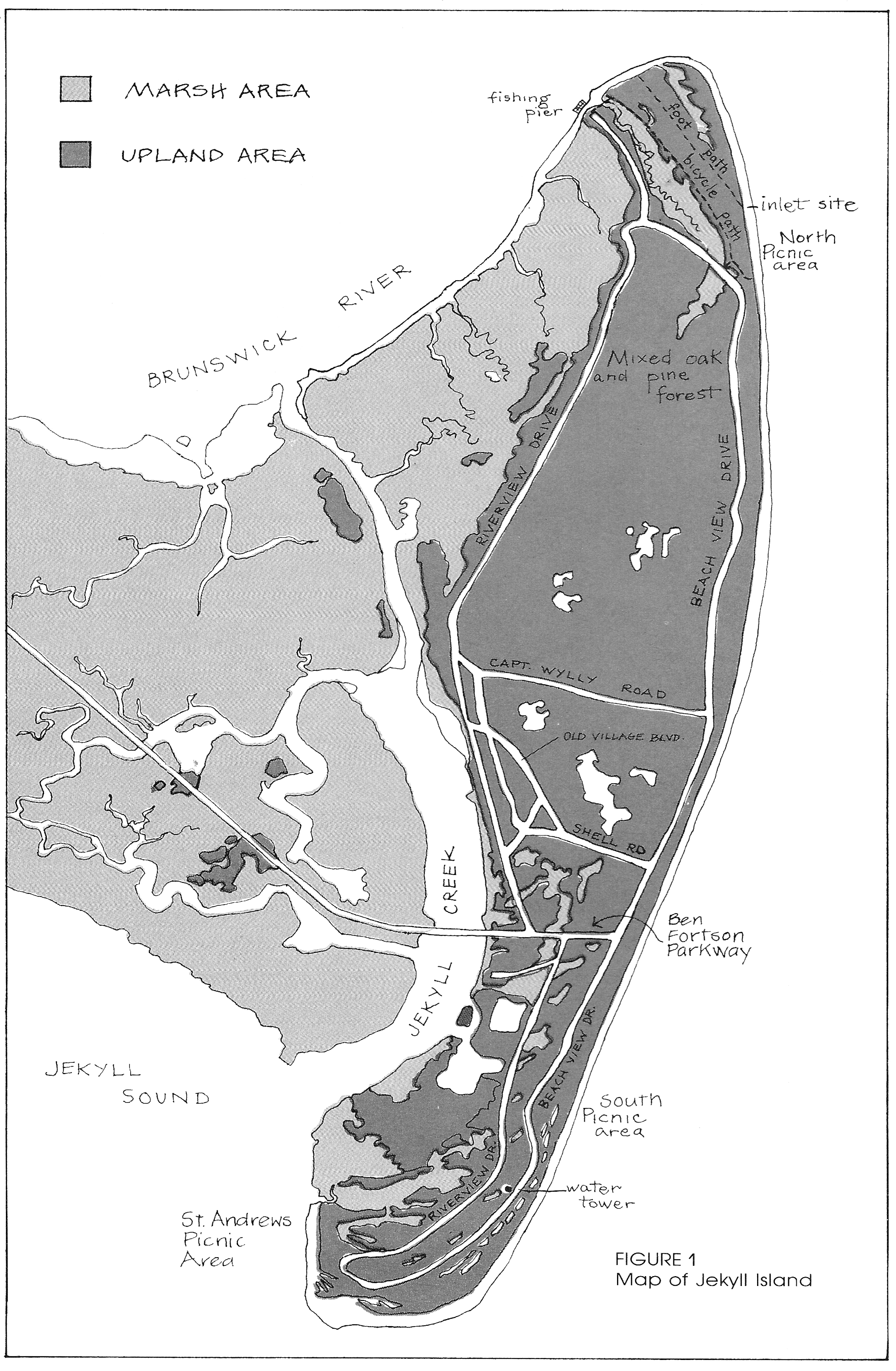
Jekyll Island, Georgia
Jekyll Island is located off the coast of the U.S. state of Georgia, in Glynn County. It is one of the Sea Islands and one of the Golden Isles of Georgia barrier islands. The island is owned by the State of Georgia and run by a self-sustaining, self-governing body. It was long used seasonally by indigenous peoples of the region. The Guale and the Mocama, the indigenous peoples of the area when Europeans first reached the area, were killed or forced to leave by the English of the Province of Carolina and their native allies, and by raids by French pirates. Plantations were developed on the island during the British colonial period. A few structures still standing are made of tabby, a coastal building material of crushed oyster shells. The island was developed in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. It was evacuated during World War II by order of the US government. In 1947 the state of Georgia acquired all the property, for security and preservation. A popular tourist destinati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glynn County, Georgia
Glynn County is located in the southeastern part of the U.S. state of Georgia. As of the 2010 census, the population was 79,626. The county seat is Brunswick. Glynn County is part of the Brunswick, Georgia Metropolitan Statistical Area. History Glynn County, one of the state's original eight counties created on February 5, 1777, was named after John Glynn, a member of the British House of Commons who defended the cause of the American Colonies before the American Revolution. The Battle of Bloody Marsh was fought in Glynn County. James Oglethorpe built Fort Frederica, which was used a base in the American Revolutionary War. Glynn Academy, established to educate boys, is the second oldest school in Georgia. Glynn County includes the most prominent of the Sea Islands of Georgia, including Jekyll Island, St. Simons Island, and Sea Island. The Georgia poet Sidney Lanier immortalized the seacoast there in his poem, "The Marshes of Glynn", which begins: :Glooms of the live-oa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Census-designated Place
A census-designated place (CDP) is a concentration of population defined by the United States Census Bureau for statistical purposes only. CDPs have been used in each decennial census since 1980 as the counterparts of incorporated places, such as self-governing cities, towns, and villages, for the purposes of gathering and correlating statistical data. CDPs are populated areas that generally include one officially designated but currently unincorporated community, for which the CDP is named, plus surrounding inhabited countryside of varying dimensions and, occasionally, other, smaller unincorporated communities as well. CDPs include small rural communities, edge cities, colonias located along the Mexico–United States border, and unincorporated resort and retirement communities and their environs. The boundaries of any CDP may change from decade to decade, and the Census Bureau may de-establish a CDP after a period of study, then re-establish it some decades later. Most unin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horton House (1743), Jekyll Island, GA
Horton House (also known as Horton-duBignon House, Brewery Ruins, duBignon Cemetery) is a historic site on Riverview Drive in Jekyll Island, Georgia. The tabby house was originally constructed in 1743 by Major William Horton, a top military aide to General James Oglethorpe. Horton also brewed beer in Georgia's first brewery (the ruins of which are a few hundred yards down the road). This structure has been meticulously preserved over the past 100 years as an example of coastal Georgia building techniques and as one of the oldest surviving buildings in the state. Across the street from the Horton House ruins is the du Bignon cemetery, a tabby wall surrounding the graves of five people: Ann Amelia du Bignon, Joseph du Bignon, Marie Felicite Riffault, Hector deLiyannis, and George Harvey. Horton House, the Brewery Ruins, and the cemetery were added to the National Register of Historic Places in 1971. Gallery File:Horton House outside.JPG, Outside File:Horton House inside 1.JPG, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sidney Lanier Bridge
The Sidney Lanier Bridge is a cable-stayed bridge that spans the Brunswick River (Georgia), Brunswick River in Brunswick, Georgia, carrying four lanes of U.S. Route 17 in Georgia, U.S. Route 17. The current bridge was built as a replacement to the original vertical-lift bridge, which was twice struck by ships. It is currently the longest-spanning bridge in Georgia and is tall. It was named for poet Sidney Lanier. Each year (usually in February), there is the "Bridge Run" sponsored by Southeast Georgia Health System when the south side of the bridge is closed to traffic and people register to run (or walk) the bridge. The bridge hosts the WX4BWK amateur radio repeater on the top of one of its pillars. History The original Sidney Lanier Bridge was opened June 22, 1956, and was built by Sverdrup & Parcel, the same firm that designed the I-35W Mississippi River bridge which collapsed in 2007. On November 7, 1972 the ship ''African Neptune'' struck the bridge, causing parts of the b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hammock (ecology)
Hammock is a term used in the southeastern United States for stands of trees, usually hardwood, that form an ecological island in a contrasting ecosystem. Hammocks grow on elevated areas, often just a few inches high, surrounded by wetlands that are too wet to support them. The term ''hammock'' is also applied to stands of hardwood trees growing on slopes between wetlands and drier uplands supporting a mixed or coniferous forest. Types of hammocks found in the United States include tropical hardwood hammocks, temperate hardwood hammocks, and maritime or coastal hammocks. Hammocks are also often classified as hydric (wet soil), mesic (moist soil) or xeric (dry soil). The types are not exclusive, but often grade into each other. Unlike many ecosystems of the coastal plain of the southeastern United States, hammocks are not tolerant of fire. Hammocks tend to occur in locations where fire is not common, or where there is some protection from fire in neighboring ecosystems. Hammocks ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marsh
A marsh is a wetland that is dominated by herbaceous rather than woody plant species.Keddy, P.A. 2010. Wetland Ecology: Principles and Conservation (2nd edition). Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK. 497 p Marshes can often be found at the edges of lakes and streams, where they form a transition between the aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems. They are often dominated by grasses, rushes or reeds. If woody plants are present they tend to be low-growing shrubs, and the marsh is sometimes called a carr. This form of vegetation is what differentiates marshes from other types of wetland such as swamps, which are dominated by trees, and mires, which are wetlands that have accumulated deposits of acidic peat. Marshes provide habitats for many kinds of invertebrates, fish, amphibians, waterfowl and aquatic mammals. This biological productivity means that marshes contain 0.1% of global sequestered terrestrial carbon. Moreover, they have an outsized influence on climate resi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Humid Subtropical Climate
A humid subtropical climate is a zone of climate characterized by hot and humid summers, and cool to mild winters. These climates normally lie on the southeast side of all continents (except Antarctica), generally between latitudes 25° and 40° and are located poleward from adjacent tropical climates. It is also known as warm temperate climate in some climate classifications. Under the Köppen climate classification, ''Cfa'' and ''Cwa'' climates are either described as humid subtropical climates or warm temperate climates. This climate features mean temperature in the coldest month between (or ) and and mean temperature in the warmest month or higher. However, while some climatologists have opted to describe this climate type as a "humid subtropical climate", Köppen himself never used this term. The humid subtropical climate classification was officially created under the Trewartha climate classification. In this classification, climates are termed humid subtropical when the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holocene
The Holocene ( ) is the current geological epoch. It began approximately 11,650 cal years Before Present (), after the Last Glacial Period, which concluded with the Holocene glacial retreat. The Holocene and the preceding Pleistocene together form the Quaternary period. The Holocene has been identified with the current warm period, known as MIS 1. It is considered by some to be an interglacial period within the Pleistocene Epoch, called the Flandrian interglacial.Oxford University Press – Why Geography Matters: More Than Ever (book) – "Holocene Humanity" section https://books.google.com/books?id=7P0_sWIcBNsC The Holocene corresponds with the rapid proliferation, growth and impacts of the human species worldwide, including all of its written history, technological revolutions, development of major civilizations, and overall significant transition towards urban living in the present. The human impact on modern-era Earth and its ecosystems may be considered of global si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological Epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was finally confirmed in 2009 by the International Union of Geological Sciences, the cutoff of the Pleistocene and the preceding Pliocene was regarded as being 1.806 million years Before Present (BP). Publications from earlier years may use either definition of the period. The end of the Pleistocene corresponds with the end of the last glacial period and also with the end of the Paleolithic age used in archaeology. The name is a combination of Ancient Greek grc, label=none, πλεῖστος, pleīstos, most and grc, label=none, καινός, kainós (latinized as ), 'new'. At the end of the preceding Pliocene, the previously isolated North and South American continents were joined by the Isthmus of Panama, causing Great American Interchang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marshlands
A marsh is a wetland that is dominated by herbaceous rather than woody plant species.Keddy, P.A. 2010. Wetland Ecology: Principles and Conservation (2nd edition). Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK. 497 p Marshes can often be found at the edges of lakes and streams, where they form a transition between the aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems. They are often dominated by grasses, rushes or reeds. If woody plants are present they tend to be low-growing shrubs, and the marsh is sometimes called a carr. This form of vegetation is what differentiates marshes from other types of wetland such as swamps, which are dominated by trees, and mires, which are wetlands that have accumulated deposits of acidic peat. Marshes provide habitats for many kinds of invertebrates, fish, amphibians, waterfowl and aquatic mammals. This biological productivity means that marshes contain 0.1% of global sequestered terrestrial carbon. Moreover, they have an outsized influence on climate res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jekyll Island Club
The Jekyll Island Club was a private club on Jekyll Island, on Georgia's Atlantic coast. It was founded in 1886 when members of an incorporated hunting and recreational club purchased the island for $125,000 (about $3.1 million in 2017) from John Eugene du Bignon. The original design of the Jekyll Island Clubhouse, with its signature turret, was completed in January 1888. The club thrived through the early 20th century; its members came from many of the world's wealthiest families, most notably the Morgans, Rockefellers, and Vanderbilts. The club closed at the end of the 1942 season due to complications from World War II. In 1947, after five years of funding a staff to keep up the lawn and cottages, the island was purchased from the club's remaining members for $675,000 (about $7.4 million in 2017) during condemnation proceedings by the state of Georgia. The state tried operating the club as a resort, but this was not financially successful, and the entire complex was closed by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Causeway
A causeway is a track, road or railway on the upper point of an embankment across "a low, or wet place, or piece of water". It can be constructed of earth, masonry, wood, or concrete. One of the earliest known wooden causeways is the Sweet Track in the Somerset Levels, England, which dates from the Neolithic age. Timber causeways may also be described as both boardwalks and bridges. Etymology When first used, the word ''causeway'' appeared in a form such as "causey way" making clear its derivation from the earlier form "causey". This word seems to have come from the same source by two different routes. It derives ultimately, from the Latin for heel, ''calx'', and most likely comes from the trampling technique to consolidate earthworks. Originally, the construction of a causeway utilised earth that had been trodden upon to compact and harden it as much as possible, one layer at a time, often by enslaved bodies or flocks of sheep. Today, this work is done by machines. The s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |