|
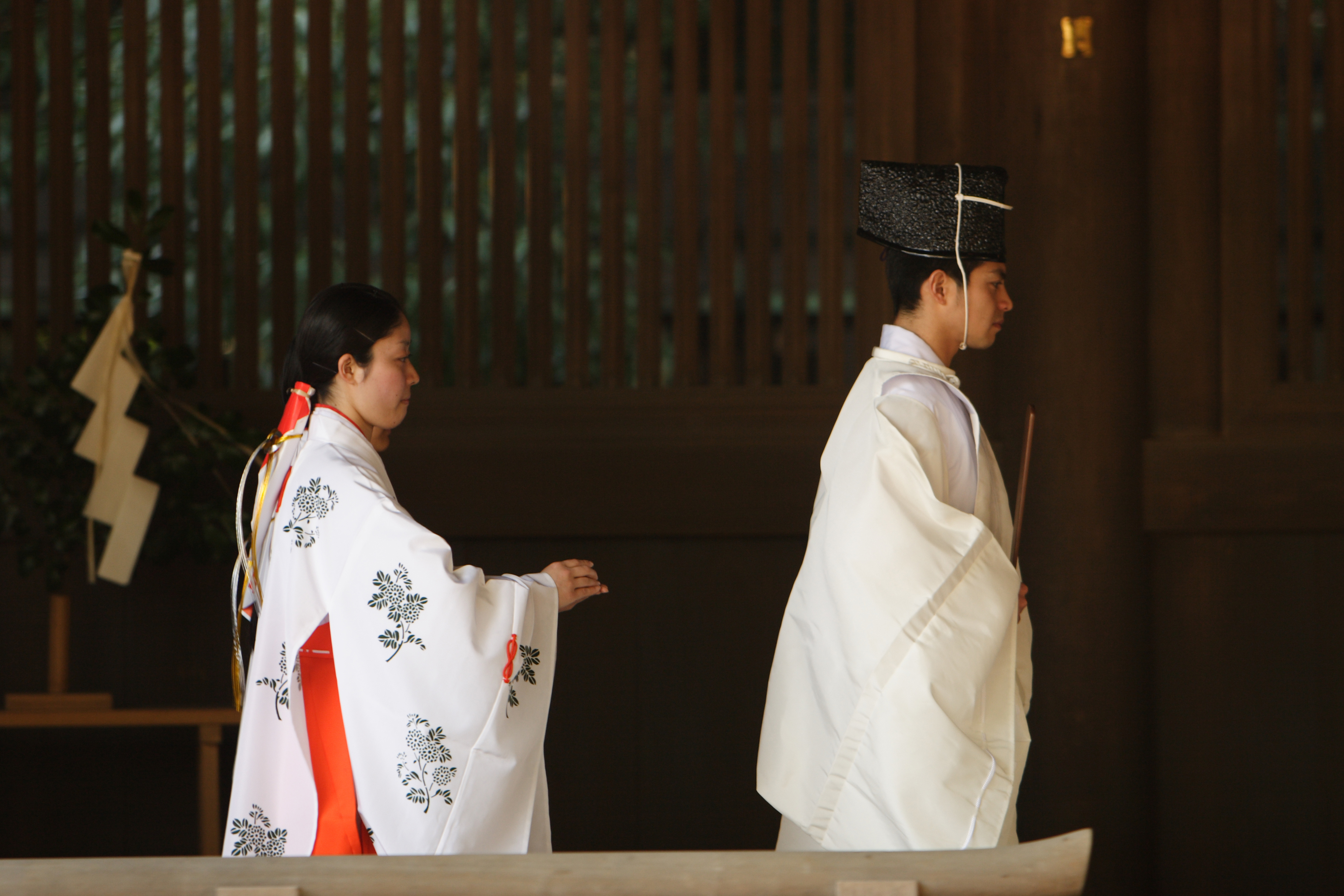
Jōe (priest)
is a garment worn in Japan by people attending religious ceremonies and activities, including Buddhist and Shinto related occasions. The is essentially a white , traditional hunting robes worn by nobles during the Heian period. Though both Shinto and Buddhist priests wear to rituals, laymen also occasionally wear the , such as when participating in pilgrimage such as the Shikoku Pilgrimage. The garment is usually white or yellow, and is made of linen or silk depending on its type and use. Shinto priests who wear the usually wear it with a peaked cap known as , alongside an outer tunic - the proper - an outer robe called , an undergarment known as the (lit. "unlined" or "one-layer"), ballooning trousers called or (a variant of the ), and a girdle called . A priest may also carry a ceremonial wand known as a , or another style of baton known as a . See also * Glossary of Shinto This is the glossary of Shinto, including major terms on the subject. Words followed by an as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kannushi And Miko At The Meiji Shrine, Tokyo
A , also called , is a person responsible for the maintenance of a as well as for leading worship of a given .* ''Kannushi'' (in Japanese), Iwanami Japanese dictionary, 6th Edition (2008), DVD version The characters for are sometimes also read as with the same meaning. History Originally, the were intermediaries between and people and could transmit their will to common humans. A was a man capable of miracles or a holy man who, because of his practice of purificatory rites, was able to work as a medium for a . Later the term evolved to being synonymous with - a man who works at a shrine and holds religious ceremonies there. In ancient times, because of the overlap of political and religious power within a clan, it was the head of the clan who led the clansmen during religious functions, or else it could be another official. Later, the role evolved into a separate and more specialized form. The term appears in both the (680 AD) and (720 AD), where the Empress Jing� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silk
Silk is a natural protein fiber, some forms of which can be woven into textiles. The protein fiber of silk is composed mainly of fibroin and is produced by certain insect larvae to form cocoons. The best-known silk is obtained from the cocoons of the larvae of the mulberry silkworm ''Bombyx mori'' reared in captivity (sericulture). The shimmering appearance of silk is due to the triangular prism-like structure of the silk fibre, which allows silk cloth to refract incoming light at different angles, thus producing different colors. Silk is produced by several insects; but, generally, only the silk of moth caterpillars has been used for textile manufacturing. There has been some research into other types of silk, which differ at the molecular level. Silk is mainly produced by the larvae of insects undergoing complete metamorphosis, but some insects, such as webspinners and raspy crickets, produce silk throughout their lives. Silk production also occurs in hymenoptera ( bee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Upper-body Garments
Japanese may refer to: * Something from or related to Japan, an island country in East Asia * Japanese language, spoken mainly in Japan * Japanese people, the ethnic group that identifies with Japan through ancestry or culture ** Japanese diaspora, Japanese emigrants and their descendants around the world * Japanese citizens, nationals of Japan under Japanese nationality law ** Foreign-born Japanese, naturalized citizens of Japan * Japanese writing system, consisting of kanji and kana * Japanese cuisine, the food and food culture of Japan See also * List of Japanese people * * Japonica (other) * Japonicum * Japonicus * Japanese studies Japanese studies (Japanese: ) or Japan studies (sometimes Japanology in Europe), is a sub-field of area studies or East Asian studies involved in social sciences and humanities research on Japan. It incorporates fields such as the study of Japanese ... {{disambiguation Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shinto Religious Clothing
Shinto () is a religion from Japan. Classified as an East Asian religion by scholars of religion, its practitioners often regard it as Japan's indigenous religion and as a nature religion. Scholars sometimes call its practitioners ''Shintoists'', although adherents rarely use that term themselves. There is no central authority in control of Shinto, with much diversity of belief and practice evident among practitioners. A polytheistic and animistic religion, Shinto revolves around supernatural entities called the . The are believed to inhabit all things, including forces of nature and prominent landscape locations. The are worshiped at household shrines, family shrines, and ''jinja'' public shrines. The latter are staffed by priests, known as , who oversee offerings of food and drink to the specific enshrined at that location. This is done to cultivate harmony between humans and and to solicit the latter's blessing. Other common rituals include the dances, rites of passag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glossary Of Shinto
This is the glossary of Shinto, including major terms on the subject. Words followed by an asterisk (*) are illustrated by an image in one of the photo galleries. __NOTOC__ A * – A red papier-mâché cow bobblehead toy; a kind of ''engimono'' and an ''omiyage'' (a regional souvenir in Japan) that is considered symbolic of Aizu. * – A type of fan held by aristocratic women of the Heian period when formally dressed; it is brightly painted with tassels and streamers on the ends. Held today in Shinto by a ''miko'' in formal costume for festivals. See also ''hiôgi''. * – The term's meaning is not limited to moral evil, and includes misfortune, inferiority and unhappiness. * - A malevolent fire spirit, demon or devil. * - Also known as the ''Akujin'', the ''Kibi-no-Ananowatari-no-Kami'' and as the ''Anato-no-Kami'', ''Akuru'' is a malevolent ''kami'' that is mentioned in the ''Keikoki'' (records regarding the time of the Emperor Keiko), the ''Nihonshoki'' (Chronicles of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shaku (Japanese Ritual Baton)
A () is a flat scepter originating from China, where they were originally used as narrow tablets for recording notes and orders. They were historically used by officials throughout East Asia, including Japan, Korea, Ryukyu, and Vietnam. They are known as in Japan, and are worn as part of the ceremonial outfit. They continue to be used in daoist and shinto ritual contexts in some parts of East Asia. Origin The use of the originated in ancient China, where the ''Classic of Rites'' required a to have a length of two six , and its mid part a width of three (). Originally, the was held by officials in court to record significant orders and instructions by the emperors. From the Jin dynasty onwards, following the increased proliferation of paper, the became a ceremonial instrument. In China, it was customary to hold the with the broad end down and the narrow end up. The was originally used at court for the taking of notes and was usually made of bamboo. Officials could re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hakama
are a type of traditional Japanese clothing. Originally stemming from (), the trousers worn by members of the Chinese imperial court in the Sui and Tang dynasties, this style was adopted by the Japanese in the form of in the 6th century. are tied at the waist and fall approximately to the ankles. They are worn over a kimono specially adapted for wearing , known as a . There are two types of : divided and undivided . The type have divided legs, similar to trousers. Both of these types appear similar. A "mountain" or "field" type of was traditionally worn by field or forest workers. They are looser in the waist and narrower in the leg. are secured by four straps (): two longer attached on either side of the front of the garment, and two shorter attached on either side of the rear. The rear of the garment may have a rigid trapezoidal section, called a . Below that on the inside, there may be a (a spoon-shaped component sometimes referred to as a ) which is tucked ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linen
Linen () is a textile made from the fibers of the flax plant. Linen is very strong, absorbent, and dries faster than cotton. Because of these properties, linen is comfortable to wear in hot weather and is valued for use in garments. It also has other distinctive characteristics, notably its tendency to wrinkle. Linen textiles appear to be some of the oldest in the world; their history goes back many thousands of years. Dyed flax fibers found in a cave in Southeastern Europe (present-day Georgia) suggest the use of woven linen fabrics from wild flax may date back over 30,000 years. Linen was used in ancient civilizations including Mesopotamia and ancient Egypt, and linen is mentioned in the Bible. In the 18th century and beyond, the linen industry was important in the economies of several countries in Europe as well as the American colonies. Textiles in a linen weave texture, even when made of cotton, hemp, or other non-flax fibers, are also loosely referred to as "linen". ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
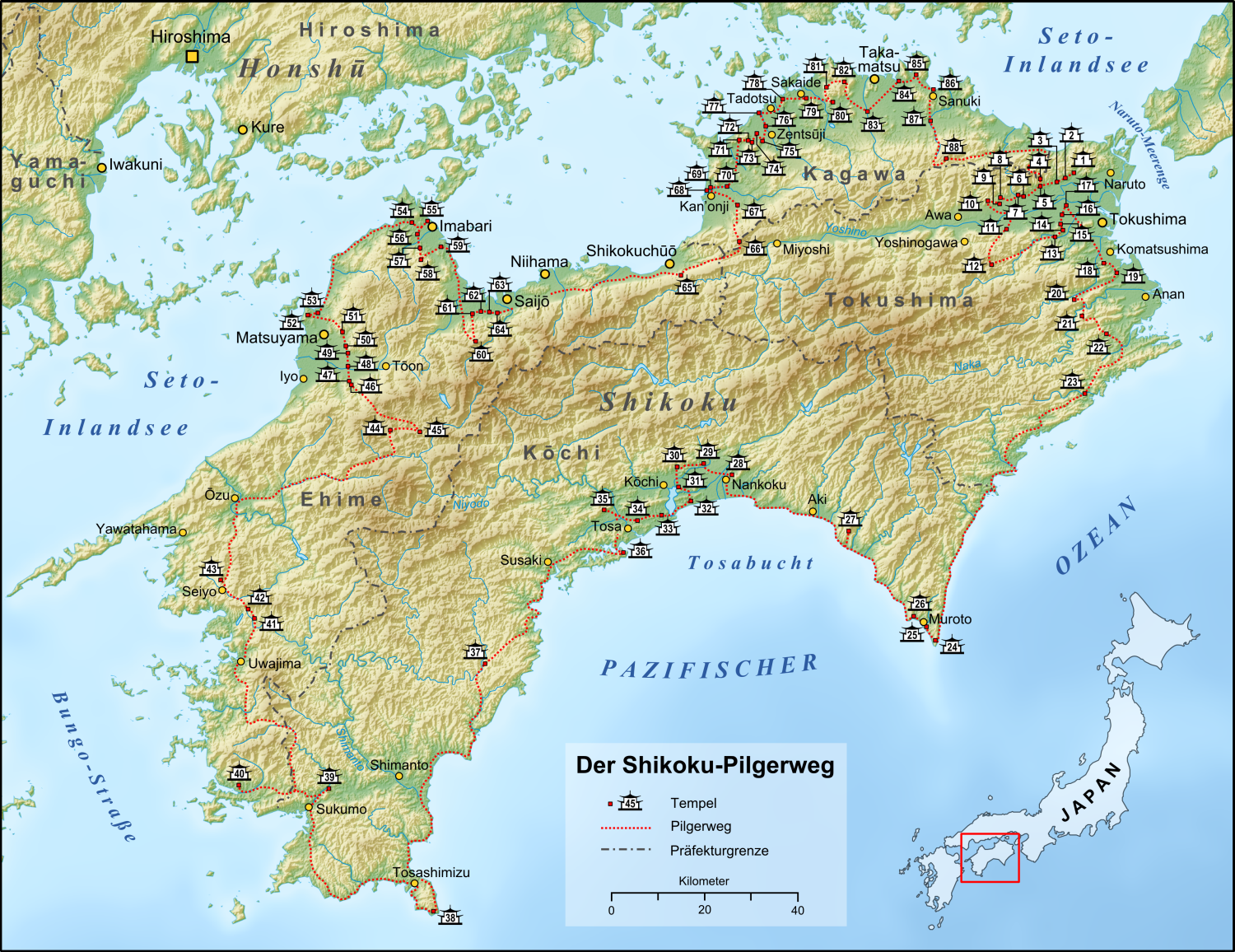
Shikoku Pilgrimage
The or is a multi-site pilgrimage of 88 temples associated with the Buddhist monk Kūkai (''Kōbō Daishi'') on the island of Shikoku, Japan. A popular and distinctive feature of the island's cultural landscape, and with a long history, large numbers of pilgrims, known as , still undertake the journey for a variety of ascetic, pious, and tourism-related purposes. The pilgrimage is traditionally completed on foot, but modern pilgrims use cars, taxis, buses, bicycles, or motorcycles, and often augment their travels with public transportation. The standard walking course is approximately long and can take anywhere from 30 to 60 days to complete. In addition to the 88 "official" temples of the pilgrimage, there are 20 ''bekkaku'' (別格) temples, which are officially associated with the Shikoku Pilgrimage (and hundreds more ''bangai'' (番外) temples, simply meaning "outside the numbers," which are not considered part of the official 88). To complete the pilgrimage, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heian Period
The is the last division of classical Japanese history, running from 794 to 1185. It followed the Nara period, beginning when the 50th emperor, Emperor Kanmu, moved the capital of Japan to Heian-kyō (modern Kyoto). means "peace" in Japanese. It is a period in Japanese history when the Chinese influences were in decline and the national culture matured. The Heian period is also considered the peak of the Japanese imperial court and noted for its art, especially poetry and literature. Two types of Japanese script emerged, including katakana, a phonetic script which was abbreviated into hiragana, a cursive alphabet with a unique writing method distinctive to Japan. This gave rise to Japan's famous vernacular literature, with many of its texts written by court women who were not as educated in Chinese compared to their male counterparts. Although the Imperial House of Japan had power on the surface, the real power was in the hands of the Fujiwara clan, a powerful aristocratic f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |