|
Junction Temperature
Junction temperature, short for transistor junction temperature, is the highest operating temperature of the actual semiconductor in an electronic device. In operation, it is higher than case temperature and the temperature of the part's exterior. The difference is equal to the amount of heat transferred from the junction to case multiplied by the junction-to-case thermal resistance. Microscopic effects Various physical properties of semiconductor materials are temperature dependent. These include the diffusion rate of dopant elements, carrier mobilities and the thermal production of charge carriers. At the low end, sensor diode noise can be reduced by cryogenic cooling. On the high end, the resulting increase in local power dissipation can lead to thermal runaway that may cause transient or permanent device failure. Maximum junction temperature calculation Maximum junction temperature (sometimes abbreviated TJMax) is specified in a part's datasheet and is used when calculating t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transistor
upright=1.4, gate (G), body (B), source (S) and drain (D) terminals. The gate is separated from the body by an insulating layer (pink). A transistor is a semiconductor device used to Electronic amplifier, amplify or electronic switch, switch electrical signals and electrical power, power. The transistor is one of the basic building blocks of modern electronics. It is composed of semiconductor material, usually with at least three terminals for connection to an electronic circuit. A voltage or current applied to one pair of the transistor's terminals controls the current through another pair of terminals. Because the controlled (output) power can be higher than the controlling (input) power, a transistor can amplify a signal. Some transistors are packaged individually, but many more are found embedded in integrated circuits. Austro-Hungarian physicist Julius Edgar Lilienfeld proposed the concept of a field-effect transistor in 1926, but it was not possible to actually constru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
JEDEC
The JEDEC Solid State Technology Association is an independent semiconductor engineering trade organization and standardization body headquartered in Arlington County, Virginia, United States. JEDEC has over 300 members, including some of the world's largest computer companies. Its scope and past activities includes standardization of part numbers, defining an electrostatic discharge (ESD) standard, and leadership in the lead-free manufacturing transition. The origin of JEDEC traces back to 1944, when RMA (subsequently renamed EIA) and NEMA established the Joint Electron Tube Engineering Council (JETEC) to coordinate vacuum tube type numberings. In 1958, with the advent of semiconductor technology, the joint JETEC-activity of EIA and NEMA was renamed into Joint Electron Device Engineering Council. NEMA discontinued its involvement in 1979. In the fall of 1999, JEDEC became a separate trade association under the current name, but maintained an EIA alliance, until EIA ceased o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
P–n Junction
A p–n junction is a boundary or interface between two types of semiconductor materials, p-type and n-type, inside a single crystal of semiconductor. The "p" (positive) side contains an excess of holes, while the "n" (negative) side contains an excess of electrons in the outer shells of the electrically neutral atoms there. This allows electrical current to pass through the junction only in one direction. The p-n junction is created by doping, for example by ion implantation, diffusion of dopants, or by epitaxy (growing a layer of crystal doped with one type of dopant on top of a layer of crystal doped with another type of dopant). If two separate pieces of material were used, this would introduce a grain boundary between the semiconductors that would severely inhibit its utility by scattering the electrons and holes. p–n junctions are elementary "building blocks" of semiconductor electronic devices such as diodes, transistors, solar cells, light-emitting diodes (LEDs) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
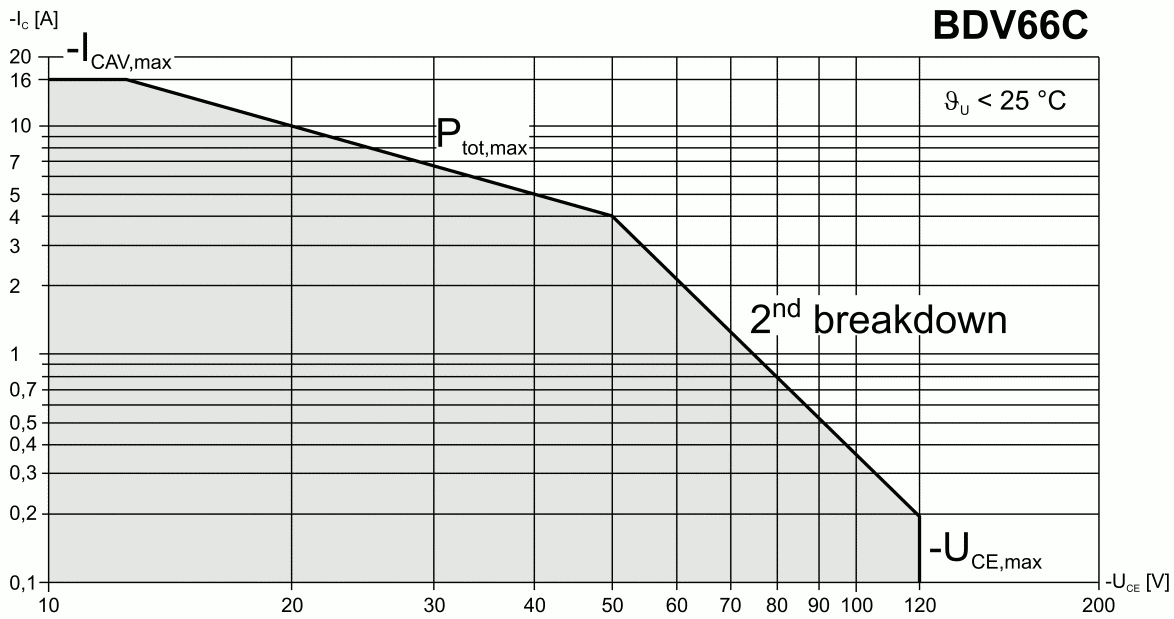
Safe Operating Area
For power semiconductor devices (such as BJT, MOSFET, thyristor or IGBT), the safe operating area (SOA) is defined as the voltage and current conditions over which the device can be expected to operate without self-damage. SOA is usually presented in transistor datasheets as a graph with VCE (collector-emitter voltage) on the abscissa and ICE (collector-emitter current) on the ordinate; the safe 'area' referring to the area under the curve. The SOA specification combines the various limitations of the device — maximum voltage, current, power, junction temperature, secondary breakdown — into one curve, allowing simplified design of protection circuitry. Often, in addition to the continuous rating, separate SOA curves are also plotted for short duration pulse conditions (1 ms pulse, 10 ms pulse, etc.). The safe operating area curve is a graphical representation of the power handling capability of the device under various conditions. The SOA curve takes into account the wire bon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Direct Current
Direct current (DC) is one-directional flow of electric charge. An electrochemical cell is a prime example of DC power. Direct current may flow through a conductor such as a wire, but can also flow through semiconductors, insulators, or even through a vacuum as in electron or ion beams. The electric current flows in a constant direction, distinguishing it from alternating current (AC). A term formerly used for this type of current was galvanic current. The abbreviations ''AC'' and ''DC'' are often used to mean simply ''alternating'' and ''direct'', as when they modify ''current'' or ''voltage''. Direct current may be converted from an alternating current supply by use of a rectifier, which contains electronic elements (usually) or electromechanical elements (historically) that allow current to flow only in one direction. Direct current may be converted into alternating current via an inverter. Direct current has many uses, from the charging of batteries to large power sup ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luminous Flux
In photometry, luminous flux or luminous power is the measure of the perceived power of light. It differs from radiant flux, the measure of the total power of electromagnetic radiation (including infrared, ultraviolet, and visible light), in that luminous flux is adjusted to reflect the varying sensitivity of the human eye to different wavelengths of light. Units The SI unit of luminous flux is the lumen (lm). One lumen is defined as the luminous flux of light produced by a light source that emits one candela of luminous intensity over a solid angle of one steradian. 1\ \text = 1\ \text \times 1\ \text In other systems of units, luminous flux may have units of power. Weighting The luminous flux accounts for the sensitivity of the eye by weighting the power at each wavelength with the luminosity function, which represents the eye's response to different wavelengths. The luminous flux is a weighted sum of the power at all wavelengths in the visible band. Light outside the vi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osram Opto Semiconductors GmbH
Osram Opto Semiconductors GmbH of Regensburg, Germany, was a wholly owned subsidiary of Osram GmbH, which was the world's second largest manufacturer of optoelectronic semiconductors after Nichia and followed in third place by Cree Inc. The company was founded in 1999 as a joint venture between Osram and Infineon Technologies. In 2021 Osram Opto Semiconductors was integrated to AMS-Osram International GmbH and is now part of the AMS Osram Group. The main products of the company are light-emitting diodes (LEDs) as well as high power laser diodes, infrared components and optical sensors. History When Siemens split off the semiconductor operations to form a separate legal entity, Osram had an opportunity to take over the LED division. On January 1, 1999 the takeover was completed with a 51% majority share. The Siemens subsidiary, Infineon, initially retained a 49% share. In the summer of 2001, Osram acquired all Infineon shares in the sale of opto-semiconductors. In 2003, the comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Illuminating Engineering Society Of North America
The Illuminating Engineering Society (IES), formerly the Illuminating Engineering Society of North America (IESNA), is an industry-backed, not-for-profit, learned society that was founded in New York City on January 10, 1906. The IES's stated mission is "to improve the lighted environment by bringing together those with lighting knowledge and by translating that knowledge into actions that benefit the public". The Society is still headquartered in New York City, with offices at 120 Wall Street. The IES is divided into approximately 100 local sections. Publications The IES is credited with over 100 publications on the subject of lighting such as ''The Lighting Handbook: 10th Edition''. Other publications, many of which are American National Standards Institute (ANSI) or ASHRAE standards, include recommended practices for a variety of specific lighting applications such as office, sports, and outdoor lighting, and lighting for healthcare facilities. The National Institute of Sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photometry (optics)
Photometry is the science of the measurement of light, in terms of its perceived brightness to the human eye. It is distinct from radiometry, which is the science of measurement of radiant energy (including light) in terms of absolute power. In modern photometry, the radiant power at each wavelength is weighted by a luminosity function that models human brightness sensitivity. Typically, this weighting function is the photopic sensitivity function, although the scotopic function or other functions may also be applied in the same way. Photometry and the eye The human eye is not equally sensitive to all wavelengths of visible light. Photometry attempts to account for this by weighting the measured power at each wavelength with a factor that represents how sensitive the eye is at that wavelength. The standardized model of the eye's response to light as a function of wavelength is given by the luminosity function. The eye has different responses as a function of wavelength when it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laser Diode
file:Laser diode chip.jpg, The laser diode chip removed and placed on the eye of a needle for scale A laser diode (LD, also injection laser diode or ILD, or diode laser) is a semiconductor device similar to a light-emitting diode in which a diode pumped directly with electrical current can create active laser medium, lasing conditions at the diode's p–n junction, junction. Driven by voltage, the doped p–n-transition allows for Carrier generation and recombination, recombination of an electron with a Electron hole, hole. Due to the drop of the electron from a higher energy level to a lower one, radiation, in the form of an emitted photon is generated. This is spontaneous emission. Stimulated emission can be produced when the process is continued and further generates light with the same phase, coherence and wavelength. The choice of the semiconductor material determines the wavelength of the emitted beam, which in today's laser diodes range from infra-red to the UV spectrum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Light-emitting Diode
A light-emitting diode (LED) is a semiconductor device that emits light when current flows through it. Electrons in the semiconductor recombine with electron holes, releasing energy in the form of photons. The color of the light (corresponding to the energy of the photons) is determined by the energy required for electrons to cross the band gap of the semiconductor. White light is obtained by using multiple semiconductors or a layer of light-emitting phosphor on the semiconductor device. Appearing as practical electronic components in 1962, the earliest LEDs emitted low-intensity infrared (IR) light. Infrared LEDs are used in remote-control circuits, such as those used with a wide variety of consumer electronics. The first visible-light LEDs were of low intensity and limited to red. Early LEDs were often used as indicator lamps, replacing small incandescent bulbs, and in seven-segment displays. Later developments produced LEDs available in visible, ultraviolet (UV) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
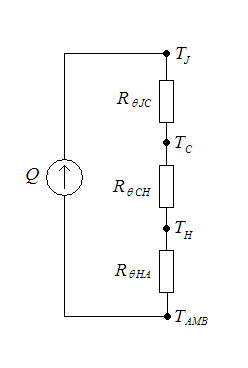
Thermal Resistance
Thermal resistance is a heat property and a measurement of a temperature difference by which an object or material resists a heat flow. Thermal resistance is the reciprocal of thermal conductance. * (Absolute) thermal resistance ''R'' in kelvins per watt (K/W) is a property of a particular component. For example, a characteristic of a heat sink. * Specific thermal resistance or thermal resistivity ''Rλ'' in kelvin–metres per watt (K⋅m/W), is a material constant. * Thermal insulance has the units square metre kelvin per watt (m2⋅K/W) in SI units or square foot degree Fahrenheit– hours per British thermal unit (ft2⋅°F⋅h/Btu) in imperial units. It is the thermal resistance of unit area of a material. In terms of insulation, it is measured by the R-value. Absolute thermal resistance Absolute thermal resistance is the temperature difference across a structure when a unit of heat energy flows through it in unit time. It is the reciprocal of thermal conductance. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)