|
Jameel Institute (J-IDEA)
The Abdul Latif Jameel Institute for Disease and Emergency Analytics (commonly, the Jameel Institute, or J-IDEA) is a research institute at Imperial College London in the fields of epidemiology, mathematical modelling of infectious diseases and emergencies, environmental health, and health economics. Co-founded in 2019 by Imperial College London and Community Jameel, the Jameel Institute is housed in the School of Public Health, within the college's Faculty of Medicine. The mission of the Jameel Institute is "to combat threats from disease worldwide". The Jameel Institute rose to prominence in 2020 under the leadership of Professor Neil Ferguson, Director of the Jameel Institute, when, as part of the Imperial College COVID-19 Response Team, the Jameel Institute published mathematical modelling of the COVID-19 pandemic. As part of the COVID-19 pandemic response, researchers from the Jameel Institute provided expert advice to the UK government's Scientific Pandemic Influenza Group ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematical Modelling Of Infectious Disease
Mathematical models can project how infectious diseases progress to show the likely outcome of an epidemic (including in plants) and help inform public health and plant health interventions. Models use basic assumptions or collected statistics along with mathematics to find parameters for various infectious diseases and use those parameters to calculate the effects of different interventions, like mass vaccination programs. The modelling can help decide which intervention(s) to avoid and which to trial, or can predict future growth patterns, etc. History The modeling of infectious diseases is a tool that has been used to study the mechanisms by which diseases spread, to predict the future course of an outbreak and to evaluate strategies to control an epidemic. The first scientist who systematically tried to quantify causes of death was John Graunt in his book ''Natural and Political Observations made upon the Bills of Mortality'', in 1662. The bills he studied were listings of nu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Signing Ceremony
A signing ceremony is a ceremony in which a document of importance is signed (approved). Typically the document is a bill passed by a legislature, thus becoming a law by an executive's signature. However, the document may also be, for example, an executive order, international agreement, or a veto statement that invalidates a legislative measure. "The President should have had the veto signing ceremony at the local gas station./ref> The act of Electronic signature, electronically signing a document may be referred to as a signing ceremony. The act of physically signing a signature is seen as adding gravitas to the moment. History Signing ceremonies are derived from ceremonies that occurred when the British monarch gave Royal Assent to acts of Parliament. Signing ceremonies became an aspect of American politics. Signing ceremonies may be performed by U.S. state governors upon signing a state document (generally an act of the state legislature, making it into state law) or by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chief Medical Officer For England
In the United Kingdom, a Chief Medical Officer (CMO) is the most senior government advisor on matter relating to health. There are four CMOs in the United Kingdom who are appointed to advise their respective governments: * His Majesty's Government ''(CMO for England and medical adviser to the United Kingdom government)'' * Scottish Government * Welsh Government * Northern Ireland Executive Each CMO is assisted by one or more Deputy Chief Medical Officers, and complemented by a Chief Nursing Officer. The Chief Medical Officer is a qualified medical doctor whose medical speciality traditionally was public health medicine, and whose work focused on the health of communities rather than health of individuals. More recently, some appointees have been senior clinicians without training in public health medicine. In the UK, the CMO is one of the chief professional officers who advise the government in their respective health and social care disciplines. The CMO has independent stat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sally Davies (doctor)
Dame Sally Claire Davies (born 24 November 1949) is a British physician and academic administrator who was the Chief Medical Officer (United Kingdom) from 2010 to 2019 and Chief Scientific Adviser at the Department of Health from 2004 to 2016 and worked as a clinician specialising in the treatment of diseases of the blood and bone marrow. She was appointed Master of Trinity College, Cambridge, on 8 February 2019, effective from 8 October 2019. She is one of the founders of the National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR). Early life and education Davies was born on 24 November 1949 in Birmingham, England. Her father John Gordon Davies was an Anglican priest and theologian, and her mother Emily Mary Tordoff was a scientist: they both became academics at the University of Birmingham. She failed her eleven-plus exam but was nevertheless able to study at the private Edgbaston High School for Girls in Birmingham, where she excelled on the viola. Davies studied medicine a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coursera
Coursera Inc. () is a U.S.-based massive open online course provider founded in 2012 by Stanford University computer science professors Andrew Ng and Daphne Koller. Coursera works with universities and other organizations to offer online courses, certifications, and degrees in a variety of subjects. In 2021 it was estimated that about 150 universities offered more than 4,000 courses through Coursera. History Coursera was founded in 2012 by Stanford University computer science professors Andrew Ng and Daphne Koller. Ng and Koller started offering their Stanford courses online in fall 2011, and soon after left Stanford to launch Coursera. Princeton, Stanford, the University of Michigan, and the University of Pennsylvania were the first universities to offer content on the platform. In 2014 Coursera received both the Webby Winner (Websites and Mobile Sites Education 2014) and the People's Voice Winner (Websites and Mobile Sites Education) awards. Finances Coursera's revenues ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Massive Open Online Course
A massive open online course (MOOC ) or an open online course is an online course aimed at unlimited participation and open access via the Web. In addition to traditional course materials, such as filmed lectures, readings, and problem sets, many MOOCs provide interactive courses with user forums or social media discussions to support community interactions among students, professors, and teaching assistants (TAs), as well as immediate feedback to quick quizzes and assignments. MOOCs are a widely researched development in distance education, first introduced in 2008, that emerged as a popular mode of learning in 2012, a year called the "Year of the MOOC". Early MOOCs (cMOOCs: Connectivist MOOCs) often emphasized open-access features, such as open licensing of content, structure and learning goals, to promote the reuse and remixing of resources. Some later MOOCs (xMOOCs: extended MOOCs) use closed licenses for their course materials while maintaining free access for students. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quarantine
A quarantine is a restriction on the movement of people, animals and goods which is intended to prevent the spread of disease or pests. It is often used in connection to disease and illness, preventing the movement of those who may have been exposed to a communicable disease, yet do not have a confirmed medical diagnosis. It is distinct from medical isolation, in which those confirmed to be infected with a communicable disease are isolated from the healthy population. Quarantine considerations are often one aspect of border control. The concept of quarantine has been known since biblical times, and is known to have been practised through history in various places. Notable quarantines in modern history include the village of Eyam in 1665 during the bubonic plague outbreak in England; East Samoa during the 1918 flu pandemic; the Diphtheria outbreak during the 1925 serum run to Nome, the 1972 Yugoslav smallpox outbreak, the SARS pandemic, the Ebola pandemic and extensive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
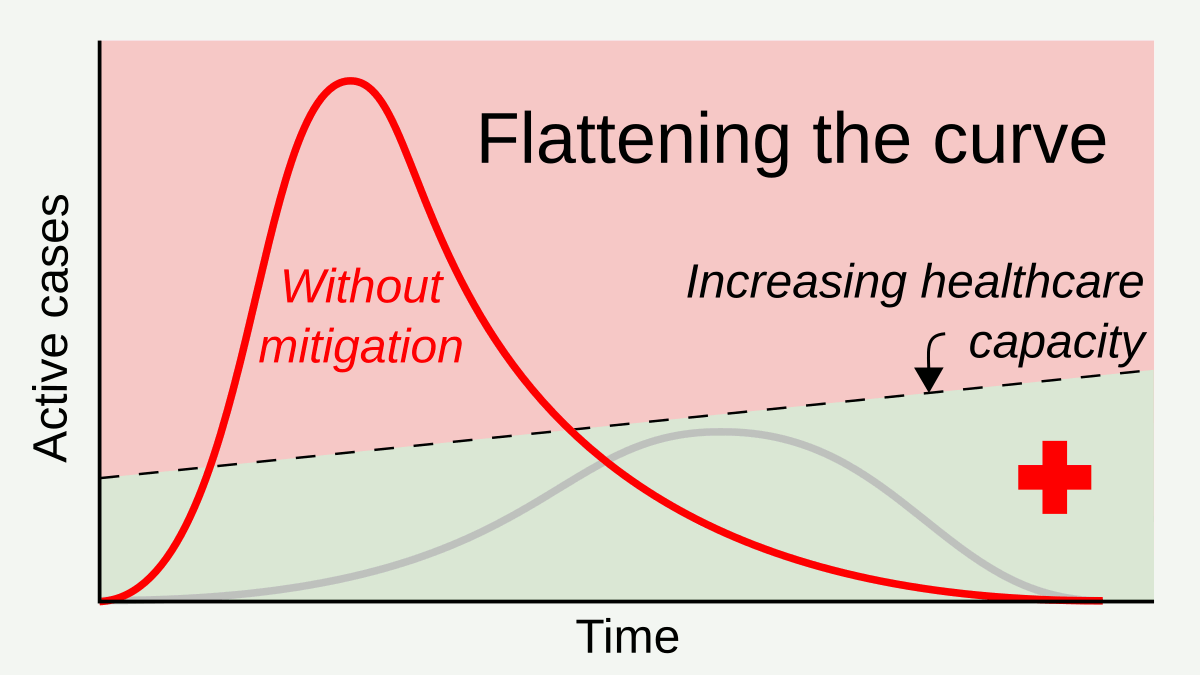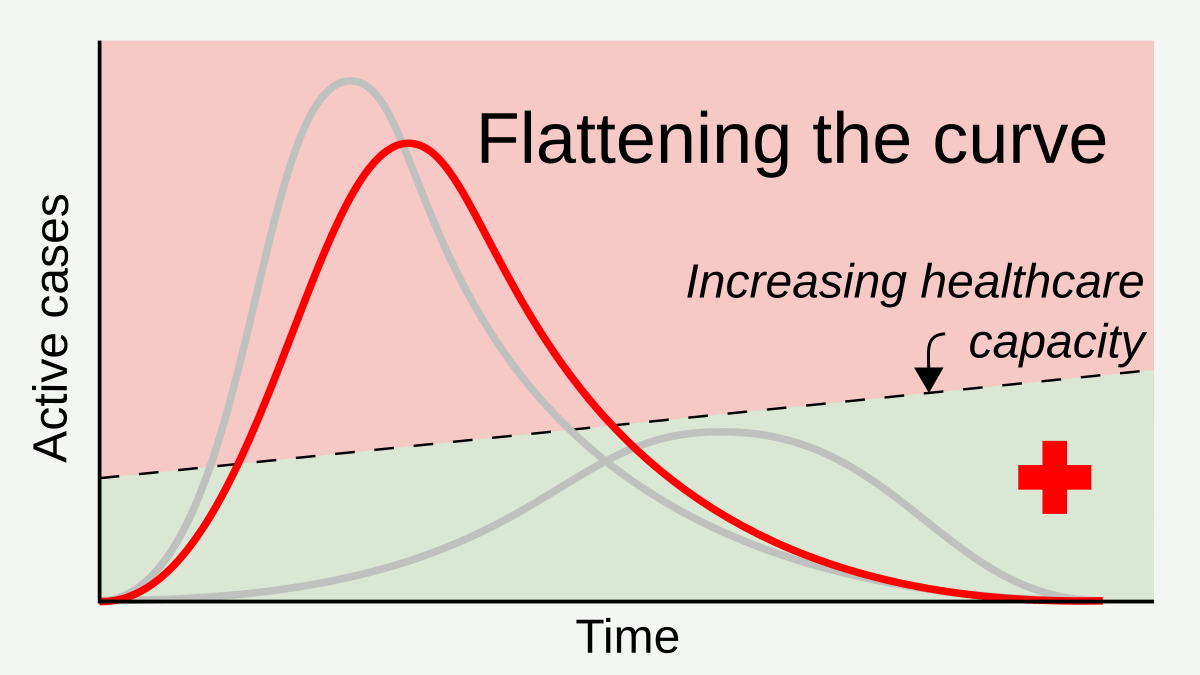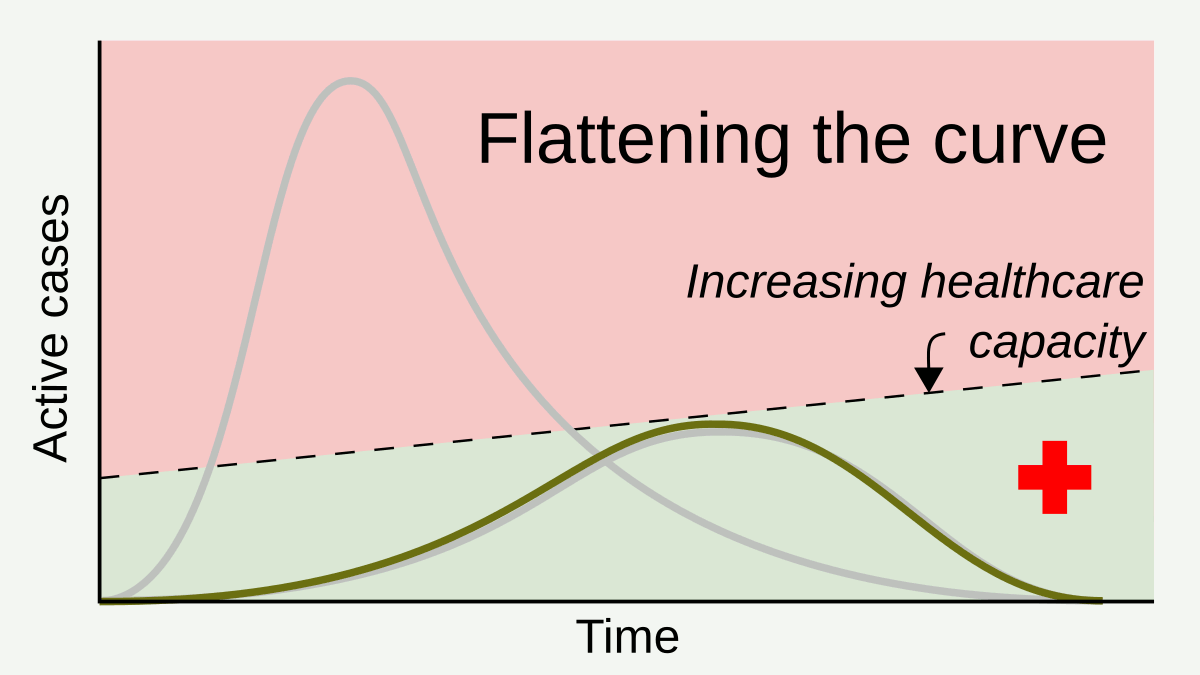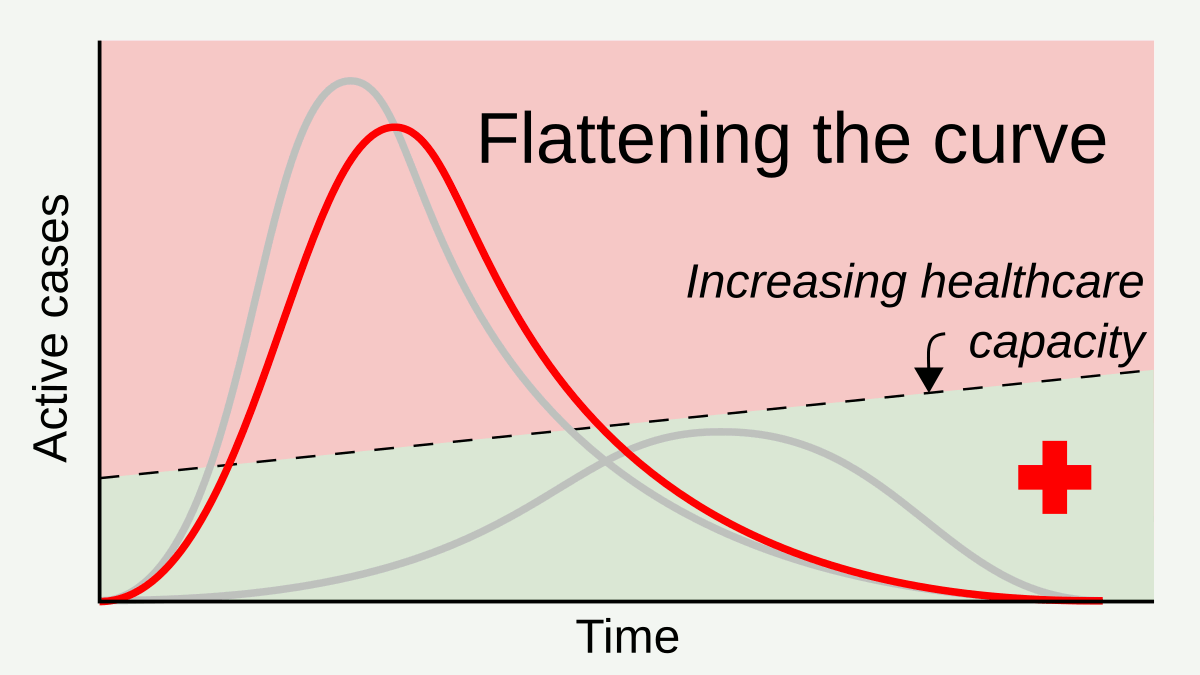
Social Distancing
In public health, social distancing, also called physical distancing, (NB. Regula Venske is president of the PEN Centre Germany.) is a set of non-pharmaceutical interventions or measures intended to prevent the spread of a contagious disease by maintaining a physical distance between people and reducing the number of times people come into close contact with each other. It usually involves keeping a certain distance from others (the distance specified differs from country to country and can change with time) and avoiding gathering together in large groups. By minimising the probability that a given uninfected person will come into physical contact with an infected person, the disease transmission can be suppressed, resulting in fewer deaths. The measures may be used in combination with others, such as good respiratory hygiene, face masks and hand washing. To slow down the spread of infectious diseases and avoid overburdening healthcare systems, particularly during a pand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-pharmaceutical Intervention (epidemiology)
In epidemiology, a non-pharmaceutical intervention (NPI) is any method used to reduce the spread of an epidemic disease without requiring pharmaceutical drug treatments. Examples of non-pharmaceutical interventions that reduce the spread of infectious diseases include wearing a face mask and staying away from sick people. The US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) points to personal, community, and environmental interventions. NPI have been recommended for pandemic influenza at both local and global levels, and studied at large scale during the 2009 swine flu pandemic and the COVID-19 pandemic. NPIs are a set of measures that can be utilized at any time, and are used in the period between the emergence of an epidemic disease and the deployment of an effective vaccine. Types Choosing to stay home to prevent the spread of symptoms of a potential sickness, covering coughs and sneezes, and washing one's hands on a regular basis are all examples of non-pharmaceutical i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MRC Centre For Global Infectious Disease Analysis
The MRC Centre for Global Infectious Disease Analysis is a Medical Research Council funded research centre at Imperial College London and a WHO collaborating centre. It is part of the Department of Infectious Disease Epidemiology at School of Public Health within the Imperial College Faculty of Medicine. Neil Ferguson is the director of the centre, along with four associate directors: Christl Donnelly, Azra Ghani, Nicholas Grassly, and Timothy Hallett. The centre also collaborates UK Health Protection Agency, and the US Centre for Disease Control. The centre's main research areas are disease outbreak analysis and modelling, vaccines, global health analytics, antimicrobial resistance, and developing methods and tools for studying these areas. The centre was previously called the MRC Centre for Outbreak Analysis and Modelling. COVID-19 pandemic response The centre—together with the Jameel Institute for Disease and Emergency Analytics—formed the COVID-19 Response Te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World Health Organization Collaborating Centre
World Health Organization collaborating centres are institutions that work with the World Health Organization (WHO) in disciplines such as occupational health, food safety, and communicable disease prevention. There are over 700 such centres across 80 countries. Collaborating centres may be research institutes, parts of universities, or academies. The participating institutions partner with WHO to perform research, provide training, or offer other services in furthering the WHO health agenda. These partners are designated by the WHO director-general as a part of a collaborative network. By using networks of established organizations, WHO is able to strengthen the scientific validity of its work and lower the costs of research. Centres worldwide The World Health Organization has established networks related to a variety of health topics. For example, WHO has put in place centres focused on Organ transplantation, organ transplants, hearing loss prevention, hepatitis, leprosy, medical e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hassan Jameel
Hassan Mohammed Abdul Latif Jameel"BRJ creates thousands more job opportunities" ''Arab News''. July 7, 2012. is a Saudi Arabia, Saudi businessman and philanthropist. He is Deputy President and Vice Chairman of Saudi Arabia operations of the family-owned international conglomerate business Abdul Latif Jameel, which, among numerous business operations, has distribution rights to Toyota vehicles in Saudi Arabia and other countries. His philanthropy work promotes health and safety, and assists job-seekers and those in need in Saudi Arabia. Early life and education Hassan is the middle son of Mohammed Abdul Latif Jameel, who has been the chairman and president of the diversified international business Abdul Latif Jameel since 1993.Chandler, Da ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)