|
James MacLachlan (architect)
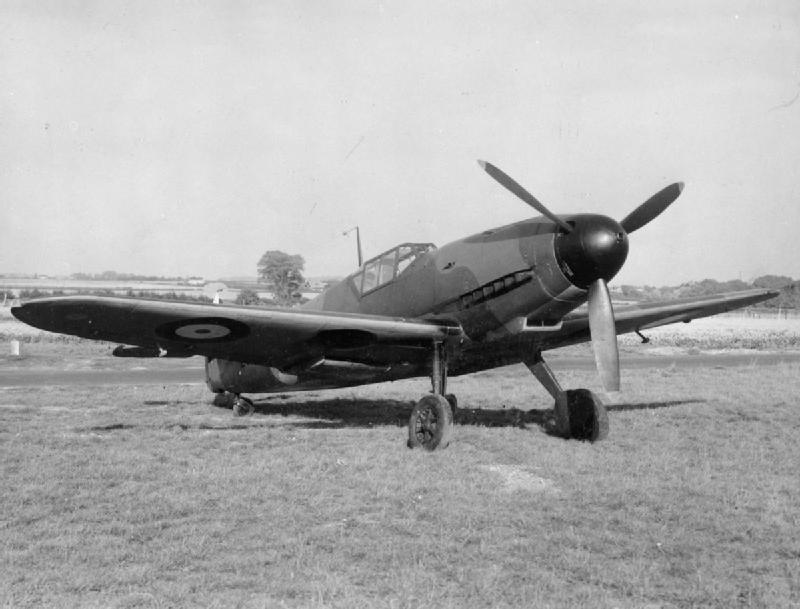
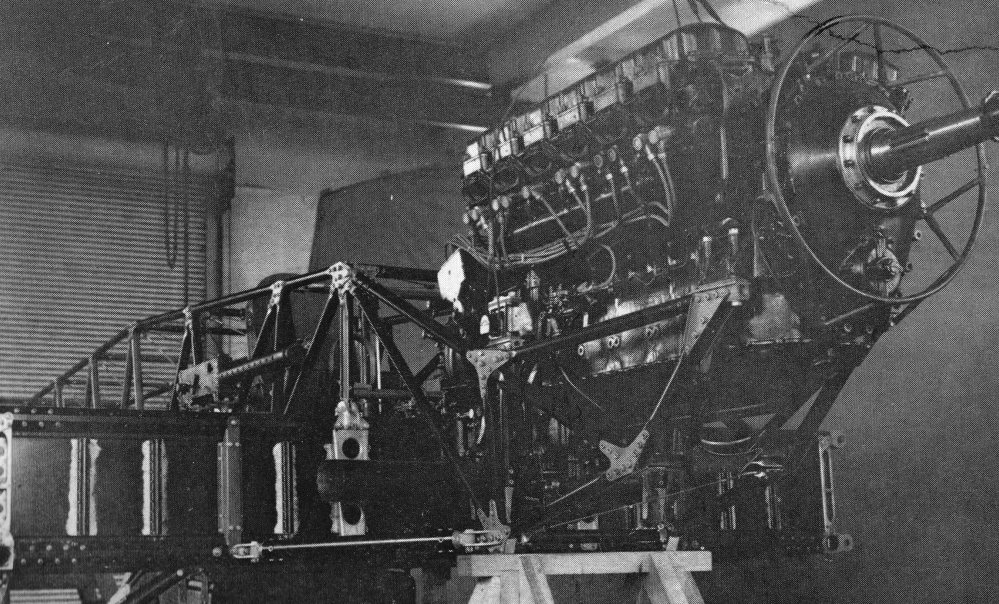
James Archibald Findlay MacLachlan (1 April 1919 – 31 July 1943) was a Royal Air Force (RAF) fighter pilot and flying ace of the Second World War. MacLachlan was credited with 16 German and Italian aircraft shot down in approximately 250 missions—7 were at night of which two were achieved over Malta in 1941 and 5 over France in 1942. Born in Cheshire and educated at Monkton Combe School in Somerset, MacLachlan joined the RAF aged 17 in March 1937. He progressed quickly through flight training and was granted a commission as acting pilot officer on 3 May 1937. He completed his flight training in early 1939 and had considerable time to gain experience in operational types upon the outbreak of the Second World War. When the Battle of France began in May 1940 he was serving with No. 88 Squadron RAF flying the Fairey Battle light bomber he was credited with two enemy aircraft damaged and was awarded the Distinguished Flying Cross (DFC). Surviving the battle he transferred to f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
P-36 Hawk
The Curtiss P-36 Hawk, also known as the Curtiss Hawk Model 75, is an American-designed and built fighter aircraft of the 1930s and 40s. A contemporary of the Hawker Hurricane and Messerschmitt Bf 109, it was one of the first of a new generation of combat aircraft—a sleek monoplane design with a retractable undercarriage making extensive use of metal in its construction. Perhaps best known as the predecessor of the Curtiss P-40 Warhawk, the P-36 saw little combat with the United States Army Air Forces during World War II. It was the fighter used most extensively and successfully by the French Air Force during the Battle of France. The P-36 was also ordered by the governments of the Netherlands and Norway but did not arrive in time to see action before both were occupied by Nazi Germany. The type was also manufactured under license in China, for the Republic of China Air Force, as well as in British India, for the Royal Air Force (RAF) and Royal Indian Air Force (RIAF). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of France
The Battle of France (french: bataille de France) (10 May – 25 June 1940), also known as the Western Campaign ('), the French Campaign (german: Frankreichfeldzug, ) and the Fall of France, was the Nazi Germany, German invasion of French Third Republic, France during the Second World War. On 3 September 1939, France French declaration of war on Germany (1939), declared war on Germany following the German invasion of Poland. In early September 1939, France began the limited Saar Offensive and by mid-October had withdrawn to their start lines. German armies German invasion of Belgium (1940), invaded Belgium, German invasion of Luxembourg, Luxembourg and German invasion of the Netherlands, the Netherlands on 10 May 1940. Fascist Italy (1922-1943), Italy entered the war on 10 June 1940 and attempted an Italian invasion of France, invasion of France. France and the Low Countries were conquered, ending land operations on the Western Front (World War II), Western Front until the Normandy l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monkton Combe (Somerset) School Chapel - Geograph
Monkton Combe is a village and civil parish in north Somerset, England, south of Bath. The parish, which includes the hamlet of Tucking Mill, had a population of 554 in 2013. It was formerly known as Combe, owing to its geography, while it was also known as Monckton Combe and Combe Monckton until last century. History The pre-Saxon history of Monkton Combe is poorly recorded. It lay close to the Roman road from Bath to London, which has prompted the construction of a Roman villa in Combe Down. More activity is noted in the sub-Roman period, when it formed the end of the western section of the protective Wansdyke, which had been designed to protect Somerset from Saxon invasion. Combe was settled and cultivated by the Anglo-Saxon period, when it formed part of the hundred of Bath Forum. It was probably given to Bath Abbey, along with other surrounding villages, in the early 1060's by either Edward the Confessor or Harold Godwinson. The Abbey had been impoverished, and Bishop Gis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supermarine Spitfire
The Supermarine Spitfire is a British single-seat fighter aircraft used by the Royal Air Force and other Allied countries before, during, and after World War II. Many variants of the Spitfire were built, from the Mk 1 to the Rolls-Royce Griffon engined Mk 24 using several wing configurations and guns. It was the only British fighter produced continuously throughout the war. The Spitfire remains popular among enthusiasts; around 70 remain airworthy, and many more are static exhibits in aviation museums throughout the world. The Spitfire was designed as a short-range, high-performance interceptor aircraft by R. J. Mitchell, chief designer at Supermarine Aviation Works, which operated as a subsidiary of Vickers-Armstrong from 1928. Mitchell developed the Spitfire's distinctive elliptical wing with innovative sunken rivets (designed by Beverley Shenstone) to have the thinnest possible cross-section, achieving a potential top speed greater than that of several contemporary figh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hawker Hurricane
The Hawker Hurricane is a British single-seat fighter aircraft of the 1930s–40s which was designed and predominantly built by Hawker Aircraft Ltd. for service with the Royal Air Force (RAF). It was overshadowed in the public consciousness by the Supermarine Spitfire during the Battle of Britain in 1940, but the Hurricane inflicted 60 percent of the losses sustained by the Luftwaffe in the campaign, and fought in all the major theatres of the Second World War. The Hurricane originated from discussions between RAF officials and aircraft designer Sir Sydney Camm about a proposed monoplane derivative of the Hawker Fury biplane in the early 1930s. Despite an institutional preference for biplanes and lack of interest by the Air Ministry, Hawker refined their monoplane proposal, incorporating several innovations which became critical to wartime fighter aircraft, including retractable landing gear and the more powerful Rolls-Royce Merlin engine. The Air Ministry ordered Hawker's ''Int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prisoner Of War
A prisoner of war (POW) is a person who is held captive by a belligerent power during or immediately after an armed conflict. The earliest recorded usage of the phrase "prisoner of war" dates back to 1610. Belligerents hold prisoners of war in custody for a range of legitimate and illegitimate reasons, such as isolating them from the enemy combatants still in the field (releasing and repatriating them in an orderly manner after hostilities), demonstrating military victory, punishing them, prosecuting them for war crimes, exploiting them for their labour, recruiting or even conscripting them as their own combatants, collecting military and political intelligence from them, or indoctrinating them in new political or religious beliefs. Ancient times For most of human history, depending on the culture of the victors, enemy fighters on the losing side in a battle who had surrendered and been taken as prisoners of war could expect to be either slaughtered or enslaved. Ear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
P-51 Mustang
The North American Aviation P-51 Mustang is an American long-range, single-seat fighter and fighter-bomber used during World War II and the Korean War, among other conflicts. The Mustang was designed in April 1940 by a team headed by James H. Kindelberger of North American Aviation (NAA) in response to a requirement of the British Purchasing Commission. The Purchasing Commission approached North American Aviation to build Curtiss P-40 fighters under license for the Royal Air Force (RAF). Rather than build an old design from another company, North American Aviation proposed the design and production of a more modern fighter. The prototype NA-73X airframe was rolled out on 9 September 1940, 102 days after the contract was signed, and first flew on 26 October. The Mustang was designed to use the Allison V-1710 engine, which had limited high-altitude performance in its earlier variants. The aircraft was first flown operationally by the RAF as a tactical-reconnaissance aircraf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air Fighting Development Unit
The Air Fighting Development Unit (AFDU) was an air technical intelligence part of the Royal Air Force which developed tactics and tested captured enemy aircraft. It was based at Royal Air Force Stations Northolt, Duxford and Wittering. The AFDU was under the control of RAF Fighter Command and the Air Ministry; the AFDU performed comparative trials, developed and promulgated tactics effective against opposing aircraft types. Also sharing Wittering with the AFDU was the Naval Air Fighting Development Unit. These units also carried out tests and evaluations on a wide range of fighter aircraft, aircraft modifications and new equipment prior to entering Allied service. The AFDU was formed as the Air Fighting Development Establishment at Northolt on 20 October 1934; being re-named the Air Fighting Development Unit in July 1940. The units were absorbed into the Central Fighter Establishment and moved to RAF Tangmere in 1945. Operation Banquet Under the Operation Banquet anti-invasio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karel Kuttelwascher
Karel Miloslav Kuttelwascher DFC and Bar (23 September 1916 – 17 August 1959) was a Czech fighter pilot, and a flying ace of the UK's Royal Air Force (RAF) in the Second World War. He was in combat service from May 1940 to October 1942, first with the French Air Force and then with the RAF. Kuttelwascher, nicknamed "Kut", was the RAF's most successful Czechoslovak pilot, and one of the RAF's highest-scoring flying aces overall. In RAF service he shot down 18 enemy aircraft. He may also have scored numerous victories in French Air Force service, but these are unconfirmed as many French records were lost. In 1945 Kuttelwascher returned to Czechoslovakia but in 1946 he returned to Britain, where he made a civilian flying career with British European Airways. He died of a heart attack in 1959, aged 42. Early life Kuttelwascher was born in 1916 in the village of Svatý Kříž in Bohemia, now part of Havlíčkův Brod in the Czech Republic. He was the third of six children. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Night Fighter
A night fighter (also known as all-weather fighter or all-weather interceptor for a period of time after the Second World War) is a fighter aircraft adapted for use at night or in other times of bad visibility. Night fighters began to be used in World War I and included types that were specifically modified to operate at night. During the Second World War, night fighters were either purpose-built night fighter designs, or more commonly, heavy fighters or light bombers adapted for the mission, often employing radar or other systems for providing some sort of detection capability in low visibility. Many night fighters of the conflict also included instrument landing systems for landing at night, as turning on the runway lights made runways into an easy target for opposing intruders. Some experiments tested the use of day fighters on night missions, but these tended to work only under very favourable circumstances and were not widely successful. Avionics systems were greatly mini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wounded In Action
Wounded in Action (WIA) describes combatants who have been wounded while fighting in a combat zone during wartime, but have not been killed. Typically, it implies that they are temporarily or permanently incapable of bearing arms or continuing to fight. Generally, the Wounded in Action are far more numerous than those killed. Common combat injuries include second and third degree burns, broken bones, shrapnel wounds, brain injuries, spinal cord injuries, nerve damage, paralysis, loss of sight and hearing, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and limb loss. For the U.S. military, becoming WIA in combat generally results in subsequent conferral of the Purple Heart, because the purpose of the medal itself (one of the highest awards, military or civilian, officially given by the American government) is to recognize those killed, incapacitated, or wounded in battle. NATO's definitions Wounded in action A battle casualty other than '' killed in action'' who has incurred an injur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mediterranean Theatre Of Operations
The Mediterranean and Middle East Theatre was a major Theater (warfare)#Theater of operations, theatre of operations during the Second World War. The vast size of the Mediterranean and Middle East theatre saw interconnected naval, land, and air campaigns fought for control of the Mediterranean, North Africa, the Horn of Africa, the Middle East and Southern Europe. The fighting in this theatre lasted from 10 June 1940, when Fascist Italy (1922–1943), Italy entered the war on the side of Nazi Germany, Germany, until 2 May 1945 when all Axis powers, Axis forces in Italy surrendered. However, fighting would continue in Kingdom of Greece, Greece – where British Army, British troops had been dispatched to aid the Government of Greece, Greek government – during the early stages of the Greek Civil War. The British referred to this theatre as the Mediterranean and Middle East Theatre (so called due to the location of the fighting and the name of Middle East Command), the Americans c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_School_Chapel_-_geograph.org.uk_-_67831.jpg)