|
Jakobidae
''Jakoba'' is a genus in the taxon Excavata, and currently has a single described species, ''Jakoba libera'' described by Patterson in 1990, and named in honour of Dutch botanist (Algology, Myology and Lichenology) Jakoba Ruinen. (Previously described ''Jakoba incarcerata'' has been renamed ''Andalucia incarcerata'', and ''Jakoba bahamensis'' /''Jakoba bahamiensis'' is not formally described.) Appearance and characteristics ''Jakoba'' are small bacterivorous zooflagellates (jakobids) found in marine and hypersaline environments. They are free swimming trophic cells with two flagella and range between five and ten micrometers in length. Cells rotate along their longitudinal axis to allow for swimming in straight lines unless deformation and “squirming” occurs due to compression in debris. During feeding, bacteria are removed from the water column by a current created by the posterior flagellum. This current causes the bacteria to collect in the groove on the right ventra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jakobea
Jakobids are an order of free-living, heterotrophic, flagellar eukaryotes in the supergroup Excavata. They are small (less than 15 μm), and can be found in aerobic and anaerobic environments. The order Jakobida, believed to be monophyletic, consists of only twenty species at present, and was classified as a group in 1993. There is ongoing research into the mitochondrial genomes of jakobids, which are unusually large and bacteria-like, evidence that jakobids may be important to the evolutionary history of eukaryotes. Molecular phylogenetic evidence suggests strongly that jakobids are most closely related to Heterolobosea (Percolozoa) and Euglenozoa. Structure and Biology Jakobids have two flagella, inserted in the anterior end of the cell, and, like other members of order Excavata, have a ventral feeding groove and associated cytoskeleton support. The posterior flagella has a dorsal vane and is aligned within the ventral groove, where it generates a current that the cell uses f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jakobid
Jakobids are an order of free-living, heterotrophic, flagellar eukaryotes in the supergroup Excavata. They are small (less than 15 μm), and can be found in aerobic and anaerobic environments. The order Jakobida, believed to be monophyletic, consists of only twenty species at present, and was classified as a group in 1993. There is ongoing research into the mitochondrial genomes of jakobids, which are unusually large and bacteria-like, evidence that jakobids may be important to the evolutionary history of eukaryotes. Molecular phylogenetic evidence suggests strongly that jakobids are most closely related to Heterolobosea (Percolozoa) and Euglenozoa. Structure and Biology Jakobids have two flagella, inserted in the anterior end of the cell, and, like other members of order Excavata, have a ventral feeding groove and associated cytoskeleton support. The posterior flagella has a dorsal vane and is aligned within the ventral groove, where it generates a current that the cell uses f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jakobidae
''Jakoba'' is a genus in the taxon Excavata, and currently has a single described species, ''Jakoba libera'' described by Patterson in 1990, and named in honour of Dutch botanist (Algology, Myology and Lichenology) Jakoba Ruinen. (Previously described ''Jakoba incarcerata'' has been renamed ''Andalucia incarcerata'', and ''Jakoba bahamensis'' /''Jakoba bahamiensis'' is not formally described.) Appearance and characteristics ''Jakoba'' are small bacterivorous zooflagellates (jakobids) found in marine and hypersaline environments. They are free swimming trophic cells with two flagella and range between five and ten micrometers in length. Cells rotate along their longitudinal axis to allow for swimming in straight lines unless deformation and “squirming” occurs due to compression in debris. During feeding, bacteria are removed from the water column by a current created by the posterior flagellum. This current causes the bacteria to collect in the groove on the right ventra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jakoba Libera Atcc 50422 200
''Jakoba'' is a genus in the taxon Excavata, and currently has a single described species, ''Jakoba libera'' described by Patterson in 1990, and named in honour of Dutch botanist (Algology, Myology and Lichenology) Jakoba Ruinen. (Previously described ''Jakoba incarcerata'' has been renamed ''Andalucia incarcerata'', and ''Jakoba bahamensis'' /''Jakoba bahamiensis'' is not formally described.) Appearance and characteristics ''Jakoba'' are small bacterivorous zooflagellates (jakobids) found in marine and hypersaline environments. They are free swimming trophic cells with two flagella and range between five and ten micrometers in length. Cells rotate along their longitudinal axis to allow for swimming in straight lines unless deformation and “squirming” occurs due to compression in debris. During feeding, bacteria are removed from the water column by a current created by the posterior flagellum. This current causes the bacteria to collect in the groove on the right ventra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jakoba Bahamiensis
''Jakoba'' is a genus in the taxon Excavata, and currently has a single described species, ''Jakoba libera'' described by Patterson in 1990, and named in honour of Dutch botanist (Algology, Myology and Lichenology) Jakoba Ruinen. (Previously described ''Jakoba incarcerata'' has been renamed ''Andalucia incarcerata'', and ''Jakoba bahamensis'' /''Jakoba bahamiensis'' is not formally described.) Appearance and characteristics ''Jakoba'' are small bacterivorous zooflagellates (jakobids) found in marine and hypersaline environments. They are free swimming trophic cells with two flagella and range between five and ten micrometers in length. Cells rotate along their longitudinal axis to allow for swimming in straight lines unless deformation and “squirming” occurs due to compression in debris. During feeding, bacteria are removed from the water column by a current created by the posterior flagellum. This current causes the bacteria to collect in the groove on the right ventra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jakoba Bahamensis
''Jakoba'' is a genus in the taxon Excavata, and currently has a single described species, ''Jakoba libera'' described by Patterson in 1990, and named in honour of Dutch botanist (Algology, Myology and Lichenology) Jakoba Ruinen. (Previously described ''Jakoba incarcerata'' has been renamed ''Andalucia incarcerata'', and ''Jakoba bahamensis'' /''Jakoba bahamiensis'' is not formally described.) Appearance and characteristics ''Jakoba'' are small bacterivorous zooflagellates (jakobids) found in marine and hypersaline environments. They are free swimming trophic cells with two flagella and range between five and ten micrometers in length. Cells rotate along their longitudinal axis to allow for swimming in straight lines unless deformation and “squirming” occurs due to compression in debris. During feeding, bacteria are removed from the water column by a current created by the posterior flagellum. This current causes the bacteria to collect in the groove on the right ventra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eukaryotic
Eukaryotes () are organisms whose cells have a nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are Eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the three domains of life. Bacteria and Archaea (both prokaryotes) make up the other two domains. The eukaryotes are usually now regarded as having emerged in the Archaea or as a sister of the Asgard archaea. This implies that there are only two domains of life, Bacteria and Archaea, with eukaryotes incorporated among archaea. Eukaryotes represent a small minority of the number of organisms, but, due to their generally much larger size, their collective global biomass is estimated to be about equal to that of prokaryotes. Eukaryotes emerged approximately 2.3–1.8 billion years ago, during the Proterozoic eon, likely as flagellated phagotrophs. Their name comes from the Greek εὖ (''eu'', "well" or "good") and κάρυον (''karyon'', "nut" or "kernel"). Euka ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jakoba Libera
''Jakoba'' is a genus in the taxon Excavata, and currently has a single described species, ''Jakoba libera'' described by Patterson in 1990, and named in honour of Dutch botanist (Algology, Myology and Lichenology) Jakoba Ruinen. (Previously described ''Jakoba incarcerata'' has been renamed ''Andalucia incarcerata'', and ''Jakoba bahamensis'' /''Jakoba bahamiensis'' is not formally described.) Appearance and characteristics ''Jakoba'' are small bacterivorous zooflagellates (jakobids) found in marine and hypersaline environments. They are free swimming trophic cells with two flagella and range between five and ten micrometers in length. Cells rotate along their longitudinal axis to allow for swimming in straight lines unless deformation and “squirming” occurs due to compression in debris. During feeding, bacteria are removed from the water column by a current created by the posterior flagellum. This current causes the bacteria to collect in the groove on the right ventra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eukaryota
Eukaryotes () are organisms whose Cell (biology), cells have a cell nucleus, nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are Eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the Three-domain system, three domains of life. Bacteria and Archaea (both prokaryotes) make up the other two domains. The eukaryotes are usually now regarded as having emerged in the Archaea or as a sister of the Asgard (archaea), Asgard archaea. This implies that there are only Two-domain system, two domains of life, Bacteria and Archaea, with eukaryotes incorporated among archaea. Eukaryotes represent a small minority of the number of organisms, but, due to their generally much larger size, their collective global biomass (ecology), biomass is estimated to be about equal to that of prokaryotes. Eukaryotes emerged approximately 2.3–1.8 billion years ago, during the Proterozoic eon, likely as Flagellated cell, flagellated phagotrophs. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Histiona
''Histiona'' is a genus of Excavata. It is a jakobid Jakobids are an order of free-living, heterotrophic, flagellar eukaryotes in the supergroup Excavata. They are small (less than 15 μm), and can be found in aerobic and anaerobic environments. The order Jakobida, believed to be monophyletic, con .... References Excavata genera Jakobids {{Excavata-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genomes
In the fields of molecular biology and genetics, a genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding genes, other functional regions of the genome such as regulatory sequences (see non-coding DNA), and often a substantial fraction of 'junk' DNA with no evident function. Almost all eukaryotes have mitochondria and a small mitochondrial genome. Algae and plants also contain chloroplasts with a chloroplast genome. The study of the genome is called genomics. The genomes of many organisms have been sequenced and various regions have been annotated. The International Human Genome Project reported the sequence of the genome for ''Homo sapiens'' in 200The Human Genome Project although the initial "finished" sequence was missing 8% of the genome consisting mostly of repetitive sequences. With advancements in technology that could handle sequencing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
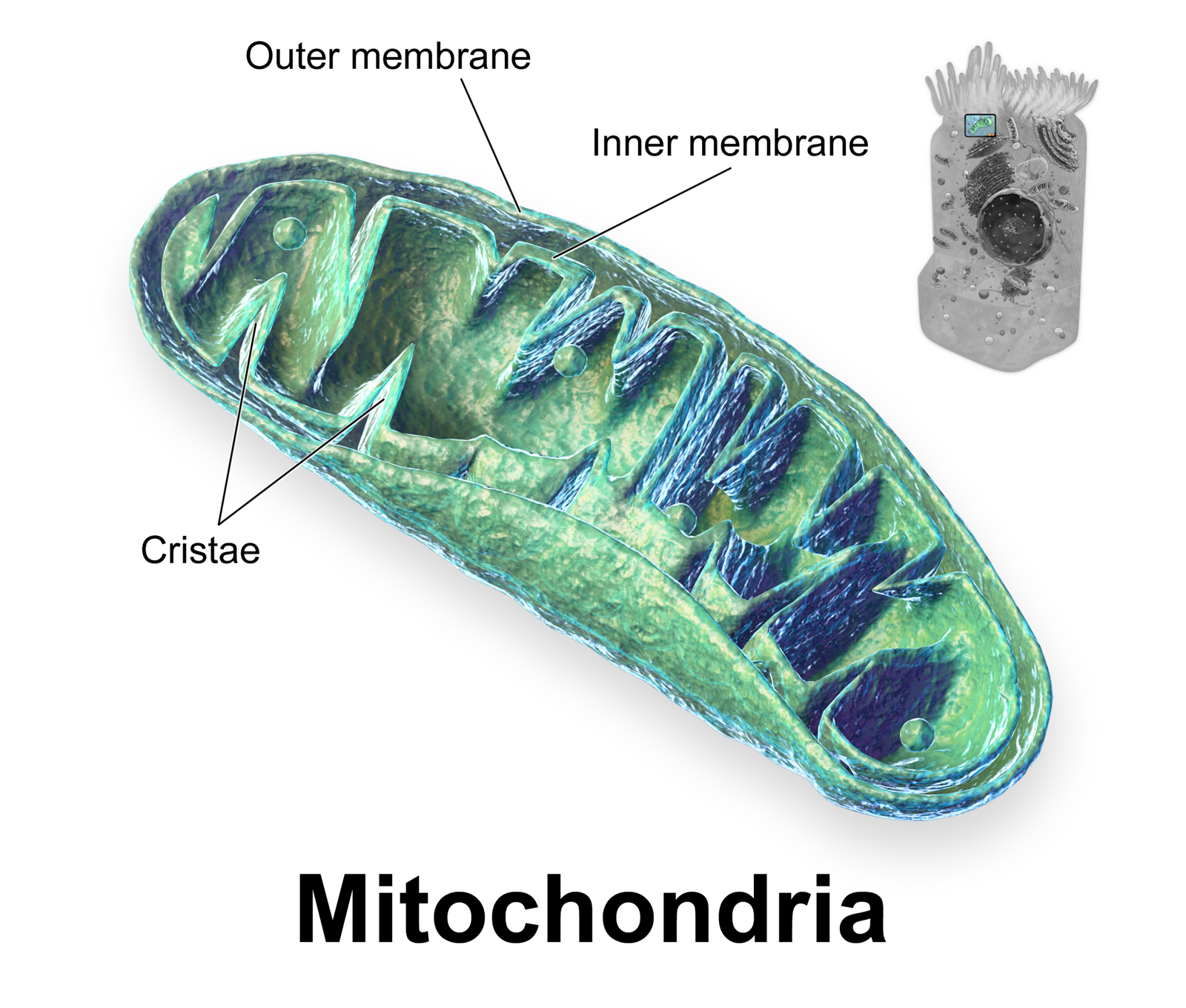
Cristae
A crista (; plural cristae) is a fold in the inner membrane of a mitochondrion. The name is from the Latin for ''crest'' or ''plume'', and it gives the inner membrane its characteristic wrinkled shape, providing a large amount of surface area for chemical reactions to occur on. This aids aerobic cellular respiration, because the mitochondrion requires oxygen. Cristae are studded with proteins, including ATP synthase and a variety of cytochromes. Background With the discovery of the dual-membrane nature of mitochondria, the pioneers of mitochondrial ultrastructural research proposed different models for the organization of the mitochondrial inner membrane. Three models proposed were: *Baffle model – According to Palade (1953), the mitochondrial inner membrane is convoluted in a baffle-like manner with broad openings towards the intra-cristal space. This model entered most textbooks and was widely believed for a long time. *Septa model – Sjöstrand (1953) suggested that s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |