|
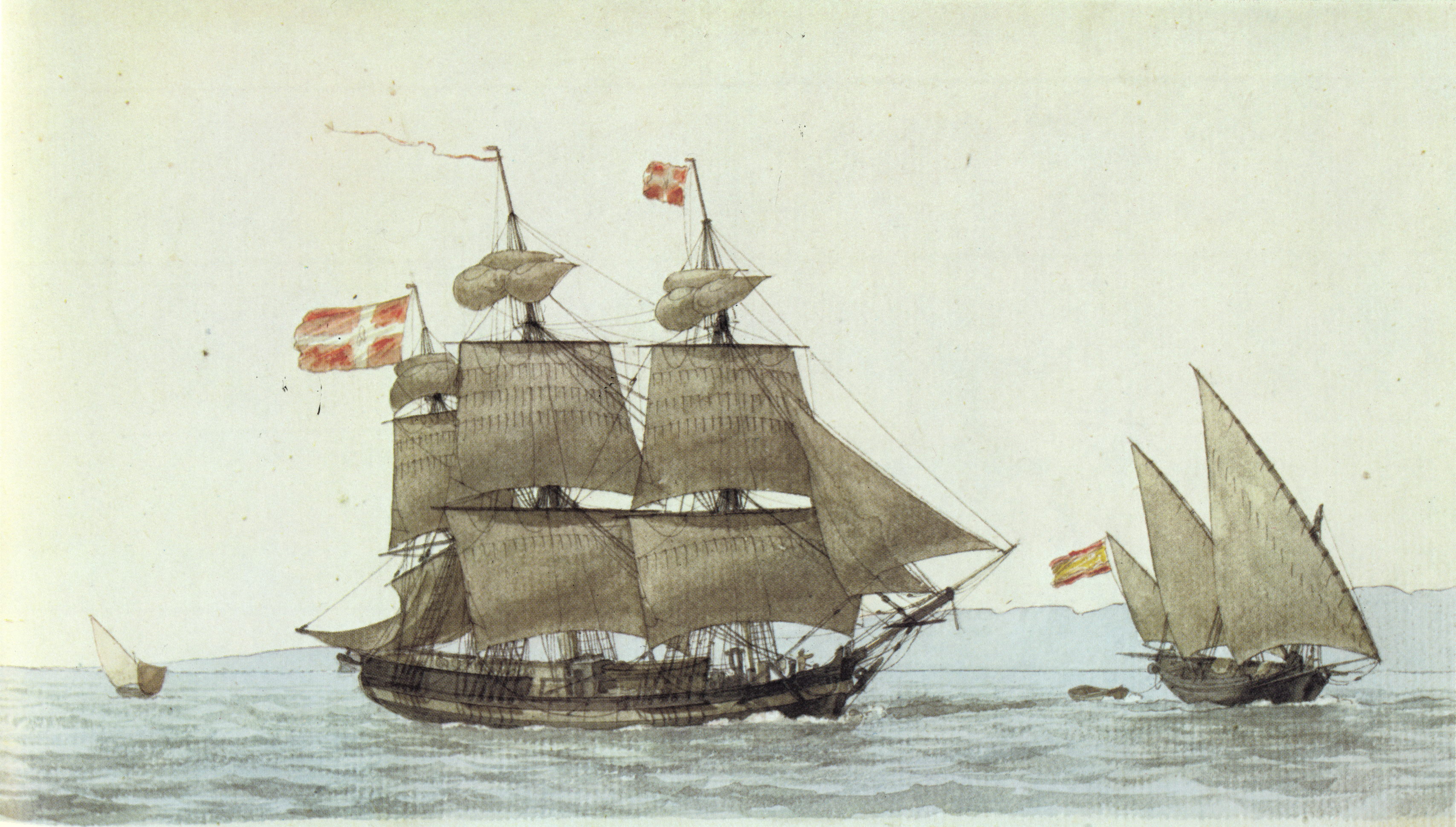
Jean Bart (1807 Ship)
''Jean Bart'' was a French privateer launched in Marseille in 1807, and commissioned as a privateer by the Daumas brothers.''Guerre et Commerce en Méditerranée'', p.325 She was the first privateer captained by Jean-Joseph Roux. She is depicted in two watercolours by Antoine Roux the Elder, dated 1810 and 1811. Career First captain ''Jean Bart'' sailed for her first cruise in 1807, returning to Marseille in 1808. Career under Jean-Joseph Roux From May 1809 to July 1810, she was captained by Jean-Joseph Roux. ''Jean Bart'' a 109-man crew, with four 12-pounder carronades, two six-pounder long guns, one chase 10-pounder gun mounted on a pivot at the bow, along with 60 rifles, 28 pistols, 33 sabres and 13 spears.''Guerre et Commerce en Méditerranée'', p.320 The crew comprised 11 officiers (including one surgeon), 6 masters and 2 second masters (including two crew masters, two master gunners, one captain-at-arms, one master helmsman, one master carpenter and one load ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean Bart Vs Eagle-1810
Jean may refer to: People * Jean (female given name) * Jean (male given name) * Jean (surname) Fictional characters * Jean Grey, a Marvel Comics character * Jean Valjean, fictional character in novel ''Les Misérables'' and its adaptations * Jean Pierre Polnareff, a fictional character from ''JoJo's Bizarre Adventure'' Places * Jean, Nevada, USA; a town * Jean, Oregon, USA Entertainment * Jean (dog), a female collie in silent films * "Jean" (song) (1969), by Rod McKuen, also recorded by Oliver * ''Jean Seberg'' (musical), a 1983 musical by Marvin Hamlisch Other uses * JEAN (programming language) * USS ''Jean'' (ID-1308), American cargo ship c. 1918 * Sternwheeler Jean, a 1938 paddleboat of the Willamette River See also *Jehan * * Gene (other) * Jeanne (other) * Jehanne (other) * Jeans (other) * John (other) John is a common English name and surname: * John (given name) * John (surname) John may also refer to: New Testa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Civil And Naval Ensign Of France
Civil may refer to: *Civic virtue, or civility *Civil action, or lawsuit *Civil affairs *Civil and political rights *Civil disobedience *Civil engineering *Civil (journalism), a platform for independent journalism *Civilian, someone not a member of armed forces *Civil law (other), multiple meanings *Civil liberties *Civil religion *Civil service *Civil society *Civil war *Civil (surname) {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean Bart
Jean Bart (; ; 21 October 1650 – 27 April 1702) was a French Admiral, naval commander and privateer. Early life Jean Bart was born in Dunkirk, France, Dunkirk in 1650 to a seafaring family, the son of Jean-Cornil Bart (c. 1619-1668) who has been described variously as a fisherman or French corsairs, corsair commander serving for the Dutch Republic. His grandfather, Cornil weus, was a vice-admiral and fought the Dutch on behalf of Spain at the beginning of the Eighty Years' War. His great-grandfather, Michel Jacobsen (1560-1632) distinguished himself in the service of the Spanish crown, bringing back the Invincible Armada after his failed attempt to invade England in 1588. He was appointed vice-admiral by Philip IV of Spain. In 1622, his great-uncle, Jan Jacobsen, also in the service of Spain, blew himself up with his ship, the ''Saint-Vincent'', rather than surrender. He almost certainly spoke French Flemish, Dutch, at that time the native language in the region, and his birth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean-Joseph Roux
Jean-Joseph Roux (Marseille, 1769 — Odessa, 1817) was a French privateer. Career Roux became captain in 1809. He captained ships in six commerce raiding cruises: three on ''Jean Bart'', one on ''Payan-Latour'', and two on ''Babiole'', totalling 21 prizes. Citations References * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Roux, Jean-Joseph 1769 births 1817 deaths People of the Quasi-War French privateers Military personnel from Marseille French military personnel of the Napoleonic Wars ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antoine Roux
Ange-Joseph Antoine Roux, "Antoine Roux" (1765–1835) was a French fine art painter who specialised in maritime painting, sometimes referred to as marine art. Career Roux came from a family of artists and primarily worked in Marseille. Early in life he was apprenticed to his father, Joseph Roux (1752–93), a hydrographer as well as an artist in his own right, spending his leisure hours painting and drawing.The Sketchbooks of Antoine Roux , Peabody Essex Museum, 2006. French galley at Marseilles (PAG9744) '', National Maritime Museum, Greenwich, London. Antoine died of cholera in Marseille in 1835. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carronade
A carronade is a short, smoothbore, cast-iron cannon which was used by the Royal Navy. It was first produced by the Carron Company, an ironworks in Falkirk, Scotland, and was used from the mid-18th century to the mid-19th century. Its main function was to serve as a powerful, short-range, anti-ship and anti-crew weapon. The technology behind the carronade was greater dimensional precision, with the shot fitting more closely in the barrel thus transmitting more of the propellant charge's energy to the projectile, allowing a lighter gun using less gunpowder to be effective. Carronades were initially found to be very successful, but they eventually disappeared as naval artillery advanced, with the introduction of rifling and consequent change in the shape of the projectile, exploding shells replacing solid shot, and naval engagements being fought at longer ranges. History The carronade was designed as a short-range naval weapon with a low muzzle velocity for merchant ships, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Six-pounder Long Gun
6-pounder gun or 6-pdr, usually denotes a gun firing a projectile weighing approximately . Guns of this type include: *QF 6 pounder Hotchkiss, a 57 mm naval gun of the 1880s; a similar weapon was designed by Driggs-Schroeder for the US Navy *Driggs-Schroeder Marks II and III and Driggs-Seabury M1898 and M1900 57 mm guns on mobile mounts, used by the US Army circa 1890–1920 *QF 6 pounder 6 cwt Hotchkiss, a British 57 mm tank gun of 1917 *QF 6 pounder Nordenfelt, a 57 mm naval gun of the 1880s very similar to the Hotchkiss *Ordnance QF 6-pounder, a British 57 mm anti-tank and tank gun of World War II *QF 6 pounder 10 cwt gun, a British twin mount naval and coast defence gun 1937–1956. Older types include: *Canon de 6 système An XI, a French 6-pounder muzzle-loading cannon of the Napoleonic era *M1841 6-pounder field gun, an American 6-pounder smoothbore muzzle-loading cannon of the mid-1800s Guns denoted by calibre Examples simply referred to by ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Continental System
The Continental Blockade (), or Continental System, was a large-scale embargo against British trade by Napoleon Bonaparte against the British Empire from 21 November 1806 until 11 April 1814, during the Napoleonic Wars. Napoleon issued the Berlin Decree on 21 November 1806 in response to the naval blockade of the French coasts enacted by the British government on 16 May 1806.Jean Tulard, ''Napoléon'', Hachette, 2008, p. 207 The embargo was applied intermittently, ending on 11 April 1814 after Napoleon's first abdication. Aside from subduing Britain, the blockade was also intended to establish French industrial and commercial hegemony in Europe. Within the French Empire, the newly acquired territories and client states were subordinate to France itself, as there was a unified market within France (no internal barriers or tariffs) while economic distortions were maintained on the borders of the new territories. The Berlin Decree forbade the import of British goods into any Europe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pink (ship)
A pink (french: pinque) is a sailing ship with a very narrow stern. The term was applied to two different types of ship. The first was a small, flat-bottomed ship with a narrow stern; the name derived from the Italian word . It was used primarily in the Mediterranean Sea as a cargo ship. In the Atlantic Ocean the word pink was used to describe any small ship with a narrow stern, having derived from the Dutch word meaning pinched. They had a large cargo capacity, and were generally square rigged. Their flat bottoms (and resulting shallow draught) made them more useful in shallow waters than some similar classes of ship. They were most often used for short-range missions in protected channels, as both merchantmen and warships. A number saw service in the English Navy during the second half of the 17th century. In the 1730s pinks were used in cross-Atlantic voyages to bring Palatinate immigrants to America. This model of ship was often used in the Mediterranean because it coul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polacca
A polacca (or ''polacre'') is a type of seventeenth- to nineteenth-century sailing vessel, similar to the xebec. The name is the feminine of "Polish" in the Italian language. The polacca was frequently seen in the Mediterranean. It had two or three single-pole masts, the three-masted vessels often with a lateen hoisted on the foremast (which was slanted forward to accommodate the large lateen yard) and a gaff or lateen on the mizzen mast. The mainmast was square-rigged after the European style. Special polaccas were used by Murat Reis, whose ships had lateen sails in front and fore-and-aft rig behind. Some polacca pictures show what appears to be a ship-rigged vessel (sometimes with a lateen on the mizzen) with a galley-like hull and single-pole masts. Thus, the term "polacca" seems to refer primarily to the masting and possibly the hull type as opposed to the type of rig used for the sails. Two-masted polaccas were referred to as brig-polaccas with square sails on both masts. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Golfe Juan
Golfe-Juan (; oc, Lo Gorg Joan, Lo Golfe Joan) is a seaside resort on France's Côte d'Azur. The distinct local character of Golfe-Juan is indicated by the existence of a demonym, "Golfe-Juanais", which is applied to its inhabitants. Overview Golfe-Juan belongs to the commune of Vallauris in the Grasse arrondissement of the Alpes-Maritimes department, which belongs in turn to the Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur region of France. The area is served by the ''Golfe Juan-Vallauris'' railway station. On March 1, 1815, Napoléon Bonaparte landed at Golfe-Juan with 607 Grenadiers of the Old Guard, 118 Polish Lancers, some 300 Corsicans, 50 Elite Gendarmes, 80 civilians, and 2 light artillery pieces, having escaped exile on the island of Elba. His return to Paris, commemorated by the Route Napoléon, and the campaign that led to his ultimate defeat at the Battle of Waterloo are known as the "Hundred Days". "Golfe Juan" is also the name of a pointillist painting done by Paul Signac (1863� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Santa Margherita Ligure
Santa Margherita Ligure ( lij, Santa Margaita) is a ''comune'' (municipality) in the Metropolitan City of Genoa in the Italian region Liguria, located about southeast of Genoa, in the area traditionally known as Tigullio. It has a port, used for both tourism and fishing activities. Part of ''comune '' territory is included in the Regional Natural Park of Portofino. Santa Margherita Ligure borders the following municipalities: Camogli, Portofino, Rapallo. History The presence of a Roman settlement has not been definitely proven. The burgh, known as ''Pescino'', was devastated by Rothari in 641 and by the Saracens in the 10th century. Later it was a fief of the Fieschi family until 1229, when it was acquired by the Republic of Genoa. In 1432 it was attacked by the fleet of Venice and in 1549, together with Rapallo, by that of Turgut. In 1813, under the Napoleonic domination, the two burghs of ''Pescino'' and ''Corte'' were unified as ''Porto Napoleone''. Two years later it was ann ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |