|
James Stephen Hodson
James Stephen Hodson DD FRSE (1816-1890) was a British academic and Anglican priest who served as rector of Edinburgh Academy from 1854 to 1869. Life He was born in Clifton, Bristol, in 1816 or 1817, the eldest son of George Hodson (1787–1855), later archdeacon of Stafford and chancellor of Lichfield Cathedral. His mother was Mary Stephen. A younger brother was William Stephen Raikes Hodson, who adopted a military career and founded Hodsons Horse Regiment. Hodson studied divinity at Balliol College and Merton College in Oxford, graduating in 1837. He served as a curate at Sanderstead in Croydon. He moved to be perpetual curate of St Giles' Church, Longstone in Derbyshire around 1847. During this period he is listed as a member of the British Archaeological Association. He succeeded John Hannah (1818-1888) as rector of Edinburgh Academy in 1855. For his time as rector of Edinburgh Academy he was living at 62, Great King Street (the former home of Robert Graham) in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Stephen Raikes Hodson
William Stephen Raikes Hodson (19 March 182111 March 1858) was a British leader of irregular light cavalry during the Indian Rebellion of 1857, commonly referred to as the Indian Mutiny or the Sepoy Mutiny. He was known as "Hodson of Hodson's Horse". His most celebrated action was to apprehend Bahadur Shah II, the Mughal king of Delhi (also referred to as emperor of India). The following day Hodson rode to the enemy camp, heavily outnumbered by the rebels, and demanded the surrender of the Mughal princes who were leading the rebellion around Delhi and subsequently shot his prisoners. Hodson's career received praise from a number of senior military commanders, such as General Hugh Gough,''Old Memories'' 1897 memoirs published by H. Gough but there were dissenting voices from other members of the military. There were also politicians who felt the killing of Mughal princes by Hodson had been "dishonourable". However, Hodson's career received praise from more senior politicians ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doctor Of Divinity
A Doctor of Divinity (D.D. or DDiv; la, Doctor Divinitatis) is the holder of an advanced academic degree in divinity. In the United Kingdom, it is considered an advanced doctoral degree. At the University of Oxford, doctors of divinity are ranked first in "academic precedence and standing", while at the University of Cambridge they rank ahead of all other doctors in the "order of seniority of graduates". In some countries, such as in the United States, the degree of doctor of divinity is usually an honorary degree and not a research or academic degree. Doctor of Divinity by country or church British Isles In the United Kingdom and Ireland, the degree is a higher doctorate conferred by universities upon a religious scholar of standing and distinction, usually for accomplishments beyond the Ph.D. level. Bishops of the Church of England have traditionally held Oxford, Cambridge, Dublin, or Lambeth degrees making them doctors of divinity. At the University of Oxford, docto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
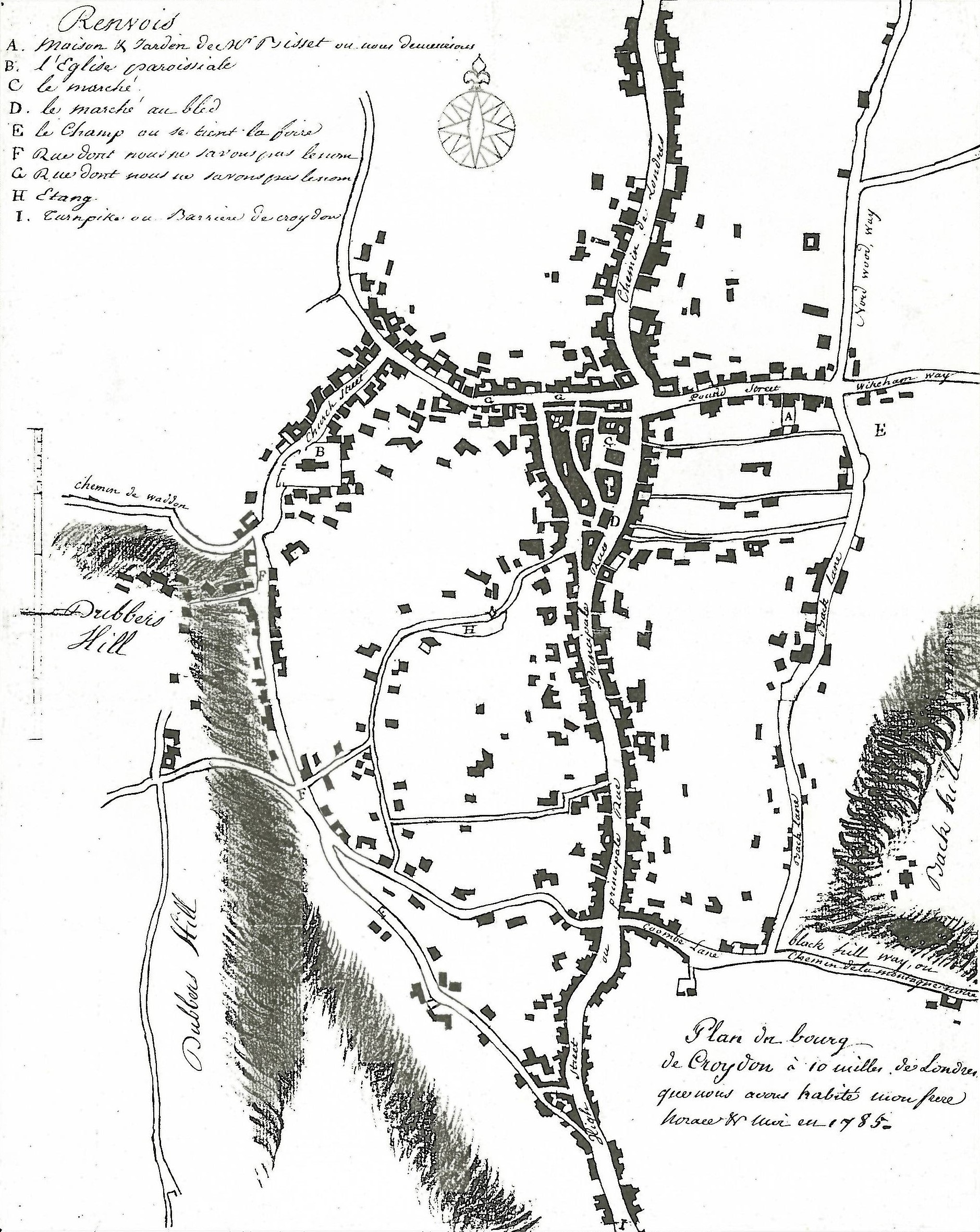
Croydon
Croydon is a large town in south London, England, south of Charing Cross. Part of the London Borough of Croydon, a local government district of Greater London. It is one of the largest commercial districts in Greater London, with an extensive shopping district and night-time economy. The entire town had a population of 192,064 as of 2011, whilst the wider borough had a population of 384,837. Historically an ancient parish in the Wallington hundred of Surrey, at the time of the Norman conquest of England Croydon had a church, a mill, and around 365 inhabitants, as recorded in the Domesday Book of 1086. Croydon expanded in the Middle Ages as a market town and a centre for charcoal production, leather tanning and brewing. The Surrey Iron Railway from Croydon to Wandsworth opened in 1803 and was an early public railway. Later 19th century railway building facilitated Croydon's growth as a commuter town for London. By the early 20th century, Croydon was an important industria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steventon, Oxfordshire
Steventon is a village and civil parish in Oxfordshire, England, about south of Abingdon and a similar distance west of Didcot. It was part of Berkshire until the 1974 boundary changes transferred it to Oxfordshire. The 2011 Census recorded the parish population as 1,485. Toponym Steventon's toponym evolved from ''Stivetune'' in the 11th century via ''Estiventona'' in the 12th century, ''Stiveton'', ''Stivington'', ''Estiventon'', ''Stiventon'', ''Stuvinton'' and ''Steveington'' in the 13th century and ''Stephyngton'' in the 16th century before reaching its present form. Priory Steventon Priory was founded early in the 12th century in the reign of Henry I. It was an alien priory, controlled by the Benedictine Bec Abbey in Normandy. In the 14th century alien priories became unpopular with the Crown, and in the reign of Edward III the abbey was allowed to sell Steventon Priory to an English squire, Sir Hugh Calveley. Church and chapel Church of England The Domesday Book of 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berkshire
Berkshire ( ; in the 17th century sometimes spelt phonetically as Barkeshire; abbreviated Berks.) is a historic county in South East England. One of the home counties, Berkshire was recognised by Queen Elizabeth II as the Royal County of Berkshire in 1957 because of the presence of Windsor Castle, and letters patent were issued in 1974. Berkshire is a county of historic origin, a ceremonial county and a non-metropolitan county without a county council. The county town is Reading. The River Thames formed the historic northern boundary, from Buscot in the west to Old Windsor in the east. The historic county, therefore, includes territory that is now administered by the Vale of White Horse and parts of South Oxfordshire in Oxfordshire, but excludes Caversham, Slough and five less populous settlements in the east of the Royal Borough of Windsor and Maidenhead. All the changes mentioned, apart from the change to Caversham, took place in 1974. The towns of Abingdon, Didcot, Far ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bradfield College
Bradfield College, formally St Andrew's College, Bradfield, is a public school (English independent day and boarding school) for pupils aged 11–18, located in the small village of Bradfield in the English county of Berkshire. It is noted for producing plays in Ancient Greek and its open-air amphitheatre. The school is a member of the Rugby Group, which also includes Rugby, Harrow, Shrewsbury, Wellington College and Charterhouse. The college was founded in 1850 by Thomas Stevens, Rector and Lord of the Manor of Bradfield. It has around 490 male and 320 female pupils. Overview According to the ''Good Schools Guide'', "Thoroughly unpretentious yet with lots to boast about, Bradfield is a heavenly place to learn and to grow. Very difficult to imagine who would not thrive here. There's something for everyone and lots for all." The school, which admits pupils between the ages of 13–18, has been fully co-educational since September 2005. All first year pupils (Fourth Form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Terrot
Charles Hughes Terrot FRSE (19 September 1790 – 2 April 1872) was a Scottish Episcopalian minister, theologian and mathematician. He served as Primus of the Scottish Episcopal Church from 1857 to 1862. Life Charles Terrot was born on 19 September 1790 at Cuddalore in southern India, the son of Captain Elias Terrot of the Indian Army who was killed at the siege of Bangalore a few weeks after Charles' birth. His mother, Mary Fonteneau, returned to England soon after, and raised Charles in Berwick-upon-Tweed. He was educated at Carlisle Grammar School and Trinity College, Cambridge, where he graduated BA in 1812. He became a Fellow of Trinity in 1813. In 1813 he served as a Deacon in Bristol before moving to Chester as a priest. He returned to Scotland in 1814 to serve as an Incumbent in Haddington. In 1833 he served in St Pauls in Edinburgh leading to his rise to Dean in 1837 and Bishop in 1841. During this time he lived at 19 Northumberland Street in Edinburgh's New Town. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bishop Of Edinburgh
The Bishop of Edinburgh, or sometimes the Lord Bishop of Edinburgh is the ordinary of the Scottish Episcopal Diocese of Edinburgh. Prior to the Reformation, Edinburgh was part of the Diocese of St Andrews, under the Archbishop of St Andrews and throughout the mediaeval period the episcopal seat was St Andrew's Cathedral. The line of Bishops of Edinburgh began with the creation of the See of Edinburgh in 1633: the See was founded in 1633 by King Charles I. William Forbes was consecrated at St Giles' Cathedral as the first bishop on 23 January 1634 though he died later that year. The General Assembly of 1638 deposed David Lindsay and all the other bishops, so the next, George Wishart, was consecrated in 1662 after the Stuart Restoration. In 1690, it was Alexander Rose (bishop 1687–1720) whose unwelcome reply to King William III ( and II) led to the disestablishment of the Scottish Episcopalians as Jacobite sympathisers, and it was he who led his congregation from St Giles' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Society Of Edinburgh
The Royal Society of Edinburgh is Scotland's national academy of science and letters. It is a registered charity that operates on a wholly independent and non-partisan basis and provides public benefit throughout Scotland. It was established in 1783. , there are around 1,800 Fellows. The Society covers a broader selection of fields than the Royal Society of London, including literature and history. Fellowship includes people from a wide range of disciplines – science & technology, arts, humanities, medicine, social science, business, and public service. History At the start of the 18th century, Edinburgh's intellectual climate fostered many clubs and societies (see Scottish Enlightenment). Though there were several that treated the arts, sciences and medicine, the most prestigious was the Society for the Improvement of Medical Knowledge, commonly referred to as the Medical Society of Edinburgh, co-founded by the mathematician Colin Maclaurin in 1731. Maclaurin was unhappy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Town, Edinburgh
The New Town is a central area of Edinburgh, the capital of Scotland. It was built in stages between 1767 and around 1850, and retains much of its original neo-classical and Georgian period architecture. Its best known street is Princes Street, facing Edinburgh Castle and the Old Town across the geological depression of the former Nor Loch. Together with the West End, the New Town was designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site alongside the Old Town in 1995. The area is also famed for the New Town Gardens, a heritage designation since March 2001. Proposal and planning The idea of a New Town was first suggested in the late 17th century when the Duke of Albany and York (later King James VII and II), when resident Royal Commissioner at Holyrood Palace, encouraged the idea of having an extended regality to the north of the city and a North Bridge. He gave the city a grant:That, when they should have occasion to enlarge their city by purchasing ground without the town, or to build ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Graham (botanist)
Robert Graham (3 December 1786 – 7 August 1845) was a Scottish physician and botanist. Life Graham was born in Stirling Stirling (; sco, Stirlin; gd, Sruighlea ) is a city in central Scotland, northeast of Glasgow and north-west of Edinburgh. The market town, surrounded by rich farmland, grew up connecting the royal citadel, the medieval old town with its me ... the son of Dr Robert Graham, physician. After studying at Stirling Grammar School he continued first to the University of Glasgow and then to the University of Edinburgh where he graduated around 1806, and completed his Doctor of Medicine, MD in 1808. He trained further at St Bartholomew's Hospital, London, where he qualified as a surgeon. He then returned to Scotland to practice at Glasgow Royal Infirmary 1812-3 and 1816–19. In 1816 he began lecturing in botany at the University of Glasgow, taking over from Thomas Brown of Lanfine and Waterhaughs following his resignation. He was a major figure in the cr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rector (academia)
A rector (Latin for 'ruler') is a senior official in an educational institution, and can refer to an official in either a university or a secondary school. Outside the English-speaking world the rector is often the most senior official in a university, whilst in the United States the most senior official is often referred to as president and in the United Kingdom and Commonwealth of Nations the most senior official is the chancellor, whose office is primarily ceremonial and titular. The term and office of a rector can be referred to as a rectorate. The title is used widely in universities in EuropeEuropean nations where the word ''rector'' or a cognate thereof (''rektor'', ''recteur'', etc.) is used in referring to university administrators include Albania, Austria, the Benelux, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia, Cyprus, Czech Republic, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Iceland, Italy, Latvia, Malta, Moldova, North Macedonia, Poland, Portugal, Romani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



_by_Smith.jpg)
