|
János Kendi
János Kendi de Nagykend ( hu, nagykendi Kendi János; died 1677) was a Hungarian jurist, who served as assistant notary of Michael I Apafi, Prince of Transylvania from 1661 to 1677. Career He was of serf origin (thus he was not related to the Kendi de Szarvaskend noble family). According to his last will and testament, Kendi liberated his parents himself from serfdom, when he was already notary. Based on his noble prefix, it is possible that he was born in the early 1600s in Nagykend (today ''Chendu'', part of Bălăușeri commune in Romania). In 1623, he was a scribe at the Princely Court of Justice during the reign of Gabriel Bethlen. He was a scribe at the Lesser Chancellery between 1632 and 1638. He compiled the ''urbarium'' of Székelyudvarhely (present-day Odorheiu Secuiesc, Romania) and its surrounding areas in 1644. In the last years of Prince George II Rákóczi, Kendi served as notary of Marosszék, mentioned in this capacity in 1656. He became a judge of the Prin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bălăușeri
Bălăușeri ( hu, Balavásár; Hungarian pronunciation: ; german: Bladenmarkt) is a commune in Mureș County, Transylvania, Romania. It is composed of six villages: Agrișteu, Bălăușeri, Chendu, Dumitreni, Filitelnic and Senereuș. History Bălăușeri is a commune in Mureș County, Transylvania, Romania. It is composed of six villages: Agrișteu, Bălăușeri, Chendu, Dumitreni, Filitelnic and Senereuș. The village was in the northern reaches of Küküllő County in Transylvania, just over the border from the Székely Land; in the 1876 administrative reform, the county was split and thereafter the village belonged to Kis-Küküllő County in the Kingdom of Hungary. After the 1920 Treaty of Trianon, it became part of Romania along with the rest of Transylvania. Demographics According to the 2011 census, the commune had a population of 4,698, of which 3,195 (68.01%) were Hungarian people, Hungarians, 905 (17.58%) Romanian people, Romanians, 662 (14.09%) Roma in Romania, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transylvanian Saxons
The Transylvanian Saxons (german: Siebenbürger Sachsen; Transylvanian Saxon: ''Siweberjer Såksen''; ro, Sași ardeleni, sași transilvăneni/transilvani; hu, Erdélyi szászok) are a people of German ethnicity who settled in Transylvania (german: Siebenbürgen) in waves starting from the mid- 12th century until the mid 19th century. The legal foundation of the settlement was laid down in the Diploma Andreanum issued by King Andrew II of Hungary that is known for providing the first territorial autonomy hitherto in the history. The Transylvanian "Saxons" originally came from Flanders, Hainaut, Brabant, Liège, Zeeland, Moselle, Lorraine, and Luxembourg, then situated in the north-western territories of the Holy Roman Empire around the 1140s. After 1918 and the dissolution of Austria-Hungary, in the wake of the Treaty of Trianon, Transylvania united with the Kingdom of Romania. Consequently, the Transylvanian Saxons, together with other ethnic German sub-groups in newly e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1677 Deaths
Events January–March * January 1 – Jean Racine's tragedy ''Phèdre'' is first performed, in Paris. * January 21 – The first medical publication in America (a pamphlet on smallpox) is produced in Boston. * February 15 – Four members of the English House of Lords embarrass King Charles II at the opening of the latest session of the "Cavalier Parliament" by proclaiming that the session is not legitimate because it hadn't met in more than a year. The Duke of Buckingham, backed by Lord Shaftesbury, Lord Salisbury and Baron Wharton, makes an unsuccessful motion to end the session. When the four Lords refuse to apologize, they are arrested and imprisoned in the Tower of London. * February 26 – ** The first arrests are made in the case that will develop into the "Affair of the Poisons" in France, as Magdelaine de La Grange and her accused accomplice, Father Nail, are detained on suspicion of poisoning her lover, a Messr. Faurie. While in prison i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fântânele, Mureș
Fântânele ( hu, Gyulakuta; Hungarian pronunciation: ) is a commune in Mureș County, Transylvania, Romania composed of six villages: *Bordoșiu / Bordos *Călimănești / Kelementelke *Cibu / Csöb *Fântânele *Roua / Rava *Viforoasa / Havadtő The commune is located in the southern part of the county, from the county seat, Târgu Mureș, on the border with Harghita County. It lies on the right bank of the Balta River. Demographics The commune has a Székely Hungarian majority. According to the 2011 census it has a population of 4,595 of which 93.84% or 4,312 are Hungarian. See also *List of Hungarian exonyms (Mureș County) This is a list of Hungarian names for towns and communes in Mureș County, Transylvania, Romania. {{DEFAULTSORT:List of Hungarian exonyms (Mures County) Mures County Hungarian exonyms in Mures Hungarian Hungarian Exonyms An endonym ... References {{DEFAULTSORT:Fantanele, Mures Communes in Mureș County Localities in Tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Udvarhelyszék
Udvarhelyszék (; formerly called ''Telegdiszék'') was one of the Székely seats in the historical Székely Land. Situated on the western part of the Székely Land, it was the main seat ( hu, anyaszék, la, sedes principalis, ''sedes capitalis'') for a significant period, being the home of the Count of the Székelys and the Székely National Assembly; it also fulfilled the main administrative and judiciary functions. It administered two sub-seats (Hungarian: ''fiúszék'', Latin: ''sedes filialis''): Bardócszék and Keresztúrszék. Population The religious make-up of Udvarhelyszék in 1867 was the following: *Calvinist: 35,759 *Roman Catholic: 34,282 * Unitarian: 22,263 *Greek Catholic: 2,054 *Greek Orthodox: 1,847 *Jewish: 115 *Lutheran Lutheranism is one of the largest branches of Protestantism, identifying primarily with the theology of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German monk and reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practice of the Catholic Church l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seat (territorial Administrative Unit)
Seats ( la, sedes, hu, szék, german: stuhl, ro, scaun) were administrative divisions in the medieval Kingdom of Hungary. The seats were autonomous regions within the Kingdom, and were independent from the feudal county system. Their autonomy was granted in return for the military services they provided to the Hungarian Kings. The following divisions were at one point Székely seats: * Marosszék * Udvarhelyszék * Csíkszék * Gyergyószék * * Sepsiszék * Orbaiszék * Kézdiszék * Aranyosszék Seats were formed by the: * Székelys * Transylvanian Saxons * Cumans * Jassic people The Jász (''Latin'': Jazones) are an Eastern Iranic ethnic group who have lived in Hungary since the 13th century. They live mostly in a region known as ''Jászság'', which comprises the north-western part of Jász-Nagykun-Szolnok county. ... * Ten Lance Bearers Most seats gave up their autonomous status and military traditions in late medieval times and paid tax instead. Medie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
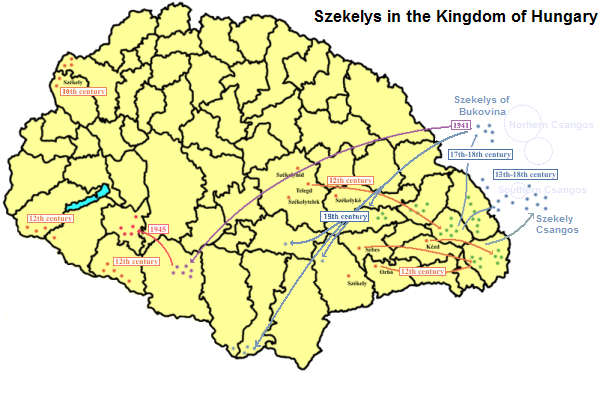
Székelys
The Székelys (, Székely runes: 𐳥𐳋𐳓𐳉𐳗), also referred to as Szeklers,; ro, secui; german: Szekler; la, Siculi; sr, Секељи, Sekelji; sk, Sikuli are a Hungarian subgroup living mostly in the Székely Land in Romania. A significant population descending from the Székelys of Bukovina lives in Tolna and Baranya counties in Hungary and certain districts of Vojvodina, Serbia. In the Middle Ages, the Székelys played a role in the defense of the Kingdom of Hungary against the Ottomans in their posture as guards of the eastern border. With the Treaty of Trianon of 1920, Transylvania (including the Székely Land) became part of Romania, and the Székely population was a target of Romanianization efforts. In 1952, during the communist rule of Romania, the former counties with the highest concentration of Székely population – Mureș, Odorhei, Ciuc, and Trei Scaune – were legally designated as the Magyar Autonomous Region. It was superseded in 1960 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torda County
Torda County (german: Komitat Torda,Fallenbüchl 1994, p. 153. hu, Torda vármegye, la, comitatus Thordensis) was a county in Transylvania between the 11th century and 1876. History Kingdom of Hungary Counties (districts formed around royal fortresses) were the basic units of royal administration in the Kingdom of Hungary from the 11th century. The fortress initially serving as the seat of Torda County was located at a distance of about Kristó 1988, p. 92. from modern Torda (now Turda, Romania), above the village Várfalva (now Moldovenești, Romania), on the river Aranyos (now Arieș in Romania).Bóna 1994, p. 163. A cemetery near the castle was used from the turn of the 10th and 11th centuries. The earliest royal charter mentioning the castle is from 1075, but only its interpolated version has been preserved. The earliest authentic charter referring to the same castle is dated to 1177. Although the county itself was only first mentioned in 1227, a reference in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Küküllő County
Küküllő County ( hu, Küküllő vármegye; ro, Comitatul Târnava; german: Komitat Kokelburg) was a county of the Kingdom of Hungary. Located in the Transylvania region between the rivers Maros (''Mureș'') and Nagy-Küküllő (''Târnava Mare''), it existed from the 11th century until 1876, when it was split off into Kis-Küküllő County and Nagy-Küküllő County Nagy-Küküllő ( ro, Comitatul Târnava-Mare) was an administrative county (comitatus) of the Kingdom of Hungary. Its territory is now in central Romania (central Transylvania). Nagy-Küküllő is the Hungarian name for the river Târnava Mare. .... Its capital was Küküllővár (german: Kokelburg, ro, Cetatea de Baltă). in the Magyar Katolikus Lexikon Notes {{DEFAULTSORT:Kukullo County[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ákos Barcsay
Ákos Barcsay (Achatius) (1619 ? - Kozmatelke July 1661) , was Prince of Transylvania from September 1658 to August 1659 and June to December 1660. Biography Barcsay was born in a respected noble family from Hunyad County. He grew up at the court of Gabriel Bethlen. The first significant station in his career was an embassy to the Sublime Porte in 1642 in the service of George I Rákóczy. In 1648 he was chief governor of the Hunyad county. Prince George II Rákóczy appointed him princely councilor in 1657 and governor for the time of his campaign to Poland. The Turks deposed Rákóczy after his unfortunate an unauthorised campaign and had Ferenc Rhédey elected prince on 2 November 1657. However, Rákóczy returned in January 1658 and forced the Diet to recognize him on 25 January 1658. As a reaction the Turks invaded Transylvania, leaving a trail of destruction through the country. Grand Vizier Köprülü Mehmed Pasha appointed Barcsay as prince on 14 September 1658, and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miklós Bethlen
Miklós () is a given name or surname, the Hungarian form of the Greek (English ''Nicholas''), and may refer to: In Hungarian politics * Miklós Bánffy, Hungarian nobleman, politician, and novelist * Miklós Horthy, Regent of the Kingdom of Hungary * Miklós Kállay, Hungarian politician who served as Prime Minister of Hungary during World War II * Miklós Lukáts, Hungarian politician and state secretary * Miklós Németh, Prime Minister of Hungary * Miklós Pálffy (1657 – 1732), Hungarian nobleman * Miklós Wesselényi, Hungarian statesman In Hungarian literature * Miklós Radnóti, Hungarian poet from Budapest who fell victim to the Holocaust * Miklós Vámos, Hungarian writer * Miklós Mészöly, Hungarian writer In artistry * Miklós Barabás, Hungarian painter * Miklós Izsó, Hungarian sculptorMiklós Izsó * Miklós Ybl, one of Europe's leading architects in the mid to late nineteenth century In sport * Miklós Fehér, Hungarian football player * Miklós Gaál ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chancellor Of Transylvania
The following is the list of chancellors of Transylvania during the Principality of Transylvania. List of chancellors Principality of Transylvania Habsburg rule The Transylvanian Court Chancellery was established in 1694, according to the ''Diploma Leopoldinum'', modeled on its Hungarian counterpart. Leopold I also created the Gubernium ("Governorate") which was the main governmental body of Transylvania until the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of 1867. During the reign of Joseph II the Hungarian and Transylvanian Court Chancelleries were merged in 1787. The King withdrew his, among others, regulation on his deathbed. See also * Governor of Transylvania * List of rulers of Transylvania * Principality of Transylvania (1570–1711) * Voivode of Transylvania The Voivode of Transylvania (german: Vojwode von Siebenbürgen;Fallenbüchl 1988, p. 77. hu, erdélyi vajda;Zsoldos 2011, p. 36. la, voivoda Transsylvaniae; ro, voievodul Transilvaniei) was the highest-ranking o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |