|
Jan Swammerdam
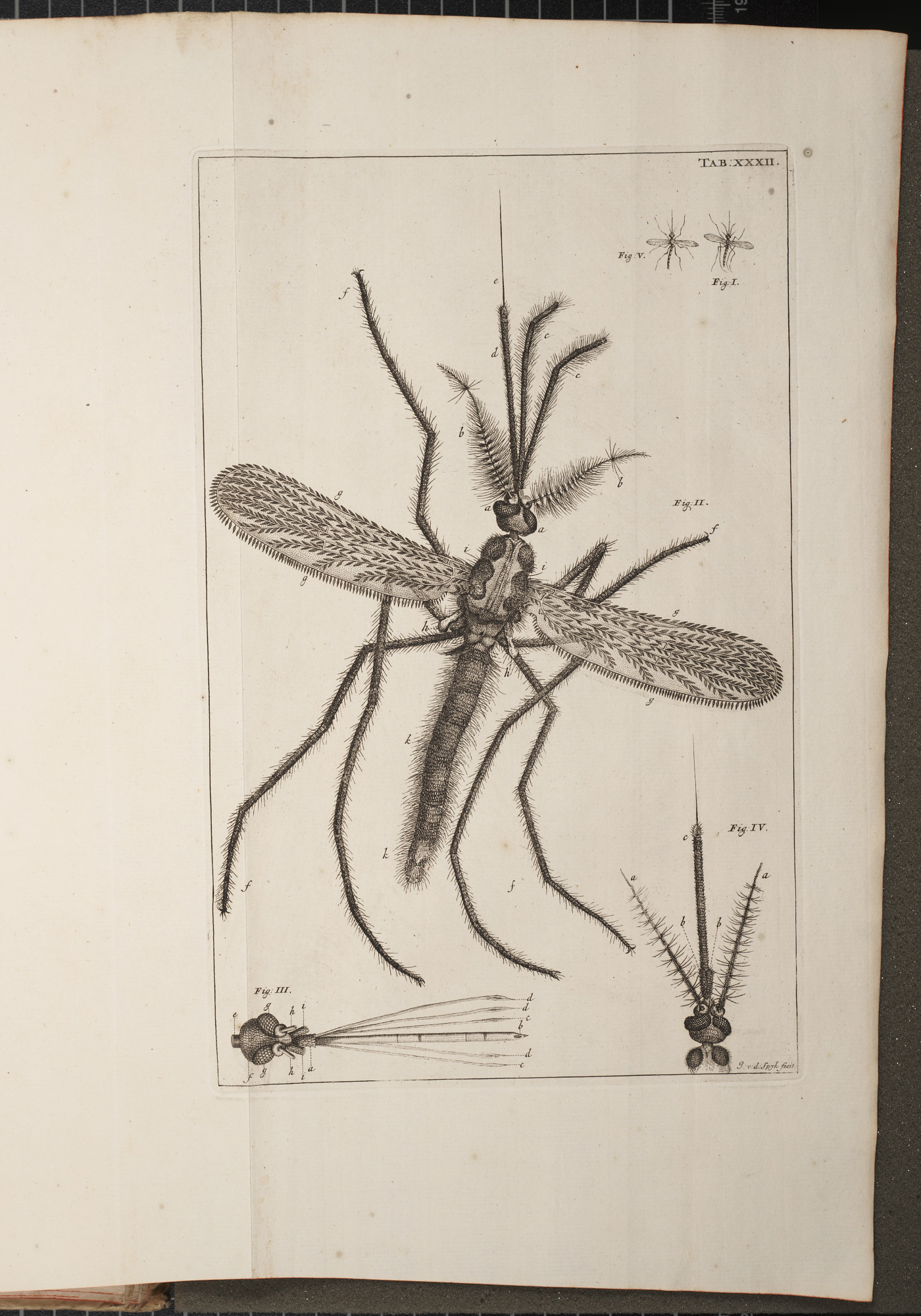
Jan Swammerdam (February 12, 1637 – February 17, 1680) was a Dutch biologist and microscopist. His work on insects demonstrated that the various phases during the life of an insect— egg, larva, pupa, and adult—are different forms of the same animal. As part of his anatomical research, he carried out experiments on muscle contraction. In 1658, he was the first to observe and describe red blood cells. He was one of the first people to use the microscope in dissections, and his techniques remained useful for hundreds of years. Education Swammerdam was baptized on 15 February 1637 in the Oude Kerk Amsterdam. His father was an apothecary, and an amateur collector of minerals, coins, fossils, and insects from around the world. His mother Baertje Jans Corvers died in 1661. As a youngster, Swammerdam had helped his father to take care of his curiosity collection. Despite his father's wish that he should study theology Swammerdam started to study medicine in 1661 at the Unive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Anatomy Lesson Of Dr
''The'' () is a grammatical article in English, denoting persons or things already mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the most frequently used word in the English language; studies and analyses of texts have found it to account for seven percent of all printed English-language words. It is derived from gendered articles in Old English which combined in Middle English and now has a single form used with pronouns of any gender. The word can be used with both singular and plural nouns, and with a noun that starts with any letter. This is different from many other languages, which have different forms of the definite article for different genders or numbers. Pronunciation In most dialects, "the" is pronounced as (with the voiced dental fricative followed by a schwa) when followed by a consonant sound, and as (homophone of pronoun ''thee'') when followed by a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apothecary
''Apothecary'' () is a mostly archaic term for a medical professional who formulates and dispenses '' materia medica'' (medicine) to physicians, surgeons, and patients. The modern chemist (British English) or pharmacist (British and North American English) now perform this role. In some languages and regions, the word "apothecary" is still used to refer to a retail pharmacy or a pharmacist who owns one. Apothecaries' investigation of herbal and chemical ingredients was a precursor to the modern sciences of chemistry and pharmacology. In addition to dispensing herbs and medicine, apothecaries offered general medical advice and a range of services that are now performed by other specialist practitioners, such as surgeons and obstetricians. Apothecary shops sold ingredients and the medicines they prepared wholesale to other medical practitioners, as well as dispensing them to patients. In 17th-century England, they also controlled the trade in tobacco which was imported as a medici ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uterus
The uterus (from Latin ''uterus'', plural ''uteri'') or womb () is the organ in the reproductive system of most female mammals, including humans that accommodates the embryonic and fetal development of one or more embryos until birth. The uterus is a hormone-responsive sex organ that contains glands in its lining that secrete uterine milk for embryonic nourishment. In the human, the lower end of the uterus, is a narrow part known as the isthmus that connects to the cervix, leading to the vagina. The upper end, the body of the uterus, is connected to the fallopian tubes, at the uterine horns, and the rounded part above the openings to the fallopian tubes is the fundus. The connection of the uterine cavity with a fallopian tube is called the uterotubal junction. The fertilized egg is carried to the uterus along the fallopian tube. It will have divided on its journey to form a blastocyst that will implant itself into the lining of the uterus – the endometrium, where it will ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dissections
Dissection (from Latin ' "to cut to pieces"; also called anatomization) is the dismembering of the body of a deceased animal or plant to study its anatomical structure. Autopsy is used in pathology and forensic medicine to determine the cause of death in humans. Less extensive dissection of plants and smaller animals preserved in a formaldehyde solution is typically carried out or demonstrated in biology and natural science classes in middle school and high school, while extensive dissections of cadavers of adults and children, both fresh and preserved are carried out by medical students in medical schools as a part of the teaching in subjects such as anatomy, pathology and forensic medicine. Consequently, dissection is typically conducted in a morgue or in an anatomy lab. Dissection has been used for centuries to explore anatomy. Objections to the use of cadavers have led to the use of alternatives including virtual dissection of computer models. Overview Plant and animal bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melchisédech Thévenot
Melchisédech (or Melchisédec) Thévenot (c. 1620 – 29 October 1692) was a French author, scientist, traveler, cartographer, orientalist, inventor, and diplomat. He was the inventor of the spirit level and is also famous for his popular posthumously published 1696 book ''The Art of Swimming'', one of the first books on the subject and widely read during the 18th century (Benjamin Franklin, an avid swimmer in his youth, is known to have read it). The book popularized the breaststroke (see History of swimming) ; he was inducted into the International Swimming Hall of Fame in 1990. He also influenced the founding of the Académie Royale des Sciences (the French Academy of Sciences). Life Thévenot came from a family of royal office holders (nobles of the robe), which partly explains his wealth. He was reputed to speak English, Greek, Latin, Hebrew, and several oriental languages, including Arabic and Turkish. Thévenot's baptismal name was Nicolas, Melchisédech being added as th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tanaquil Faber
Tanaquil ( Etruscan: ''Thanchvil'') was the queen of Rome by marriage to Tarquinius Priscus, fifth king of Rome. Life The daughter of a powerful Etruscan family in Tarquinii, Etruria, Tanaquil thought her husband would make a good leader, but since he was the son of an immigrant, he would not be able to gain power in Tarquinii, where they lived. Knowing this, Tanaquil encouraged him to move to Rome, which was not at the time dominated by a strong local aristocracy. Her prophetic abilities helped her to install Tarquin as king and later Servius Tullius as the next king. While on the road to Rome, an eagle flew off with Tarquin's hat and then returned it to his head. Tanaquil interpreted this as a sign that the gods wanted him to become a king. Tanaquil's prophecy was eventually realized for Tarquin - he eventually became friends with King Ancus Marcius, who made Tarquin guardian of his children. When the king died before his children were old enough to become successors to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Saumur
The Academy of Saumur (french: Académie de Saumur) was a Huguenot university at Saumur in western France. It existed from 1593, when it was founded by Philippe de Mornay, until shortly after 1685, when Louis XIV decided on the revocation of the Edict of Nantes, ending the limited toleration of Protestantism in France. Amyraldism The Academy was the home of Amyraldism, an important strand of Protestant thought of the seventeenth century. Also called Saumurianism or hypothetical universalism, it was a moderate Calvinist movement, remaining within Calvinism. The Helvetic Consensus and Westminster Confession were concerned to combat the tendency Amyraldism represented. Faculty Students See also * List of early modern universities in Europe The list of early modern universities in Europe comprises all universities that existed in the early modern age (1501–1800) in Europe. It also includes short-lived foundations and educational institutions whose university statu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Niels Stensen
Niels Steensen ( da, Niels Steensen; Latinized to ''Nicolaus Steno'' or ''Nicolaus Stenonius''; 1 January 1638 – 25 November 1686History of Geology – Steno – Aber, James S. 2007. Retrieved 11 January 2012. ) was a , a pioneer in both and who became a |
Reinier De Graaf
Regnier de Graaf (English spelling), original Dutch spelling Reinier de Graaf, or Latinized Reijnerus de Graeff (30 July 164117 August 1673) was a Dutch physician, physiologist and anatomist who made key discoveries in reproductive biology. He specialized in iatrochemistry and iatrogenesis, and was the first to develop a syringe to inject dye into human reproductive organs so that he could understand their structure and function. Biography De Graaf was born in Schoonhoven as the son of an carpenter/engineer or architect and studied medicine in Leuven (1658), Utrecht and Leiden (1663).https://www.ntvg.nl/system/files/publications/1974107890001a.pdf There his co-students were Jan Swammerdam, Niels Stensen, Ole Borch and Frederik Ruysch, cooperating with professor Franciscus Sylvius, Johannes van Horne and Lucas Schacht. All of them were interested in the organs of procreation and influenced by Rene Descartes' iatrophysical approach. He submitted his doctoral thesis on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frederik Ruysch
Frederik Ruysch (; March 28, 1638 – February 22, 1731) was a Dutch botanist and anatomist. He is known for developing techniques for preserving anatomical specimens, which he used to create dioramas or scenes incorporating human parts. His anatomical preparations included over 2,000 anatomical, pathological, zoological, and botanical specimens, which were preserved by either drying or embalming. Ruysch is also known for his proof of valves in the lymphatic system, the vomeronasal organ in snakes, and ''arteria centralis oculi'' (the central artery of the eye). He was the first to describe the disease that is today known as Hirschsprung's disease, as well as several pathological conditions, including intracranial teratoma, enchondromatosis, and Majewski syndrome. Life Frederik Ruysch was born in The Hague as the son of a government functionary and started as the pupil of a druggist. Fascinated by anatomy, he studied at the university of Leiden, under Franciscus Sylvius. His fe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franciscus Sylvius
Franciscus Sylvius (15 March 1614 – 19 November 1672), born Franz de le Boë, was a Dutch physician and scientist (chemist, physiologist and anatomist) who was an early champion of Descartes', Van Helmont's and William Harvey's work and theories. He was one of the earliest defenders of the theory of circulation of the blood in the Netherlands, and commonly falsely cited as the inventor of gin – others pinpoint the origin of gin to Italy. Life Sylvius, a Latinization of "de le Boë" translated as "of the woods", was born in Hanau to an affluent family originally from Cambrai, but worked and died in the Netherlands. He studied medicine at the Protestant Academy of Sedan, and from 1632 to 1634 at Leiden University under Adolph Vorstius and Otto Heurnius. In 1634 he held a dissertation titled ''Positiones variae medicae'' (''Various Medical Positions'') under the direction of Vorstius, in which he defended the proposition that there should be a pulmonary circulation. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johannes Van Horne
Johannes van Horne, Joannis van Horne (surname Latinized as Hornius, 2 September 1621 – 5 January 1670) was a Dutch anatomist best known for his illustrated atlas of myology. He was a professor of anatomy and surgery at Leiden University where his students included Nicolaus Steno. Biography Van Horne was born in Amsterdam in a Flemish merchant family. His father Jacob was a director of the Dutch East India Company. Educated at the University of Leiden he shifted from literature to medicine and may have assisted Johannes de Wale. He then went to study medicine at Utrecht under Willem van der Straaten. He then travelled around Europe, attending Johann Vesling's classes at Padua, Marco Aurelio Severino at Naples, and visiting Montpellier and England. He received an honorary degree from the University of Basel. After returning home, he became a demonstrator of anatomy at Leiden University and became an extraordinary professor of anatomy in 1651. He was made full professor at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)