|
Jean-Baptiste Du Casse
Jean-Baptiste du Casse (2 August 1646 – 25 June 1715) was a French privateer, admiral, and colonial administrator Colonialism is a practice or policy of control by one people or power over other people or areas, often by establishing colonies and generally with the aim of economic dominance. In the process of colonisation, colonisers may impose their relig ... who served throughout the Atlantic World during the 17th and 18th centuries. Likely born 2 August 1646 in Saubusse, near Pau, Pyrénées-Atlantiques, Pau (Béarn), to a Huguenot family, du Casse joined the French merchant marine and served in the French East India Company, East India Company and the Atlantic slave trade, slave-trading Compagnie du Sénégal. Later, he joined the French Navy and took part in several victorious expeditions during the War of the League of Augsburg in the West Indies and Spanish South America. During the War of the Spanish Succession, he participated in several key naval battles, includ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lieutenant General
Lieutenant general (Lt Gen, LTG and similar) is a three-star military rank (NATO code OF-8) used in many countries. The rank traces its origins to the Middle Ages, where the title of lieutenant general was held by the second-in-command on the battlefield, who was normally subordinate to a captain general. In modern armies, lieutenant general normally ranks immediately below general and above major general; it is equivalent to the navy rank of vice admiral, and in air forces with a separate rank structure, it is equivalent to air marshal. A lieutenant general commands an army corps, made up of typically three army divisions, and consisting of around 60 000 to 70 000 soldiers (U.S.). The seeming incongruity that a lieutenant general outranks a major general (whereas a major outranks a lieutenant) is due to the derivation of major general from sergeant major general, which was a rank subordinate to lieutenant general (as a lieutenant outranks a sergeant major). In contrast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Order Of Saint Louis
The Royal and Military Order of Saint Louis (french: Ordre Royal et Militaire de Saint-Louis) is a dynastic order of chivalry founded 5 April 1693 by King Louis XIV, named after Saint Louis (King Louis IX of France). It was intended as a reward for exceptional officers, notable as the first decoration that could be granted to non-nobles. By the authorities of the French Republic, it is considered a predecessor of the Legion of Honour, with which it shares the red ribbon (though the Legion of Honour is awarded to military personnel and civilians alike). Although officially abolished by the government authorities of the July Revolution in 1830 following the French Revolution, its activities carried on as a dynastic order of the formerly sovereign royal family. As such, it is still recognised by the International Commission on Orders of Chivalry. Members The King was the Grand Master of the order, and the Dauphin was automatically a member as well. The Order had three cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Barcelona (1713–14)
{{Disambiguation ...
Siege of Barcelona may refer to: * Siege of Barcelona (801), during the Reconquista * Siege of Barcelona (1462), during the Catalan Civil War * Siege of Barcelona (1472), during the Catalan Civil War * Siege of Barcelona (1651), during the Catalan Revolt * Siege of Barcelona (1697), during the Nine Years' War * Siege of Barcelona (1705), during the War of the Spanish Succession * Siege of Barcelona (1706), during the War of the Spanish Succession * Siege of Barcelona (1713–1714), during the War of the Spanish Succession * Siege of Barcelona (1808), during the Peninsular War See also * ''The Surrender of Barcelona'' (1934–1937), a painting by Wyndham Lewis * Battle of Barcelona The Naval battle of Barcelona was a naval engagement of the Franco-Habsburg War fought off Barcelona from 29 June to 3 July 1642 between a Spanish fleet commanded by Juan Alonso Idiáquez, Duke of Ciudad Real, and a French fleet under Jean Arm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Málaga (1704)
The battle of Málaga, also known as the battle of Vélez-Málaga, was a major fleet action which took place during the War of the Spanish Succession between an Anglo- Dutch fleet and a French naval force on 24 August 1704. Both sides fought an intense engagement before the Anglo-Dutch fleet withdrew the next day. The French subsequently returned to Toulon, transforming the battle from a tactical stalemate into a strategic defeat, as they would not put out to sea again for the duration of the conflict. Occurring soon after the Anglo-Dutch capture of Gibraltar a few weeks prior, the battle served as one of the numerous engagements which took place for control over the settlement during the war. In 1701, the War of the Spanish Succession broke out, pitting the Bourbon kingdoms of France and Spain against Grand Alliance, which included the English and Dutch. An Anglo-Dutch fleet under Sir George Rooke was sent into the Mediterranean in 1704, capturing Gibraltar on 4 August. U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
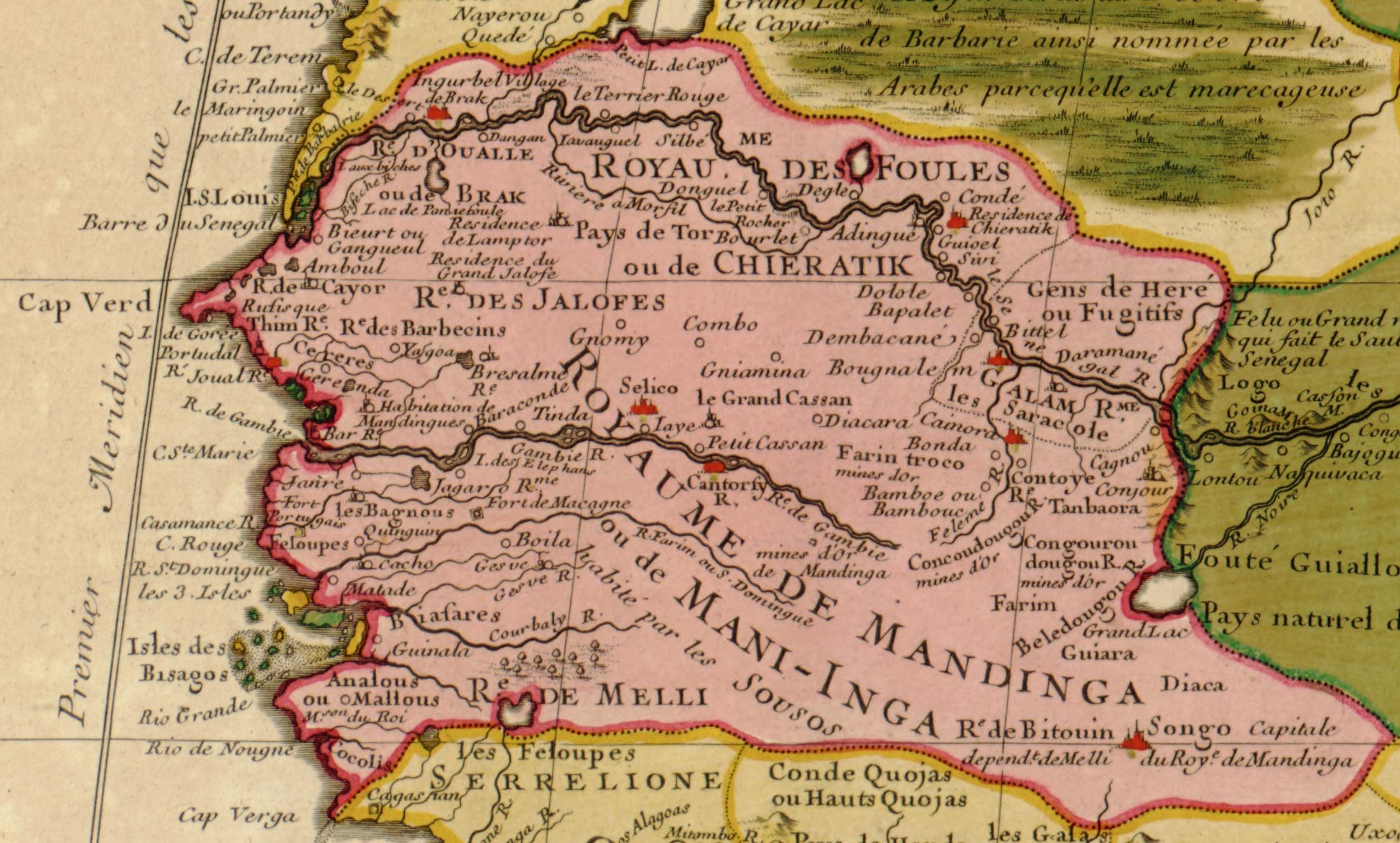
Compagnie Du Sénégal
The Compagnie du Sénégal (French for the "Senegal Company" or, more literally, the "Company of the Senegal") was a 17th-century French chartered company that administered the territories of Saint-Louis and Gorée island as part of French Senegal. First company The company succeeded to some of the territories of the French West India Company in 1672, just prior to its bankruptcy and the revocation of its charter in 1674. Sieur de Richemont served as governor of its territories from 1672 to 1673 and was succeeded by the company's director Jacques Fuméchon, who served until 1682. The company's operations were then taken over by the and . Second company In 1696, the Compagnie royale du Sénégal was established and operated by Jean Bourguignon from March 1696 to April 1697 and then by until May 1702. They traded slaves with the Hausa Kingdoms, Mali, and the Moors in Mauritania. Third company In 1709, a third Compagnie du Sénégal was established. See also * Compagnie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlantic Slave Trade
The Atlantic slave trade, transatlantic slave trade, or Euro-American slave trade involved the transportation by slave traders of enslaved African people, mainly to the Americas. The slave trade regularly used the triangular trade route and its Middle Passage, and existed from the 16th to the 19th centuries. The vast majority of those who were transported in the transatlantic slave trade were people from Central and West Africa that had been sold by other West Africans to Western European slave traders,Thornton, p. 112. while others had been captured directly by the slave traders in coastal raids; Europeans gathered and imprisoned the enslaved at forts on the African coast and then brought them to the Americas. Except for the Portuguese, European slave traders generally did not participate in the raids because life expectancy for Europeans in sub-Saharan Africa was less than one year during the period of the slave trade (which was prior to the widespread availability of qu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French East India Company
The French East India Company (french: Compagnie française pour le commerce des Indes orientales) was a colonial commercial enterprise, founded on 1 September 1664 to compete with the English (later British) and Dutch trading companies in the East Indies. Planned by Jean-Baptiste Colbert, it was chartered by King Louis XIV for the purpose of trading in the Eastern Hemisphere. It resulted from the fusion of three earlier companies, the 1660 Compagnie de Chine, the Compagnie d'Orient and Compagnie de Madagascar. The first Director General for the Company was François de la Faye, who was adjoined by two Directors belonging to the two most successful trading organizations at that time: François Caron, who had spent 30 years working for the Dutch East India Company, including more than 20 years in Japan, and Marcara Avanchintz, an Armenian trader from Isfahan, Persia. History In 1604, French king Henry IV authorized the first ''Compagnie des Indes Orientales'', granting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huguenot
The Huguenots ( , also , ) were a religious group of French Protestants who held to the Reformed, or Calvinist, tradition of Protestantism. The term, which may be derived from the name of a Swiss political leader, the Genevan burgomaster Bezanson Hugues (1491–1532?), was in common use by the mid-16th century. ''Huguenot'' was frequently used in reference to those of the Reformed Church of France from the time of the Protestant Reformation. By contrast, the Protestant populations of eastern France, in Alsace, Moselle, and Montbéliard, were mainly Lutherans. In his ''Encyclopedia of Protestantism'', Hans Hillerbrand wrote that on the eve of the St. Bartholomew's Day massacre in 1572, the Huguenot community made up as much as 10% of the French population. By 1600, it had declined to 7–8%, and was reduced further late in the century after the return of persecution under Louis XIV, who instituted the ''dragonnades'' to forcibly convert Protestants, and then finally revoked ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Béarn
The Béarn (; ; oc, Bearn or ''Biarn''; eu, Bearno or ''Biarno''; or ''Bearnia'') is one of the traditional provinces of France, located in the Pyrenees mountains and in the plain at their feet, in southwest France. Along with the three Basque provinces of Soule, Lower Navarre, and Labourd, the Principality of Bidache, as well as small parts of Gascony, it forms in the southwest the current ''département'' of Pyrénées-Atlantiques (64). The capitals of Béarn were Beneharnum (until 841), Morlaàs (from ca. 1100), Orthez (from the second half of the 13th century), and then Pau (beginning in the mid-15th century). Béarn is bordered by Basque provinces Soule and Lower Navarre to the west, by Gascony ( Landes and Armagnac) to the north, by Bigorre to the east, and by Spain (Aragon) to the south. Today, the mainstays of the Béarn area are the petroleum industry, the aerospace industry through the helicopter turboshaft engine manufacturer Turbomeca, tourism and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlantic World
The Atlantic World comprises the interactions among the peoples and empires bordering the Atlantic Ocean rim from the beginning of the Age of Discovery to the early 19th century. Atlantic history is split between three different contexts: trans-Atlantic history, meaning the international history of the Atlantic World; circum-Atlantic history, meaning the transnational history of the Atlantic World; and cis-Atlantic history within an Atlantic context. The Atlantic slave trade continued into the 19th century, but the international trade was largely outlawed in 1807 by Britain. Slavery ended in 1865 in the United States and in the 1880s in Brazil (1888) and Cuba (1886). While some scholars stress that the history of the "Atlantic World" culminates in the "Atlantic Revolutions" of the late 18th early 19th centuries, the most influential research in the field examines the slave trade and the study of slavery, thus in the late-19th century terminus as part of the transition from Atlantic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colonial Administrator
Colonialism is a practice or policy of control by one people or power over other people or areas, often by establishing colonies and generally with the aim of economic dominance. In the process of colonisation, colonisers may impose their religion, language, economics, and other cultural practices. The foreign administrators rule the territory in pursuit of their interests, seeking to benefit from the colonised region's people and resources. It is associated with but distinct from imperialism. Though colonialism has existed since ancient times, the concept is most strongly associated with the European colonial period starting with the 15th century when some European states established colonising empires. At first, European colonising countries followed policies of mercantilism, aiming to strengthen the home-country economy, so agreements usually restricted the colony to trading only with the metropole (mother country). By the mid-19th century, the British Empire gave up mer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)