|
Jackson, Kentucky
Jackson is a home rule-class city in and the county seat of Breathitt County, Kentucky, in the United States. The population was 2,231 according to the 2010 U.S. census. It was the home of the Jackson Academy, which became Lees College. History Upon the creation of Breathitt County in 1839, local landowner Simon Cockrell Sr. donated to serve as its seat of government. The community was originally known as Breathitt, Breathitt Town, or Breathitt Court House after the county, but upon its incorporation as a city by the state legislature in 1843,Commonwealth of Kentucky. Office of the Secretary of State. Land Office. "Jackson, Kentucky". Accessed 1 August 2013. it was renamed Jackson to honor former president Andrew Jackson.Rennick, Robert. ''Kentucky Place Names''p. 151 University Press of Kentucky (Lexington), 1987. Accessed 1 August 2013.''The Kentucky Encyclopedia''p. 459 "Jackson". University Press of Kentucky (Lexington), 1992. Accessed 1 August 2013. Local feuds led the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Kentucky Cities
Kentucky is a state in the United States. It has 419 active cities. Classes Since January 1, 2015, Kentucky cities have been divided into two classes based on their form of government: * First class – Mayor-alderman government * Home rule class – All other forms, including Mayor-Council, Commission, and City Manager This system went into effect on January 1, 2015, following the 2014 passage of House Bill 331 by the Kentucky General Assembly and the bill's signing into law by Governor Steve Beshear. The new system replaced one in which cities were divided into six classes based on their population at the time of their classification. Prior to the enactment of House Bill 331, over 400 classification-related laws affected public safety, alcohol beverage control, revenue options and others. Lexington and Fayette County are completely merged in a unitary urban county government (UCG); Louisville and other cities within Jefferson County have also merged into a single met ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louisville And Nashville Railroad
The Louisville and Nashville Railroad , commonly called the L&N, was a Class I railroad that operated freight and passenger services in the southeast United States. Chartered by the Commonwealth of Kentucky in 1850, the road grew into one of the great success stories of American business. Operating under one name continuously for 132 years, it survived civil war and economic depression and several waves of social and technological change. Under Milton H. Smith, president of the company for 30 years, the L&N grew from a road with less than of track to a system serving fourteen states. As one of the premier Southern railroads, the L&N extended its reach far beyond its namesake cities, stretching to St. Louis, Memphis, Atlanta, and New Orleans. The railroad was economically strong throughout its lifetime, operating freight and passenger trains in a manner that earned it the nickname, "The Old Reliable." Growth of the railroad continued until its purchase and the tumultuous rail ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AMSL
Height above mean sea level is a measure of the vertical distance (height, elevation or altitude) of a location in reference to a historic mean sea level taken as a vertical datum. In geodesy, it is formalized as ''orthometric heights''. The combination of unit of measurement and the physical quantity (height) is called "metres above mean sea level" in the metric system, while in United States customary and imperial units it would be called "feet above mean sea level". Mean sea levels are affected by climate change and other factors and change over time. For this and other reasons, recorded measurements of elevation above sea level at a reference time in history might differ from the actual elevation of a given location over sea level at a given moment. Uses Metres above sea level is the standard measurement of the elevation or altitude of: * Geographic locations such as towns, mountains and other landmarks. * The top of buildings and other structures. * Flying objects such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States National Arboretum
The United States National Arboretum is an arboretum in northeast Washington, D.C., operated by the United States Department of Agriculture's Agricultural Research Service. It was established in 1927 by an act of Congress after a campaign by USDA Chief Botanist Frederick Vernon Coville. It is in size and is located northeast of the Capitol building, with entrances on New York Avenue, NE and R Street, NE. The campus's gardens, collections, and features are connected by roadways that are long in total. In addition to the main campus in Washington, D.C., there are research locations at the Henry A. Wallace Beltsville Agricultural Research Center in Beltsville, Maryland and in McMinville, Tennessee. The Arboretum functions as a major center of botanical research conducted by the USDA, including applied research on trees, shrubs, turf, and the development of new ornamental plants. In addition to a library and a historical collection (archive), the institution also has an extensive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
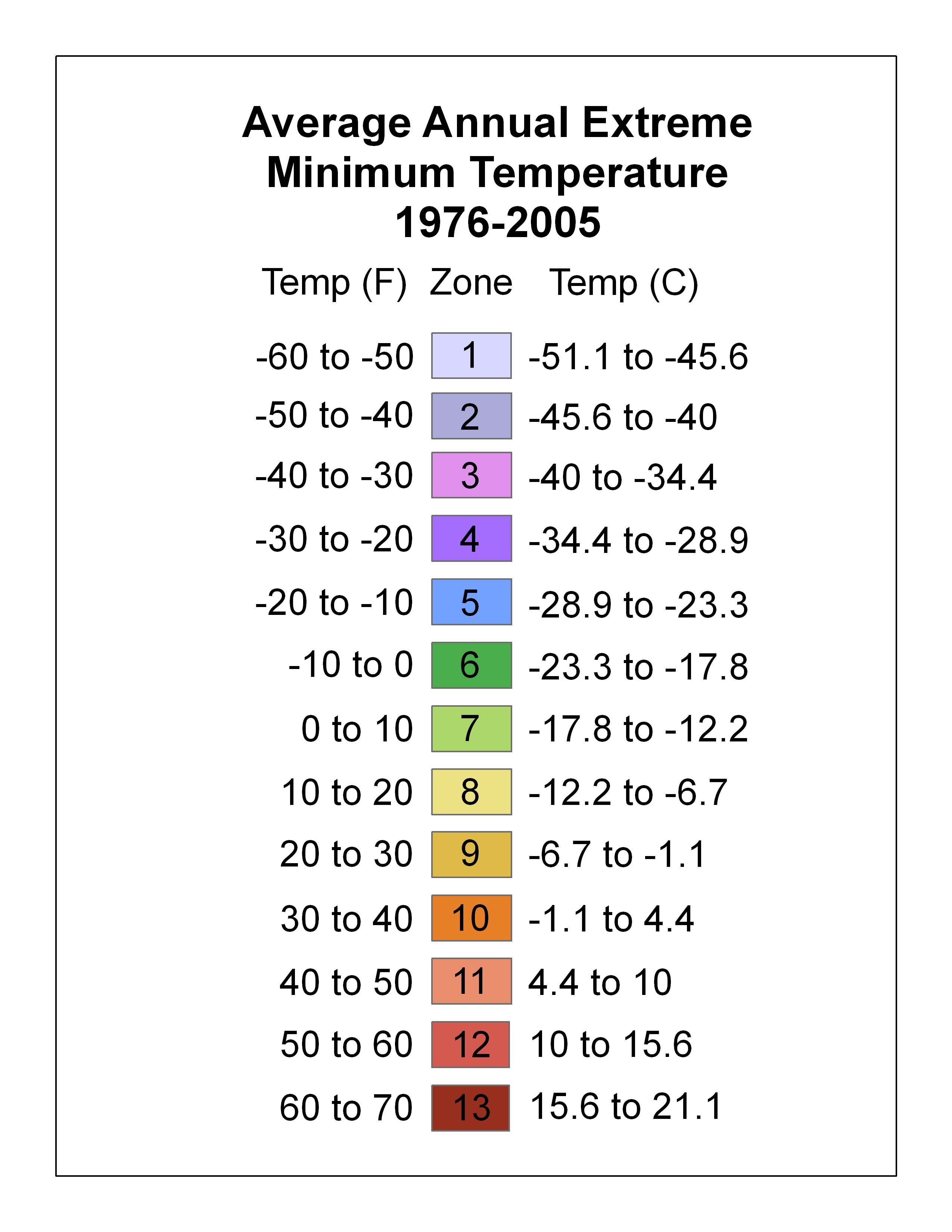
Hardiness Zone
A hardiness zone is a geographic area defined as having a certain average annual minimum temperature, a factor relevant to the survival of many plants. In some systems other statistics are included in the calculations. The original and most widely used system, developed by the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) as a rough guide for landscaping and gardening, defines 13 zones by long-term average annual extreme minimum temperatures. It has been adapted by and to other countries (such as Canada) in various forms. Unless otherwise specified, in American contexts "hardiness zone" or simply "zone" usually refers to the USDA scale. For example, a plant may be described as "hardy to zone 10": this means that the plant can withstand a minimum temperature of 30 °F (−1.1 °C) to 40 °F (4.4 °C). Other hardiness rating schemes have been developed as well, such as the UK Royal Horticultural Society and US Sunset Western Garden Book systems. A heat zone (s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Humid Subtropical Climate
A humid subtropical climate is a zone of climate characterized by hot and humid summers, and cool to mild winters. These climates normally lie on the southeast side of all continents (except Antarctica), generally between latitudes 25° and 40° and are located poleward from adjacent tropical climates. It is also known as warm temperate climate in some climate classifications. Under the Köppen climate classification, ''Cfa'' and ''Cwa'' climates are either described as humid subtropical climates or warm temperate climates. This climate features mean temperature in the coldest month between (or ) and and mean temperature in the warmest month or higher. However, while some climatologists have opted to describe this climate type as a "humid subtropical climate", Köppen himself never used this term. The humid subtropical climate classification was officially created under the Trewartha climate classification. In this classification, climates are termed humid subtropical when the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Köppen Climate Classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, notably in 1918 and 1936. Later, the climatologist Rudolf Geiger (1894–1981) introduced some changes to the classification system, which is thus sometimes called the Köppen–Geiger climate classification system. The Köppen climate classification divides climates into five main climate groups, with each group being divided based on seasonal precipitation and temperature patterns. The five main groups are ''A'' (tropical), ''B'' (arid), ''C'' (temperate), ''D'' (continental), and ''E'' (polar). Each group and subgroup is represented by a letter. All climates are assigned a main group (the first letter). All climates except for those in the ''E'' group are assigned a seasonal precipitation subgroup (the second letter). For example, ''Af'' indi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meandering River
A meander is one of a series of regular sinuous curves in the channel of a river or other watercourse. It is produced as a watercourse erodes the sediments of an outer, concave bank (cut bank) and deposits sediments on an inner, convex bank which is typically a point bar. The result of this coupled erosion and sedimentation is the formation of a sinuous course as the channel migrates back and forth across the axis of a floodplain. The zone within which a meandering stream periodically shifts its channel is known as a meander belt. It typically ranges from 15 to 18 times the width of the channel. Over time, meanders migrate downstream, sometimes in such a short time as to create civil engineering challenges for local municipalities attempting to maintain stable roads and bridges.Neuendorf, K.K.E., J.P. Mehl Jr., and J.A. Jackson, J.A., eds. (2005) ''Glossary of Geology'' (5th ed.). Alexandria, Virginia, American Geological Institute. 779 pp. Charlton, R., 2007. ''Fundamentals o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kentucky River
The Kentucky River is a tributary of the Ohio River, long,U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map , accessed June 13, 2011 in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), U.S. Commonwealth of Kentucky. The river and its tributaries drain much of the central region of the state, with its upper course passing through the coal-mining regions of the Cumberland Mountains, and its lower course passing through the Bluegrass region in the north central part of the state. Its watershed encompasses about . It supplies drinking water to about one-sixth of the population of the Commonwealth of Kentucky. The river is no longer navigable above Lock 4 at Frankfort, Kentucky, Frankfort. Concrete bulkhead (barrier), bulkheads have been poured behind the upper Lock (water transport), lock gates of Locks 5-14 to strengthen the weakest link in the dam structures. All 14 dams are now under the management of the state-run Kentucky River Authority. The pri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Appalachian Mountains
The Appalachian Mountains, often called the Appalachians, (french: Appalaches), are a system of mountains in eastern to northeastern North America. The Appalachians first formed roughly 480 million years ago during the Ordovician Period. They once reached elevations similar to those of the Alps and the Rocky Mountains before experiencing natural erosion. The Appalachian chain is a barrier to east–west travel, as it forms a series of alternating ridgelines and valleys oriented in opposition to most highways and railroads running east–west. Definitions vary on the precise boundaries of the Appalachians. The United States Geological Survey (USGS) defines the ''Appalachian Highlands'' physiographic division as consisting of 13 provinces: the Atlantic Coast Uplands, Eastern Newfoundland Atlantic, Maritime Acadian Highlands, Maritime Plain, Notre Dame and Mégantic Mountains, Western Newfoundland Mountains, Piedmont, Blue Ridge, Valley and Ridge, St. Lawrence Valley, Appalac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cumberland Plateau
The Cumberland Plateau is the southern part of the Appalachian Plateau in the Appalachian Mountains of the United States. It includes much of eastern Kentucky and Tennessee, and portions of northern Alabama and northwest Georgia. The terms "Allegheny Plateau" and the "Cumberland Plateau" both refer to the dissected plateau lands lying west of the main Appalachian Mountains. The terms stem from historical usage rather than geological difference, so there is no strict dividing line between the two. Two major rivers share the names of the plateaus, with the Allegheny River rising in the Allegheny Plateau and the Cumberland River rising in the Cumberland Plateau in Harlan County, Kentucky. Geography The Cumberland Plateau is a deeply dissected plateau, with topographic relief commonly of about , and frequent sandstone outcroppings and bluffs. At Kentucky's Pottsville Escarpment, which is the transition from the Cumberland Plateau to the Bluegrass in the north and the Pennyril ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |