|
Jurij Grós
Jurij Grós (1 January 1931 – 28 December 2019) was an ethnic Sorbian communist politician who held office before and after German reunification. Biography Grós was born in Bautzen in 1931 and educated at the Sorbian Teacher Training Institute in Radibor. He joined the Socialist Unity Party of Germany (SED) in 1949 and worked as a teacher until 1953. He joined the district leadership of the Free German Youth (FDJ) and in 1955 became a member of the Federal Executive Board of Domowina, the state-sponsored association for the Sorbian minority. In 1964, he was appointed First Secretary of the Federal Executive Board, and assumed leadership of the organization upon the retirement of its long-time Chairman, Kurt Krjeńc in 1973. He was elected to the Central Council of the FDJ in 1959 and remained in office until 1971. In the 1986 East German general election, Grós was elected to the Volkskammer. In the wake of the Peaceful Revolution, he resigned his position in Domowina, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
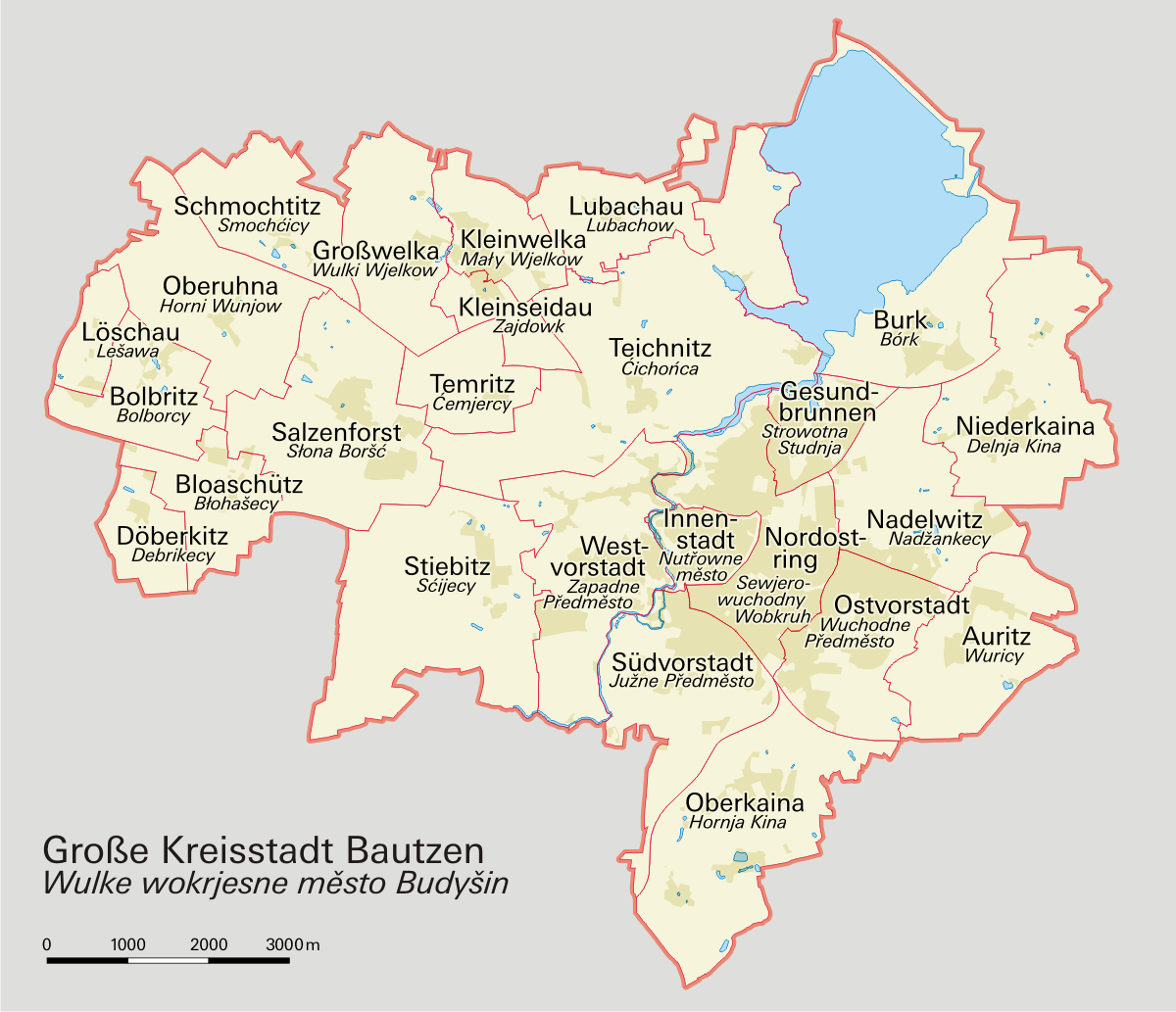
Bautzen
Bautzen () or Budyšin () is a hill-top town in eastern Saxony, Germany, and the administrative centre of the district of Bautzen. It is located on the Spree river. In 2018 the town's population was 39,087. Until 1868, its German name was ''Budissin''. In 1945 the Battle of Bautzen was Hitler’s last victory against the Soviet Union during the Battle of Berlin . Bautzen is often regarded as the unofficial, but historical capital of Upper Lusatia. The town is also the most important cultural centre of the Sorbian minority, which constitutes about 10 percent of Bautzen's population. Asteroid '' 11580 Bautzen'' is named in honour of the city. Names Like other cities and places in Lusatia, Bautzen has several different names across languages. Its German name was also officially changed in 1868. As well as ''Bautzen'' (German) and ''Budyšin'' (Upper Sorbian), the town has had the following names: * German: ''Budissin'' (variants used from c. 11th century onwards; Saxon governme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Reunification
German reunification (german: link=no, Deutsche Wiedervereinigung) was the process of re-establishing Germany as a united and fully sovereign state, which took place between 2 May 1989 and 15 March 1991. The day of 3 October 1990 when the German Reunification Treaty entered into force dissolving the German Democratic Republic (GDR; german: link=no, Deutsche Demokratische Republik, DDR, or East Germany) and integrating its recently re-established constituent federated states into the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG; german: link=no, Bundesrepublik Deutschland, BRD, or West Germany) to form present-day Germany, has been chosen as the customary ''German Unity Day'' () and has thereafter been celebrated each year from 1991 as a national holiday. East and West Berlin were united into a single city and eventually became the capital of reunited Germany. The East Germany's government led by the Socialist Unity Party of Germany (SED) (a communist party) started to falter on 2 May 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Socialist Unity Party Of Germany Politicians
Socialism is a left-wing economic philosophy and movement encompassing a range of economic systems characterized by the dominance of social ownership of the means of production as opposed to private ownership. As a term, it describes the economic, political and social theories and movements associated with the implementation of such systems. Social ownership can be state/public, community, collective, cooperative, or employee. While no single definition encapsulates the many types of socialism, social ownership is the one common element. Different types of socialism vary based on the role of markets and planning in resource allocation, on the structure of management in organizations, and from below or from above approaches, with some socialists favouring a party, state, or technocratic-driven approach. Socialists disagree on whether government, particularly existing government, is the correct vehicle for change. Socialist systems are divided into non-market and market fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
People From Bautzen
A person ( : people) is a being that has certain capacities or attributes such as reason, morality, consciousness or self-consciousness, and being a part of a culturally established form of social relations such as kinship, ownership of property, or legal responsibility. The defining features of personhood and, consequently, what makes a person count as a person, differ widely among cultures and contexts. In addition to the question of personhood, of what makes a being count as a person to begin with, there are further questions about personal identity and self: both about what makes any particular person that particular person instead of another, and about what makes a person at one time the same person as they were or will be at another time despite any intervening changes. The plural form "people" is often used to refer to an entire nation or ethnic group (as in "a people"), and this was the original meaning of the word; it subsequently acquired its use as a plural form of pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sorbian People
Sorbs ( hsb, Serbja, dsb, Serby, german: Sorben; also known as Lusatians, Lusatian Serbs and Wends) are a indigenous West Slavic ethnic group predominantly inhabiting the parts of Lusatia located in the German states of Saxony and Brandenburg. Sorbs traditionally speak the Sorbian languages (also known as "Wendish" and "Lusatian"), which are closely related to Czech, Polish, Kashubian, Silesian, and Slovak. Upper Sorbian and Lower Sorbian are officially recognized minority languages in Germany. Due to a gradual and increasing assimilation between the 17th and 20th centuries, virtually all Sorbs also spoke German by the early 20th century. In the newly created German nation state of the late 19th and early 20th centuries, policies were implemented in an effort to Germanize the Sorbs. These policies reached their climax under the Nazi regime, who denied the existence of the Sorbs as a distinct Slavic people by referring to them as "Sorbian-speaking Germans". The communit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2019 Deaths
This is a list of deaths of notable people, organised by year. New deaths articles are added to their respective month (e.g., Deaths in ) and then linked here. 2022 2021 2020 2019 2018 2017 2016 2015 2014 2013 2012 2011 2010 2009 2008 2007 2006 2005 2004 2003 2002 2001 2000 1999 1998 1997 1996 1995 1994 1993 1992 1991 1990 1989 1988 1987 See also * Lists of deaths by day The following pages, corresponding to the Gregorian calendar, list the historical events, births, deaths, and holidays and observances of the specified day of the year: Footnotes See also * Leap year * List of calendars * List of non-standard ... * Deaths by year {{DEFAULTSORT:deaths by year ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1931 Births
Events January * January 2 – South Dakota native Ernest Lawrence invents the cyclotron, used to accelerate particles to study nuclear physics. * January 4 – German pilot Elly Beinhorn begins her flight to Africa. * January 22 – Sir Isaac Isaacs is sworn in as the first Australian-born Governor-General of Australia. * January 25 – Mohandas Gandhi is again released from imprisonment in India. * January 27 – Pierre Laval forms a government in France. February * February 4 – Soviet leader Joseph Stalin gives a speech calling for rapid industrialization, arguing that only strong industrialized countries will win wars, while "weak" nations are "beaten". Stalin states: "We are fifty or a hundred years behind the advanced countries. We must make good this distance in ten years. Either we do it, or they will crush us." The first five-year plan in the Soviet Union is intensified, for the industrialization and collectivization of agriculture. * February 10 � ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peaceful Revolution
The Peaceful Revolution (german: Friedliche Revolution), as a part of the Revolutions of 1989, was the process of sociopolitical change that led to the opening of East Germany's borders with the West, the end of the ruling of the Socialist Unity Party of Germany (SED) (communist regime) in the German Democratic Republic (GDR or "East Germany") in 1989 and the transition to a parliamentary democracy, which later enabled the reunification of Germany in October 1990. This happened through non-violent initiatives and demonstrations. This period of change is referred to in German as ' (, "the turning point"). These events were closely linked to Soviet leader Mikhail Gorbachev's decision to abandon Soviet hegemony in Eastern Europe as well as the reformist movements that spread through Eastern Bloc countries. In addition to the Soviet Union's shift in foreign policy, the GDR's lack of competitiveness in the global market, as well as its sharply rising national debt, hastened the des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1986 East German General Election
General elections were held in East Germany on 8 June 1986. 500 deputies were elected to the Volkskammer, with all of them being candidates of the single-list National Front. 703 Front candidates were put forward, with 500 being elected and 203 becoming substitute deputies. At its first session on 16 June, the Volkskammer re-elected Willi Stoph as Chairman of the Council of Ministers, while Erich Honecker, General Secretary of the ruling Socialist Unity Party, was also re-elected Chairman of the State Council. This would be the last election held in East Germany before the Peaceful Revolution in 1989, three years into the Volkskammer's term. Results See also *List of Volkskammer members (9th election period) References ;General * Peter W. Sperlich. ''Oppression and Scarcity: The History and Institutional Structure of the Marxist-Leninist Government of East Germany and Some Perspectives on Life in a Socialist System''. Westport, CT: Greenwood Publishing Group. 2006. p.&n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free German Youth
The Free German Youth (german: Freie Deutsche Jugend; FDJ) is a youth movement in Germany. Formerly, it was the official youth movement of the German Democratic Republic (GDR) and the Socialist Unity Party of Germany. The organization was meant for young adults, both male and female, between the ages of 14 and 25 and comprised about 75% of the young adult population of former East Germany. In 1981–1982, this meant 2.3 million members. After joining the Thälmann Pioneers, which was for school children between ages 6 to 13, East German youths would usually join the FDJ. The FDJ was intended to be the "reliable assistant and fighting reserve of the Worker's Party", while Socialist Unity Party of Germany was a member of the National Front and had representatives in the People's Chamber. The political and ideological goal of the FDJ was to influence every aspect of life of young people in the GDR, distribute Marxist–Leninist teachings and promote communist behavior. Membe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radibor
Radibor (German) or Radwor (Upper Sorbian) is a municipality in Saxony in Germany. It is situated in Upper Lusatia about 10 km north of Bautzen, which is also the main city of the District of Bautzen to which Radibor belongs. Radibor was first mentioned in a written source in 1359. Its name is of Sorbian origin and generally means "place of the council". The municipality belongs to the central settlement area of the Sorbs. Following villages belong to the municipality of Radibor (names given in German/Upper Sorbian, followed by the number of inhabitants): *Bornitz/Boranecy, 125 inh. *Brohna/Bronjo, 73 inh. *Camina/Kamjenej, 119 inh. *Cölln/Chelno, 356 inh. *Droben/Droby, 89 inh. *Großbrösern/Wulki Přezdrěń, 46 inh. * Lippitsch/Lipič, 193 inh. *Lomske/Łomsk, 205 inh. *Luppa/Łupoj, 205 inh. *Luppedubrau/Łupjanska Dubrawka, 79 inh. *Luttowitz/Lutobč, 162 inh. *Merka/Měrkow, 139 inh. *Milkel/Minakał, 420 inh. *Milkwitz/Miłkecy, 113 inh. *Neu-Bornitz/Nowe Boranecy, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communism
Communism (from Latin la, communis, lit=common, universal, label=none) is a far-left sociopolitical, philosophical, and economic ideology and current within the socialist movement whose goal is the establishment of a communist society, a socioeconomic order centered around common ownership of the means of production, distribution, and exchange which allocates products to everyone in the society.: "One widespread distinction was that socialism socialised production only while communism socialised production and consumption." Communist society also involves the absence of private property, social classes, money, and the state. Communists often seek a voluntary state of self-governance, but disagree on the means to this end. This reflects a distinction between a more libertarian approach of communization, revolutionary spontaneity, and workers' self-management, and a more vanguardist or communist party-driven approach through the development of a constitutional socialist st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)
_1938.jpg)



