|
Juncus Milashanensis
''Juncus'' is a genus of monocotyledonous flowering plants, commonly known as rushes. It is the largest genus in the family Juncaceae, containing around 300 species. Description Rushes of the genus ''Juncus'' are herbaceous plants that superficially resemble grasses or sedges. They have historically received little attention from botanists; in his 1819 monograph, James Ebenezer Bicheno described the genus as "obscure and uninviting". The form of the flower differentiates rushes from grasses or sedges. The flowers of ''Juncus'' comprise five whorls of floral parts: three sepals, three petals (or, taken together, six tepals), two to six stamens (in two whorls) and a stigma with three lobes. The stems are round in cross-section, unlike those of sedges, which are typically somewhat triangular in cross-section. In ''Juncus'' section ''Juncotypus'' (formerly called ''Juncus'' subg. ''Genuini''), which contains some of the most widespread and familiar species, the leaves are reduced t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Juncus Conglomeratus
''Juncus conglomeratus'', the compact rush, is a perennial, herbaceous flowering plant species in the rush family Juncaceae. In the British Isles it is one of six rush species that can dominate lowland damp grasslands.The Lowland Grassland Management Handbook 2nd edition, A Crofts and R G Jefferson (eds) English Nature , 1999 
References Juncus, conglomeratus Plants described in 1753 Taxa named by Carl Linnaeus {{Poales-stub ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poaceae
Poaceae ( ), also called Gramineae ( ), is a large and nearly ubiquitous family of monocotyledonous flowering plants commonly known as grasses. It includes the cereal grasses, bamboos, the grasses of natural grassland and species cultivated in lawns and pasture. The latter are commonly referred to collectively as grass. With around 780 genera and around 12,000 species, the Poaceae is the fifth-largest plant family, following the Asteraceae, Orchidaceae, Fabaceae and Rubiaceae. The Poaceae are the most economically important plant family, including staple foods from domesticated cereal crops such as maize, wheat, rice, oats, barley, and millet for people and as feed for meat-producing animals. They provide, through direct human consumption, just over one-half (51%) of all dietary energy; rice provides 20%, wheat supplies 20%, maize (corn) 5.5%, and other grains 6%. Some members of the Poaceae are used as building materials ( bamboo, thatch, and straw); oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Montane
Montane ecosystems are found on the slopes of mountains. The alpine climate in these regions strongly affects the ecosystem because temperatures lapse rate, fall as elevation increases, causing the ecosystem to stratify. This stratification is a crucial factor in shaping plant community, biodiversity, metabolic processes and ecosystem dynamics for montane ecosystems. Dense montane forests are common at moderate elevations, due to moderate temperatures and high rainfall. At higher elevations, the climate is harsher, with lower temperatures and higher winds, preventing the growth of trees and causing the plant community to transition to montane grasslands and shrublands or alpine tundra. Due to the unique climate conditions of montane ecosystems, they contain increased numbers of endemic species. Montane ecosystems also exhibit variation in ecosystem services, which include carbon storage and water supply. Life zones As elevation increases, the alpine climate, climate becomes co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean (also known as the Antarctic Ocean), it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest continent, being about 40% larger than Europe, and has an area of . Most of Antarctica is covered by the Antarctic ice sheet, with an average thickness of . Antarctica is, on average, the coldest, driest, and windiest of the continents, and it has the highest average elevation. It is mainly a polar desert, with annual Climate of Antarctica#Precipitation, precipitation of over along the coast and far less inland. About 70% of the world's freshwater reserves are frozen in Antarctica, which, if melted, would raise global sea levels by almost . Antarctica holds the record for the Lowest temperature recorded on Earth, lowest measured temperature on Earth, . The coastal regions can reach temperatures over in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosmopolitan Distribution
In biogeography, a cosmopolitan distribution is the range of a taxon that extends across most or all of the surface of the Earth, in appropriate habitats; most cosmopolitan species are known to be highly adaptable to a range of climatic and environmental conditions, though this is not always so. Killer whales ( orcas) are among the most well-known cosmopolitan species on the planet, as they maintain several different resident and transient (migratory) populations in every major oceanic body on Earth, from the Arctic Circle to Antarctica and every coastal and open-water region in-between. Such a taxon (usually a species) is said to have a ''cosmopolitan'' distribution, or exhibit cosmopolitanism, as a species; another example, the rock dove (commonly referred to as a ' pigeon'), in addition to having been bred domestically for centuries, now occurs in most urban areas around the world. The extreme opposite of a cosmopolitan species is an endemic (native) species, or one foun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telopea (journal)
''Telopea'' is a fully open-access, online, peer-reviewed scientific journal that rapidly publishes original research on plant systematics Systematics is the study of the diversification of living forms, both past and present, and the relationships among living things through time. Relationships are visualized as evolutionary trees (synonyms: phylogenetic trees, phylogenies). Phy ..., with broad content that covers Australia and the Asia-Pacific region. The journal was established in 1975 and is published by the National Herbarium of New South Wales, Royal Botanic Gardens & Domain Trust. As from Volume 9, part 1, 2000, full text of papers is available electronically in pdf format. It is named for the genus ''Telopea'', commonly known as waratahs. The forerunner of ''Telopea'' was ''Contributions from the New South Wales National Herbarium'' which was first published in July 1939 as Volume 1(1). Publication was suspended between 1941 and resumed in 1948 with the publication ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bract
In botany, a bract is a modified or specialized leaf, associated with a reproductive structure such as a flower, inflorescence axis or cone scale. Bracts are usually different from foliage leaves in size, color, shape or texture. They also look different from the parts of the flower, such as the petals or sepals. A plant having bracts is referred to as bracteate or bracteolate, while one that lacks them is referred to as ebracteate or ebracteolate. Variants Some bracts are brightly coloured which aid in the attraction of pollinators, either together with the perianth or instead of it. Examples of this type of bract include those of '' Euphorbia pulcherrima'' (poinsettia) and '' Bougainvillea'': both of these have large colourful bracts surrounding much smaller, less colourful flowers. In grasses, each floret (flower) is enclosed in a pair of papery bracts, called the lemma (lower bract) and palea (upper bract), while each spikelet (group of florets) has a further pair o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stigma (botany)
The stigma (: stigmas or stigmata) is the receptive tip of a Gynoecium#Carpels, carpel, or of several fused carpels, in the gynoecium of a flower. Description The stigma, together with the Style (botany), style and ovary (botany), ovary (typically called the stigma-style-ovary system) comprises the pistil, which is part of the gynoecium or female reproductive organ of a plant. The stigma itself forms the distal portion of the style, or stylodia, and is composed of , the cells of which are receptive to pollen. These may be restricted to the apex of the style or, especially in wind pollinated species, cover a wide surface. The stigma receives pollen and it is on the stigma that the pollen grain germination, germinates. Often sticky, the stigma is adapted in various ways to catch and trap pollen with various hairs, flaps, or sculpturings. The pollen may be captured from the air (wind-borne pollen, anemophily), from visiting insects or other animals (Pollination syndrome#Biotic, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stamen
The stamen (: stamina or stamens) is a part consisting of the male reproductive organs of a flower. Collectively, the stamens form the androecium., p. 10 Morphology and terminology A stamen typically consists of a stalk called the filament and an anther which contains sporangium, microsporangia. Most commonly, anthers are two-lobed (each lobe is termed a locule) and are attached to the filament either at the base or in the middle area of the anther. The sterile (i.e. nonreproductive) tissue between the lobes is called the Connective (botany), connective, an extension of the filament containing conducting strands. It can be seen as an extension on the dorsal side of the anther. A pollen grain develops from a microspore in the microsporangium and contains the male gametophyte. The size of anthers differs greatly, from a tiny fraction of a millimeter in ''Wolfia'' spp up to five inches (13 centimeters) in ''Canna iridiflora'' and ''Strelitzia nicolai''. The stamens in a flower ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
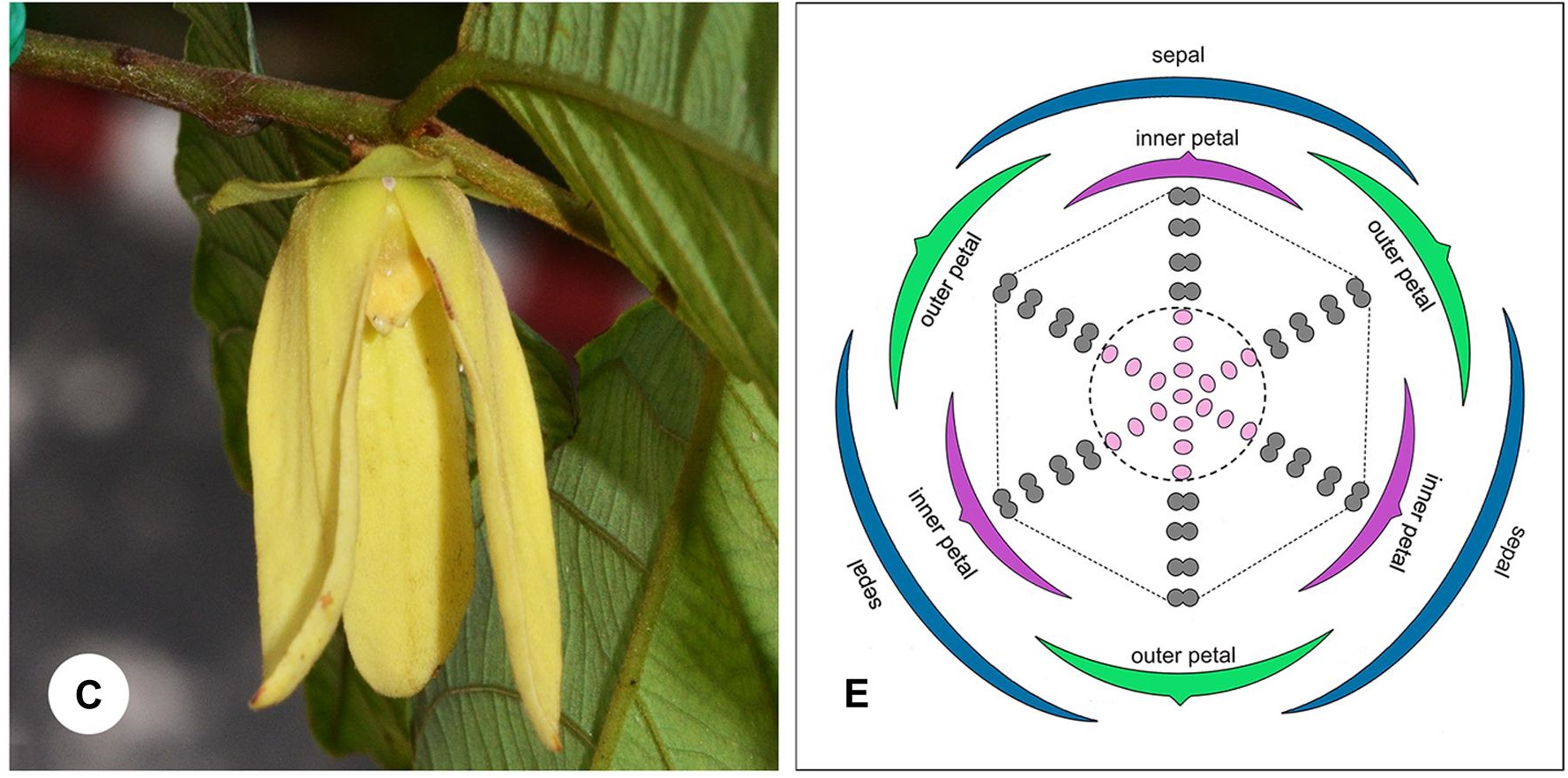
Whorl (botany)
In botany, a whorl or verticil is a whorled arrangement of Leaf, leaves, sepals, petals, stamens, or Gynoecium#Carpels, carpels that radiate from a single point and surround or wrap around the stem or stalk. A leaf whorl consists of at least three elements; a pair of opposite leaves is not called a whorl. For leaves to grow in whorls is fairly rare except in plant species with very short Plant stem, internodes and some other genera (''Galium'', ''Nerium'', ''Elodea'' etc.). Leaf whorls occur in some trees such as ''Brabejum stellatifolium'' and other species in the family Proteaceae (e.g., in the genus ''Banksia''). In plants such as these, crowded internodes within the leaf whorls alternate with long internodes between the whorls. The Morphology (biology), morphology of most flowers (called cyclic flowers) is based on four types of whorls: # The Sepal, calyx: zero or more whorls of sepals at the base # The Petal, corolla: zero or more whorls of petals above the calyx # The Stam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transactions Of The Linnean Society Of London
The Linnean Society of London is a learned society dedicated to the study and dissemination of information concerning natural history, evolution, and taxonomy. It possesses several important biological specimen, manuscript and literature collections, and publishes academic journals and books on plant and animal biology. The society also awards a number of prestigious medals and prizes. A product of the 18th-century enlightenment, the society is the oldest extant biological society in the world and is historically important as the venue for the first public presentation of the theory of evolution by natural selection on 1 July 1858. The patron of the society is Anne, Princess Royal. Honorary members include: King Charles III of the United Kingdom, Emeritus Emperor Akihito of Japan, King Carl XVI Gustaf of Sweden (both of the latter have active interests in natural history), and the eminent naturalist and broadcaster Sir David Attenborough. History Founding The Linnean ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Ebenezer Bicheno
James Ebenezer Bicheno (25 January 1785 – 25 February 1851) was a British author and colonial official. Bicheno was born in Newbury, Berkshire, the son of the Rev. James Bicheno, who was minister of the Baptist Church there. He was called to the bar in 1822 but seems to have spent most of his time until 1832 in writing and natural history pursuits, especially with the Linnean Society. He was elected a Fellow of the Royal Society in May, 1827. In 1832 he left London to live at Ty Maen, South Cornelly, Glamorgan, where he had been one of the founders of the Maesteg Ironworks in 1826. and where he was a friend of Lewis Weston Dillwyn. This investment ultimately failed and he needed to look for an income. During his years in south Wales Bicheno held conservative views at a time of considerable social and economic change. He was certainly anti- Chartist as his correspondence with the Marquis of Bute ( John Crichton-Stuart), the Lord Lieutenant of Glamorgan, clearly shows. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |