|
Just Fifth
In music theory, a perfect fifth is the musical interval corresponding to a pair of pitches with a frequency ratio of 3:2, or very nearly so. In classical music from Western culture, a fifth is the interval from the first to the last of five consecutive notes in a diatonic scale. The perfect fifth (often abbreviated P5) spans seven semitones, while the diminished fifth spans six and the augmented fifth spans eight semitones. For example, the interval from C to G is a perfect fifth, as the note G lies seven semitones above C. The perfect fifth may be derived from the harmonic series as the interval between the second and third harmonics. In a diatonic scale, the dominant note is a perfect fifth above the tonic note. The perfect fifth is more consonant, or stable, than any other interval except the unison and the octave. It occurs above the root of all major and minor chords (triads) and their extensions. Until the late 19th century, it was often referred to by one of its G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perfect Fifth On C
Perfect commonly refers to: * Perfection, completeness, excellence * Perfect (grammar), a grammatical category in some languages Perfect may also refer to: Film * ''Perfect'' (1985 film), a romantic drama * ''Perfect'' (2018 film), a science fiction thriller Literature * ''Perfect'' (Friend novel), a 2004 novel by Natasha Friend * ''Perfect'' (Hopkins novel), a young adult novel by Ellen Hopkins * ''Perfect'' (Joyce novel), a 2013 novel by Rachel Joyce * ''Perfect'' (Shepard novel), a Pretty Little Liars novel by Sara Shepard * ''Perfect'', a young adult science fiction novel by Dyan Sheldon Music * Perfect interval, in music theory * Perfect Records, a record label Artists * Perfect (musician) (born 1980), reggae singer * Perfect (Polish band) * Perfect (American band), an American alternative rock group Albums * ''Perfect'' (Intwine album) (2004) * ''Perfect'' (Half Japanese album) (2016) * ''perfecT'', an album by Sam Shaber * ''Perfect'', an album by True Fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unison
In music, unison is two or more musical parts that sound either the same pitch or pitches separated by intervals of one or more octaves, usually at the same time. ''Rhythmic unison'' is another term for homorhythm. Definition Unison or perfect unison (also called a prime, or perfect prime)Benward & Saker (2003), p. 53. may refer to the (pseudo-) interval formed by a tone and its duplication (in German, ''Unisono'', ''Einklang'', or ''Prime''), for example C–C, as differentiated from the second, C–D, etc. In the unison the two pitches have the ratio of 1:1 or 0 half steps and zero cents. Although two tones in unison are considered to be the same pitch, they are still perceivable as coming from separate sources, whether played on instruments of a different type: ; or of the same type: . This is because a pair of tones in unison come from different locations or can have different "colors" (timbres), i.e. come from different musical instruments or human voices. Voices wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equal Temperament
An equal temperament is a musical temperament or tuning system, which approximates just intervals by dividing an octave (or other interval) into equal steps. This means the ratio of the frequencies of any adjacent pair of notes is the same, which gives an equal perceived step size as pitch is perceived roughly as the logarithm of frequency. In classical music and Western music in general, the most common tuning system since the 18th century has been twelve-tone equal temperament (also known as 12 equal temperament, 12-TET or 12-ET; informally abbreviated to twelve equal), which divides the octave into 12 parts, all of which are equal on a logarithmic scale, with a ratio equal to the 12th root of 2 ( ≈ 1.05946). That resulting smallest interval, the width of an octave, is called a semitone or half step. In Western countries the term ''equal temperament'', without qualification, generally means 12-TET. In modern times, 12-TET is usually tuned relative to a standard pitch of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
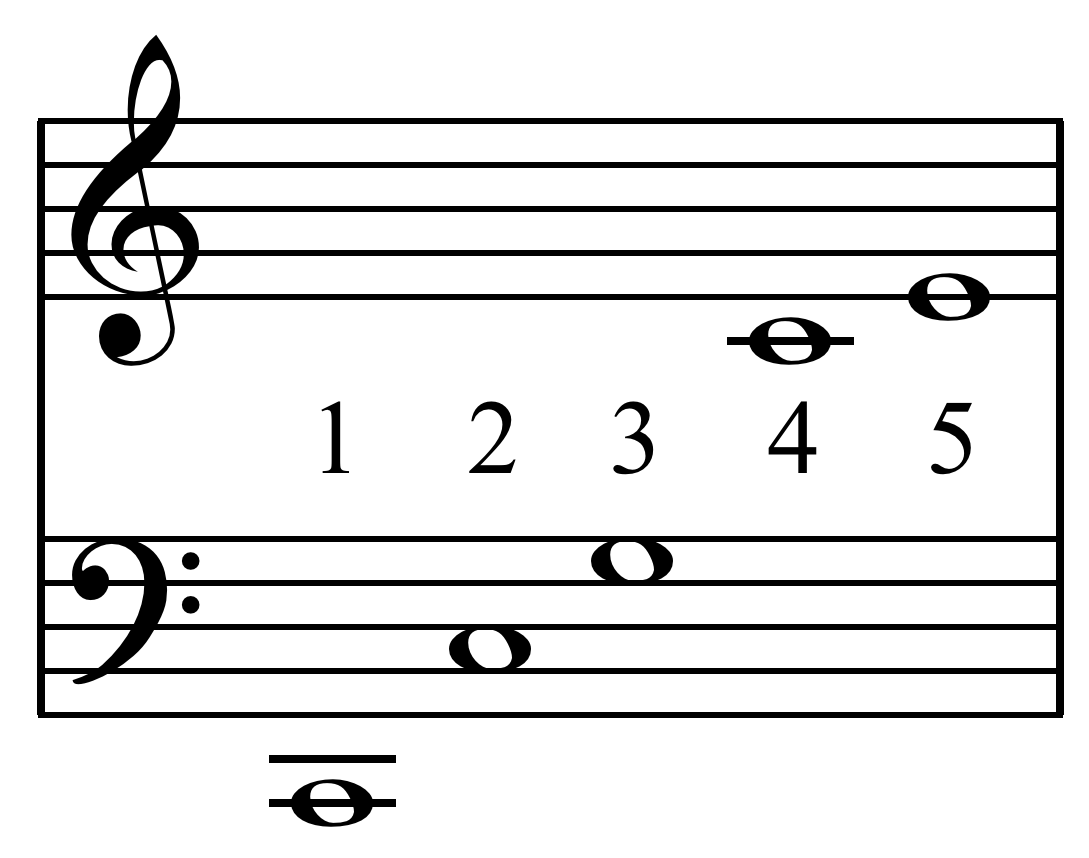
Just Interval
In music, just intonation or pure intonation is the tuning of musical intervals as whole number ratios (such as 3:2 or 4:3) of frequencies. An interval tuned in this way is said to be pure, and is called a just interval. Just intervals (and chords created by combining them) consist of tones from a single harmonic series of an implied fundamental. For example, in the diagram, if the notes G3 and C4 (labelled 3 and 4) are tuned as members of the harmonic series of the lowest C, their frequencies will be 3 and 4 times the fundamental frequency. The interval ratio between C4 and G3 is therefore 4:3, a just fourth. In Western musical practice, instruments are rarely tuned using only pure intervals—the desire for different keys to have identical intervals in Western music makes this impractical. Some instruments of fixed pitch, such as electric pianos, are commonly tuned using equal temperament, in which all intervals other than octaves consist of irrational-number frequenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diminished Sixth
In classical music from Western culture, a diminished sixth () is an interval produced by narrowing a minor sixth by a chromatic semitone.Benward & Saker (2003). ''Music: In Theory and Practice, Vol. I'', p.54. . Specific example of an d6 not given but general example of minor intervals described. For example, the interval from A to F is a minor sixth, eight semitones wide, and both the intervals from A to F, and from A to F are diminished sixths, spanning seven semitones. Being diminished, it is considered a dissonant interval,Benward & Saker (2003), p.92. despite being equivalent to an interval known for its consonance. Its inversion is the augmented third, and its enharmonic equivalent is the perfect fifth. Wolf fifth A severely dissonant diminished sixth is observed when the instrument is tuned using a Pythagorean or a meantone temperament tuning system. Typically, this is the interval between G and E. Since it seems to howl like a wolf (because of the beating), and si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enharmonic
In modern musical notation and tuning, an enharmonic equivalent is a note, interval, or key signature that is equivalent to some other note, interval, or key signature but "spelled", or named differently. The enharmonic spelling of a written note, interval, or chord is an alternative way to write that note, interval, or chord. The term is derived from Latin ''enharmonicus'', from Late Latin ''enarmonius'', from Ancient Greek ἐναρμόνιος (''enarmónios''), from ἐν (''en'') and ἁρμονία (''harmonía''). Definition For example, in any twelve-tone equal temperament (the predominant system of musical tuning in Western music), the notes C and D are ''enharmonic'' (or ''enharmonically equivalent'') notes. Namely, they are the same key on a keyboard, and thus they are identical in pitch, although they have different names and different roles in harmony and chord progressions. Arbitrary amounts of accidentals can produce further enharmonic equivalents, such as B (me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wolf Interval
In music theory, the wolf fifth (sometimes also called Procrustean fifth, or imperfect fifth) Paul, Oscar (1885). A manual of harmony for use in music-schools and seminaries and for self-instruction', p.165. Theodore Baker, trans. G. Schirmer. is a particularly dissonant musical interval spanning seven semitones. Strictly, the term refers to an interval produced by a specific tuning system, widely used in the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries: the quarter-comma meantone temperament. More broadly, it is also used to refer to similar intervals (of close, but variable magnitudes) produced by other tuning systems, including Pythagorean and most meantone temperaments. When the twelve notes within the octave of a chromatic scale are tuned using the quarter-comma mean-tone systems of temperament, one of the twelve intervals spanning seven semitones (classified as a diminished sixth) turns out to be much wider than the others (classified as perfect fifths). In mean-tone systems, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pythagorean Tuning
Pythagorean tuning is a system of musical tuning in which the frequency ratios of all intervals are based on the ratio 3:2.Bruce Benward and Marilyn Nadine Saker (2003). ''Music: In Theory and Practice'', seventh edition, 2 vols. (Boston: McGraw-Hill). Vol. I: p. 56. . This ratio, also known as the "pure" perfect fifth, is chosen because it is one of the most consonant and easiest to tune by ear and because of importance attributed to the integer 3. As Novalis put it, "The musical proportions seem to me to be particularly correct natural proportions." Alternatively, it can be described as the tuning of the syntonic temperament in which the generator is the ratio 3:2 (i.e., the untempered perfect fifth), which is ≈702 cents wide. The system dates to Ancient Mesopotamia; see . The system is named, and has been widely misattributed, to Ancient Greeks, notably Pythagoras (sixth century BC) by modern authors of music theory, while Ptolemy, and later Boethius, ascribed the divi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Twinkle, Twinkle, Little Star
"Twinkle, Twinkle, Little Star" is a popular English lullaby. The lyrics are from an early-19th-century English poem written by Jane Taylor, "The Star". The poem, which is in couplet form, was first published in 1806 in '' Rhymes for the Nursery'', a collection of poems by Taylor and her sister Ann. It is sung to the tune of the French melody " Ah! vous dirai-je, maman", which was published in 1761 and later arranged by several composers, including Mozart with Twelve Variations on "Ah vous dirai-je, Maman". The English lyrics have five stanzas, although only the first is widely known. It has a Roud Folk Song Index number of 7666. The song is in the public domain, and has many adaptations around the world, including the "Alphabet song" and "Baa, Baa, Black Sheep". Lyrics The English lyrics were written as a poem by Jane Taylor (1783–1824)M. Cryer, ''Love Me Tender: The Stories Behind the World's Best-loved Songs'' (Frances Lincoln, 2009), pp. 83–5. and published with th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inversion (interval)
In music theory, an inversion is a type of change to intervals, chords, voices (in counterpoint), and melodies. In each of these cases, "inversion" has a distinct but related meaning. The concept of inversion also plays an important role in musical set theory. Intervals An interval is inverted by raising or lowering either of the notes by one or more octaves so that the positions of the notes reverse (i.e. the higher note becomes the lower note and vice versa). For example, the inversion of an interval consisting of a C with an E above it (the third measure below) is an E with a C above it – to work this out, the C may be moved up, the E may be lowered, or both may be moved. : The tables to the right show the changes in interval quality and interval number under inversion. Thus, perfect intervals remain perfect, major intervals become minor and vice versa, and augmented intervals become diminished and vice versa. (Doubly diminished intervals become doubly augmented ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extended Chords
In music, extended chords are certain chords (built from thirds) or triads with notes ''extended'', or added, beyond the seventh. Ninth, eleventh, and thirteenth chords are extended chords. The thirteenth is the farthest extension diatonically possible as, by that point, all seven tonal degrees are represented within the chord (the next extension, the fifteenth, is the same as the root of the chord). In practice however, extended chords do not typically use all the chord members; when it is not altered, the fifth is often omitted, as are notes between the seventh and the highest note (i.e., the ninth is often omitted in an eleventh chord; the ninth and eleventh are usually omitted in a thirteenth chord), unless they are altered to give a special texture. Chords extended beyond the seventh are rarely seen in the Baroque era, and are used more frequently in the Classical era. The Romantic era saw greatly increased use of extended harmony. Extended harmony prior to the 20th c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minor Chord
In music theory, a minor chord is a chord that has a root, a minor third, and a perfect fifth. When a chord comprises only these three notes, it is called a minor triad. For example, the minor triad built on C, called a C minor triad, has pitches C–E–G: In harmonic analysis and on lead sheets, a C minor chord can be notated as Cm, C−, Cmin, or simply the lowercase "c". A minor triad is represented by the integer notation . A minor triad can also be described by its intervals: the interval between the bottom and middle notes is a minor third, and the interval between the middle and top notes is a major third. By contrast, a major triad has a major third on the bottom and minor third on top. They both contain fifths, because a minor third (three semitones) plus a major third (four semitones) equals a perfect fifth (seven semitones). Chords that are constructed of consecutive (or "stacked") thirds are called ''tertian.'' In Western classical music from 1600 to 182 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |