|
Japanese Submarine I-41
''I-41'' was an Imperial Japanese Navy Type B2 submarine#Type-B Mod.1 .28I-40 class.29, B2 type submarine. She was completed at Kure, Hiroshima, Kure Navy Yard on 18 September 1943, whereupon she entered into service with the Imperial Japanese Navy Yokosuka Naval District, SubRon 11, and sailed to Yokosuka for final trials under the command of Lt. Commander Tamori Yoshimatsu. This was completed by 15 December 1943 and command was transferred to Lt. Commander Itakura Mitsuma. ''I-41'' was reassigned to the Sixth Fleet in SubRon 1's Sub Division 15. World War II service Supply submarine On 29 December 1943 the new submarine departed Tokosuka for Truk Lagoon, Truk. Arriving at Truk on New Years Day 1944, her deck gun and all of her torpedoes were taken on shore to prepare the sub for a supply mission. Nine days later ''I-41'' was designated as the flagship of SubDiv 15. On 15 January 1943 ''I-41'' sailed from Truk for Rabaul. While en route, SubRon1 was disbanded and the submarin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Empire Of Japan
The also known as the Japanese Empire or Imperial Japan, was a historical nation-state and great power that existed from the Meiji Restoration in 1868 until the enactment of the post-World War II 1947 constitution and subsequent formation of modern Japan. It encompassed the Japanese archipelago and several colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories. Under the slogans of and following the Boshin War and restoration of power to the Emperor from the Shogun, Japan underwent a period of industrialization and militarization, the Meiji Restoration, which is often regarded as the fastest modernisation of any country to date. All of these aspects contributed to Japan's emergence as a great power and the establishment of a colonial empire following the First Sino-Japanese War, the Boxer Rebellion, the Russo-Japanese War, and World War I. Economic and political turmoil in the 1920s, including the Great Depression, led to the rise of militarism, nationa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Submarine I-36
''I-36'' was an Imperial Japanese Navy B1 type submarine. Completed and commissioned in 1942, she served in World War II, operating in the Guadalcanal campaign, New Guinea campaign, Aleutian Islands campaign, and the Marshall Islands. She finished the war as a ''kaiten'' manned suicide attack torpedo carrier, operating against Allied ships at Ulithi Atoll and in the Philippine Sea. The only submarine of her class to survive the war, she surrendered to the Allies in September 1945 after the end of the war and was scuttled by the United States Navy in 1946. Construction and commissioning ''I-36'' was laid down on 4 December 1940 at the Yokosuka Navy Yard at Yokosuka, Japan, with the name ''Submarine No. 149''. She was both renamed ''I-36'' and launched on 1 November 1941. She finished her acceptance trials on 20 September 1942, and was completed and commissioned on 30 September 1942. Service history Upon commissioning, ''I-36'' was attached to the Kure Naval District and assign ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kaiten
were crewed torpedoes and suicide craft, used by the Imperial Japanese Navy in the final stages of World War II. History In recognition of the unfavorable progress of the war, towards the end of 1943 the Japanese high command considered suggestions for various suicide craft. These suggestions were initially rejected, but later deemed necessary. Various suicide craft were developed in the Japanese Special Attack Units. For the Navy, this meant ''Kamikaze'' planes, '' Shinyo'' suicide boats, ''Kaiten'' submarines, and ''Fukuryu'' suicide divers or human mines. The ''Kamikazes'' were somewhat successful, and the second most successful were the ''Kaitens''. Research on the first Kaiten began in February 1944, followed on 25 July of the same year by the first prototype. By 1 August, an order for 100 units had been placed. Development The very first Kaiten was nothing much more than a Type 93 torpedo engine compartment attached to a cylinder that would become the pilot's comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kyushu
is the third-largest island of Japan's five main islands and the most southerly of the four largest islands ( i.e. excluding Okinawa). In the past, it has been known as , and . The historical regional name referred to Kyushu and its surrounding islands. Kyushu has a land area of and a population of 14,311,224 in 2018. In the 8th-century Taihō Code reforms, Dazaifu was established as a special administrative term for the region. Geography The island is mountainous, and Japan's most active volcano, Mount Aso at , is on Kyushu. There are many other signs of tectonic activity, including numerous areas of hot springs. The most famous of these are in Beppu, on the east shore, and around Mt. Aso in central Kyushu. The island is separated from Honshu by the Kanmon Straits. Being the nearest island to the Asian continent, historically it is the gateway to Japan. The total area is which makes it the 37th largest island in the world. It's slightly larger than Taiwan island . ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Consolidated B-24 Liberator
The Consolidated B-24 Liberator is an American heavy bomber, designed by Consolidated Aircraft of San Diego, California. It was known within the company as the Model 32, and some initial production aircraft were laid down as export models designated as various LB-30s, in the Land Bomber design category. At its inception, the B-24 was a modern design featuring a highly efficient shoulder-mounted, high aspect ratio Davis wing. The wing gave the Liberator a high cruise speed, long range and the ability to carry a heavy bomb load. Early RAF Liberators were the first aircraft to cross the Atlantic Ocean as a matter of routine. In comparison with its contemporaries, the B-24 was relatively difficult to fly and had poor low-speed performance; it also had a lower ceiling and was less robust than the Boeing B-17 Flying Fortress. While aircrews tended to prefer the B-17, General Staff favored the B-24 and procured it in huge numbers for a wide variety of roles. At approximately 18,5 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Banzai Charge
Banzai charge is the term that was used by the Allied forces of World War II to refer to Japanese human wave attacks and swarming staged by infantry units. This term came from the Japanese battle cry , and was shortened to banzai, specifically referring to the tactic used by the Imperial Japanese Army during the Pacific War. This tactic was used when the Japanese commanders of infantry battalions foresaw that a battle was about to be lost, as a last ditch effort in thwarting Allied Forces. Origin The banzai charge is considered to be one method of , a suicide attack, or suicide before being captured by the enemy such as ''seppuku''. The origin of the term is a classical Chinese phrase in the 7th-century ''Book of Northern Qi'', which states "", "A true man would atherbe the shattered jewel, ashamed to be the intact tile." Among the rules there existed a code of honor that was later used by Japanese military governments. With the revolutionary change in the Meiji Restorati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saipan
Saipan ( ch, Sa’ipan, cal, Seipél, formerly in es, Saipán, and in ja, 彩帆島, Saipan-tō) is the largest island of the Northern Mariana Islands, a Commonwealth (U.S. insular area), commonwealth of the United States in the western Pacific Ocean. According to 2020 estimates by the United States Census Bureau, the population of Saipan was 43,385, a decline of 10% from its 2010 count of 48,220. The legislative and executive branches of Commonwealth government are located in the village of Capitol Hill, Saipan, Capitol Hill on the island while the judicial branch is headquartered in the village of Susupe. Since the entire island is organized as a single municipality, most publications designate Saipan as the Commonwealth's capital. As of 2015, Saipan's mayor is David M. Apatang and the governor of the Northern Mariana Islands is Ralph Torres. History Prehistory Traces of human settlements on Saipan have been found by archaeologists ranging over 4,000 years, includ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guam
Guam (; ch, Guåhan ) is an organized, unincorporated territory of the United States in the Micronesia subregion of the western Pacific Ocean. It is the westernmost point and territory of the United States (reckoned from the geographic center of the U.S.); its capital Hagåtña (144°45'00"E) lies further west than Melbourne, Australia (144°57'47"E). In Oceania, Guam is the largest and southernmost of the Mariana Islands and the largest island in Micronesia. Guam's capital is Hagåtña, and the most populous village is Dededo. People born on Guam are American citizens but have no vote in the United States presidential elections while residing on Guam and Guam delegates to the United States House of Representatives have no vote on the floor. Indigenous Guamanians are the Chamoru, historically known as the Chamorro, who are related to the Austronesian peoples of Indonesia, the Philippines, Malaysia, Taiwan, Micronesia, and Polynesia. As of 2022, Guam's population is 168, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mariana Islands
The Mariana Islands (; also the Marianas; in Chamorro: ''Manislan Mariånas'') are a crescent-shaped archipelago comprising the summits of fifteen longitudinally oriented, mostly dormant volcanic mountains in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, between the 12th and 21st parallels north and along the 145th meridian east. They lie south-southeast of Japan, west-southwest of Hawaii, north of New Guinea and east of the Philippines, demarcating the Philippine Sea's eastern limit. They are found in the northern part of the western Oceanic sub-region of Micronesia, and are politically divided into two jurisdictions of the United States: the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands and, at the southern end of the chain, the territory of Guam. The islands were named after the influential Spanish queen Mariana of Austria following their colonization in the 17th century. The indigenous inhabitants are the Chamorro people. Archaeologists in 2013 reported findings which indicated that the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wewak
Wewak is the capital of the East Sepik province of Papua New Guinea. It is on the northern coast of the island of New Guinea. It is the largest town between Madang and Jayapura. It is the see city (seat) of the Roman Catholic Diocese of Wewak. History Between 1943 and 1945, in World War II, Wewak was the site of the largest Japanese airbase in mainland New Guinea. The base was subjected to repeated bombing by Australian and American forces, most notably in one massive attack on 17 August 1943. Directly to the west of the town centre is a peninsula known as Cape Wom, which was the site of the surrender of Japanese forces in New Guinea on 13 September 1945. The site now houses a small memorial. The former Japanese airfield is still in use as the Wewak International Airport. In August 1945 two war crimes trials were held near Wewak for mutilation and cannibalism. First Lieutenant Takehiro Tazaki was convicted and sentenced to death (later commuted to 5 years imprisonment with hard ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
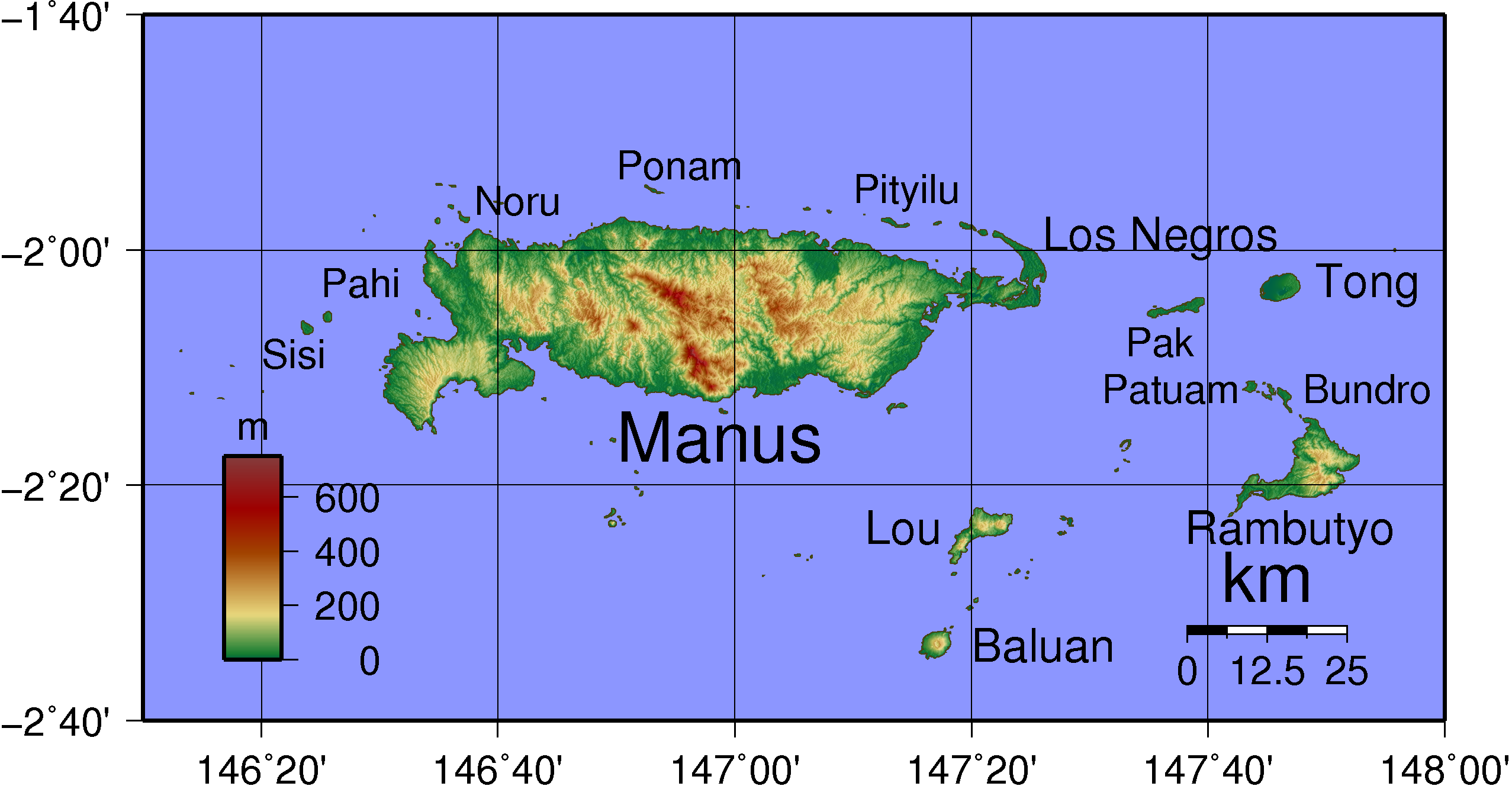
Admiralty Islands
The Admiralty Islands are an archipelago group of 18 islands in the Bismarck Archipelago, to the north of New Guinea in the South Pacific Ocean. These are also sometimes called the Manus Islands, after the largest island. These rainforest-covered islands form part of Manus Province, the smallest and least-populous province of Papua New Guinea, in its Islands Region. The total area is . Many of the Admiralty Islands are atolls and uninhabited. Islands The larger islands in the center of the group are Manus Island and Los Negros Island. The other larger islands are Tong Island, Pak Island, Rambutyo Island, Lou Island, and Baluan Island to the east, Mbuke Island to the south and Bipi Island to the west of Manus Island. Other islands that have been noted as significant places in the history of Manus include Ndrova Island, Pitylu Island and Ponam Island. Geography The temperature of the Admiralty Islands varies little throughout the year, reaching daily highs of and at night. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |