|
Javed Iqbal Kazi
Javed Iqbal Kazi ( ur, ; Born 29 May 1955) (1955–2014) was a Pakistani pathologist specialized in renal pathology, professor and chairman of Histopathology at Karachi Medical and Dental College, Sindh Institute of Urology & Transplantation, Dr. Ziauddin Hospitals & National Institute of Blood Diseases, and served as Dean of medicine of University of Karachi. He was also the board member of Journal of Pakistan Medical Association since 2005. He established the department of Histopathology at Sindh Institute of Urology & Transplantation, Karachi, in 1995 and is said to have established Renal and Transplant Pathology in Pakistan. Early life and career Javed I. Kazi was born on 29 May 1955 in Karachi, Pakistan. He graduated from Dow Medical College in 1980. Kazi served as a lecturer of pathology at Jinnah Sindh Medical University and did his M.Phil. in histopathology from BMSI, JPMC- Jinnah Postgraduate Medical Centre in 1986. He then pursued his Ph.D. in Histopathology from Unive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karachi
Karachi (; ur, ; ; ) is the most populous city in Pakistan and 12th most populous city in the world, with a population of over 20 million. It is situated at the southern tip of the country along the Arabian Sea coast. It is the former capital of Pakistan and capital of the province of Sindh. Ranked as a beta-global city, it is Pakistan's premier industrial and financial centre, with an estimated GDP of over $200 billion ( PPP) . Karachi paid $9billion (25% of whole country) as tax during fiscal year July 2021 to May 2022 according to FBR report. Karachi is Pakistan's most cosmopolitan city, linguistically, ethnically, and religiously diverse, as well as one of Pakistan's most secular and socially liberal cities. Karachi serves as a transport hub, and contains Pakistan’s two largest seaports, the Port of Karachi and Port Qasim, as well as Pakistan's busiest airport, Jinnah International Airport. Karachi is also a media center, home to news channels, film and fashi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pathology
Pathology is the study of the causes and effects of disease or injury. The word ''pathology'' also refers to the study of disease in general, incorporating a wide range of biology research fields and medical practices. However, when used in the context of modern medical treatment, the term is often used in a narrower fashion to refer to processes and tests that fall within the contemporary medical field of "general pathology", an area which includes a number of distinct but inter-related medical specialties that diagnose disease, mostly through analysis of tissue, cell, and body fluid samples. Idiomatically, "a pathology" may also refer to the predicted or actual progression of particular diseases (as in the statement "the many different forms of cancer have diverse pathologies", in which case a more proper choice of word would be " pathophysiologies"), and the affix ''pathy'' is sometimes used to indicate a state of disease in cases of both physical ailment (as in cardiomy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Renal
The kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped organs found in vertebrates. They are located on the left and right in the retroperitoneal space, and in adult humans are about in length. They receive blood from the paired renal arteries; blood exits into the paired renal veins. Each kidney is attached to a ureter, a tube that carries excreted urine to the bladder. The kidney participates in the control of the volume of various body fluids, fluid osmolality, acid–base balance, various electrolyte concentrations, and removal of toxins. Filtration occurs in the glomerulus: one-fifth of the blood volume that enters the kidneys is filtered. Examples of substances reabsorbed are solute-free water, sodium, bicarbonate, glucose, and amino acids. Examples of substances secreted are hydrogen, ammonium, potassium and uric acid. The nephron is the structural and functional unit of the kidney. Each adult human kidney contains around 1 million nephrons, while a mouse kidney contains only ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transplant Rejection
Transplant rejection occurs when Organ transplant, transplanted tissue is rejected by the recipient's immune system, which destroys the transplanted tissue. Transplant rejection can be lessened by determining the molecular similitude between donor and recipient and by use of immunosuppressant drugs after transplant. Types of transplant rejection Transplant rejection can be classified into three types: hyperacute, acute, and chronic. These types are differentiated by how quickly the recipient's immune system is activated and the specific aspect or aspects of immunity involved. Hyperacute rejection Hyperacute rejection is a form of rejection that manifests itself in the minutes to hours following transplantation. It is caused by the presence of pre-existing Antibody, antibodies in the recipient that recognize antigens in the donor organ. These antigens are located on the endothelial lining of blood vessels within the transplanted organ and, once antibodies bind, will lead to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bayesian Belief Network
A Bayesian network (also known as a Bayes network, Bayes net, belief network, or decision network) is a probabilistic graphical model that represents a set of variables and their conditional dependencies via a directed acyclic graph (DAG). Bayesian networks are ideal for taking an event that occurred and predicting the likelihood that any one of several possible known causes was the contributing factor. For example, a Bayesian network could represent the probabilistic relationships between diseases and symptoms. Given symptoms, the network can be used to compute the probabilities of the presence of various diseases. Efficient algorithms can perform inference and learning in Bayesian networks. Bayesian networks that model sequences of variables (''e.g.'' speech signals or protein sequences) are called dynamic Bayesian networks. Generalizations of Bayesian networks that can represent and solve decision problems under uncertainty are called influence diagrams. Graphical m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neural Network
A neural network is a network or circuit of biological neurons, or, in a modern sense, an artificial neural network, composed of artificial neurons or nodes. Thus, a neural network is either a biological neural network, made up of biological neurons, or an artificial neural network, used for solving artificial intelligence (AI) problems. The connections of the biological neuron are modeled in artificial neural networks as weights between nodes. A positive weight reflects an excitatory connection, while negative values mean inhibitory connections. All inputs are modified by a weight and summed. This activity is referred to as a linear combination. Finally, an activation function controls the amplitude of the output. For example, an acceptable range of output is usually between 0 and 1, or it could be −1 and 1. These artificial networks may be used for predictive modeling, adaptive control and applications where they can be trained via a dataset. Self-learning resulting from e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sindh Institute Of Urology And Transplantation
The Sindh Institute of Urology & Transplantation (SIUT) is a dialysis & kidney transplant centre located in Pakistan. SIUT was founded by Dr. Adibul Hasan Rizvi and it is Pakistan's largest kidney disease center, as well as Pakistan's largest public sector health organisation. It began as a department of urology at the government-run Civil Hospital in 1970 and became autonomous in 1991. Ten to twelve transplants are performed weekly, and in 2003, doctors at SIUT performed Pakistan's first liver transplant. In 2004, a child care unit was opened. All services provided by SIUT, including dialysis and transplantation, are provided free of cost with dignity. SIUT Chablani Medical Center Sukkur Establishing SIUT, Sukkur, was an innovative response to the need of the people of Sindh was planned in the year 2009. Since SIUT holds human life valuable and healthcare as the people's birthright, kidney patients "are not allowed to die because they cannot afford to live". Dr Rizvi anticip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambridge University
, mottoeng = Literal: From here, light and sacred draughts. Non literal: From this place, we gain enlightenment and precious knowledge. , established = , other_name = The Chancellor, Masters and Scholars of the University of Cambridge , type = Public research university , endowment = £7.121 billion (including colleges) , budget = £2.308 billion (excluding colleges) , chancellor = The Lord Sainsbury of Turville , vice_chancellor = Anthony Freeling , students = 24,450 (2020) , undergrad = 12,850 (2020) , postgrad = 11,600 (2020) , city = Cambridge , country = England , campus_type = , sporting_affiliations = The Sporting Blue , colours = Cambridge Blue , website = , logo = University of Cambridge logo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Journal Of Pathology
''The Journal of Pathology'' is a peer-reviewed medical journal that was established in 1892 as ''The Journal of Pathology and Bacteriology'' by German Sims Woodhead. It has been the official journal of the Pathological Society of Great Britain and Ireland (present name: Pathological Society) since its foundation in 1906. The journal has published important papers in pathology and experimental medicine including work by Rudolf Virchow and Ilya Ilyich Mechnikov, both of whom contributed to the inaugural issue. In 1969, the journal's title was shortened to ''The Journal of Pathology''. In January 1999, the first of an ongoing series of Annual Review issues was published, on the topic of "Molecular and Cellular Themes in Cancer Research", edited by Peter A. Hall and David P. Lane. A history of the journal was written in 2006 by former editor-in-chief C. Simon Herrington, as a chapter of a book on the history of the Pathological Society. The journal publishes research papers, review ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electron Microscopy
An electron microscope is a microscope that uses a beam of accelerated electrons as a source of illumination. As the wavelength of an electron can be up to 100,000 times shorter than that of visible light photons, electron microscopes have a higher resolving power than light microscopes and can reveal the structure of smaller objects. A scanning transmission electron microscope has achieved better than 50 pm resolution in annular dark-field imaging mode and magnifications of up to about 10,000,000× whereas most light microscopes are limited by diffraction to about 200 nm resolution and useful magnifications below 2000×. Electron microscopes use shaped magnetic fields to form electron optical lens systems that are analogous to the glass lenses of an optical light microscope. Electron microscopes are used to investigate the ultrastructure of a wide range of biological and inorganic specimens including microorganisms, cells, large molecules, biopsy samples, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
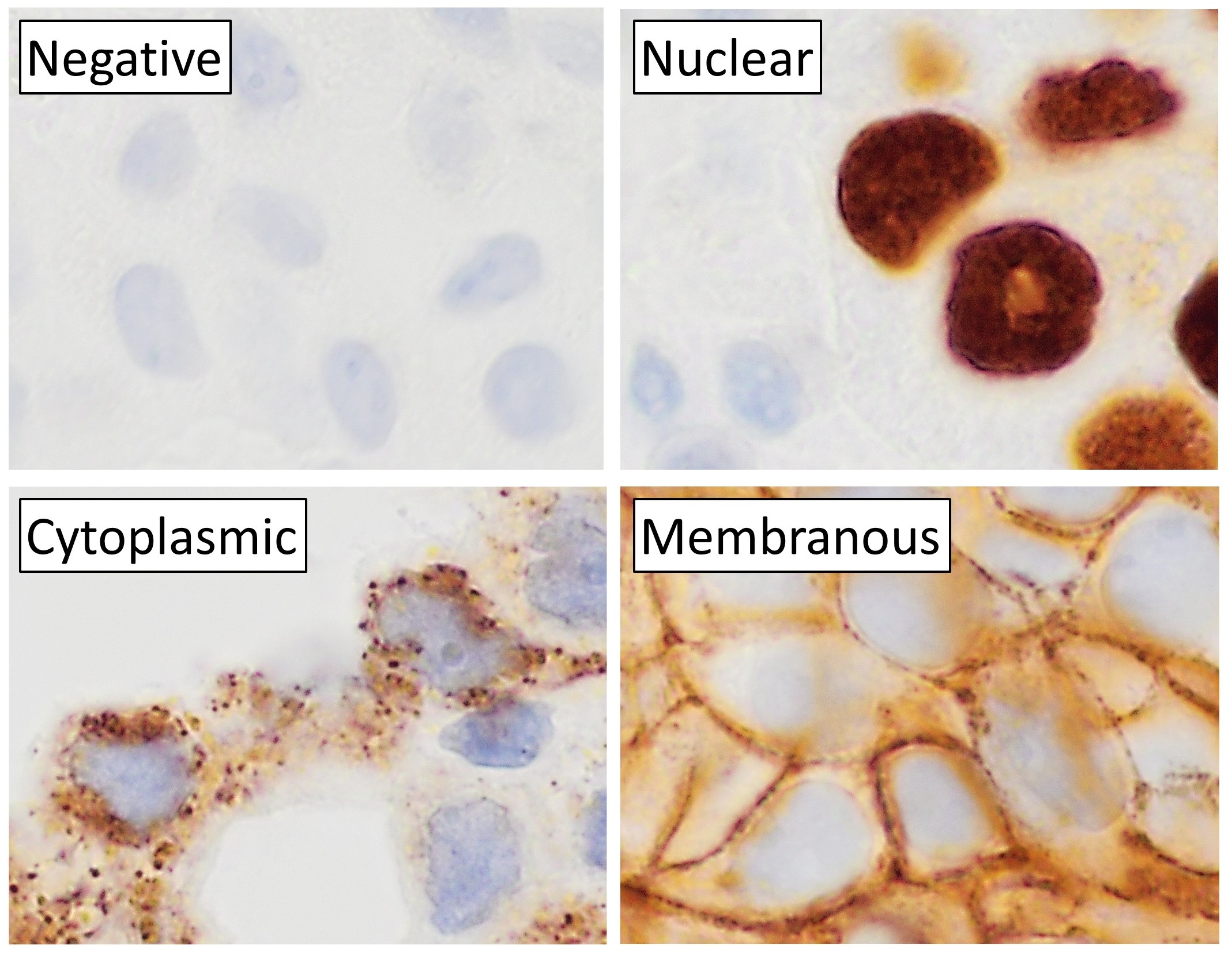
Immunohistochemistry
Immunohistochemistry (IHC) is the most common application of immunostaining. It involves the process of selectively identifying antigens (proteins) in cells of a tissue section by exploiting the principle of antibodies binding specifically to antigens in biological tissues. IHC takes its name from the roots "immuno", in reference to antibodies used in the procedure, and "histo", meaning tissue (compare to immunocytochemistry). Albert Coons conceptualized and first implemented the procedure in 1941. Visualising an antibody-antigen interaction can be accomplished in a number of ways, mainly either of the following: * ''Chromogenic immunohistochemistry'' (CIH), wherein an antibody is conjugated to an enzyme, such as peroxidase (the combination being termed immunoperoxidase), that can catalyse a colour-producing reaction. * '' Immunofluorescence'', where the antibody is tagged to a fluorophore, such as fluorescein or rhodamine. Immunohistochemical staining is widely used in the dia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helicobacter Pylori
''Helicobacter pylori'', previously known as ''Campylobacter pylori'', is a gram-negative, microaerophilic, spiral (helical) bacterium usually found in the stomach. Its helical shape (from which the genus name, helicobacter, derives) is thought to have evolved in order to penetrate the mucoid lining of the stomach and thereby establish infection. The bacterium was first identified in 1982 by the Australian doctors Barry Marshall and Robin Warren. ''H. pylori'' has been associated with cancer of the mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue in the stomach, esophagus, colon, rectum, or tissues around the eye (termed extranodal marginal zone B-cell lymphoma of the cited organ), and of lymphoid tissue in the stomach (termed diffuse large B-cell lymphoma). ''H. pylori'' infection usually has no symptoms but sometimes causes gastritis (stomach inflammation) or ulcers of the stomach or first part of the small intestine. The infection is also associated with the development of cer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)