|
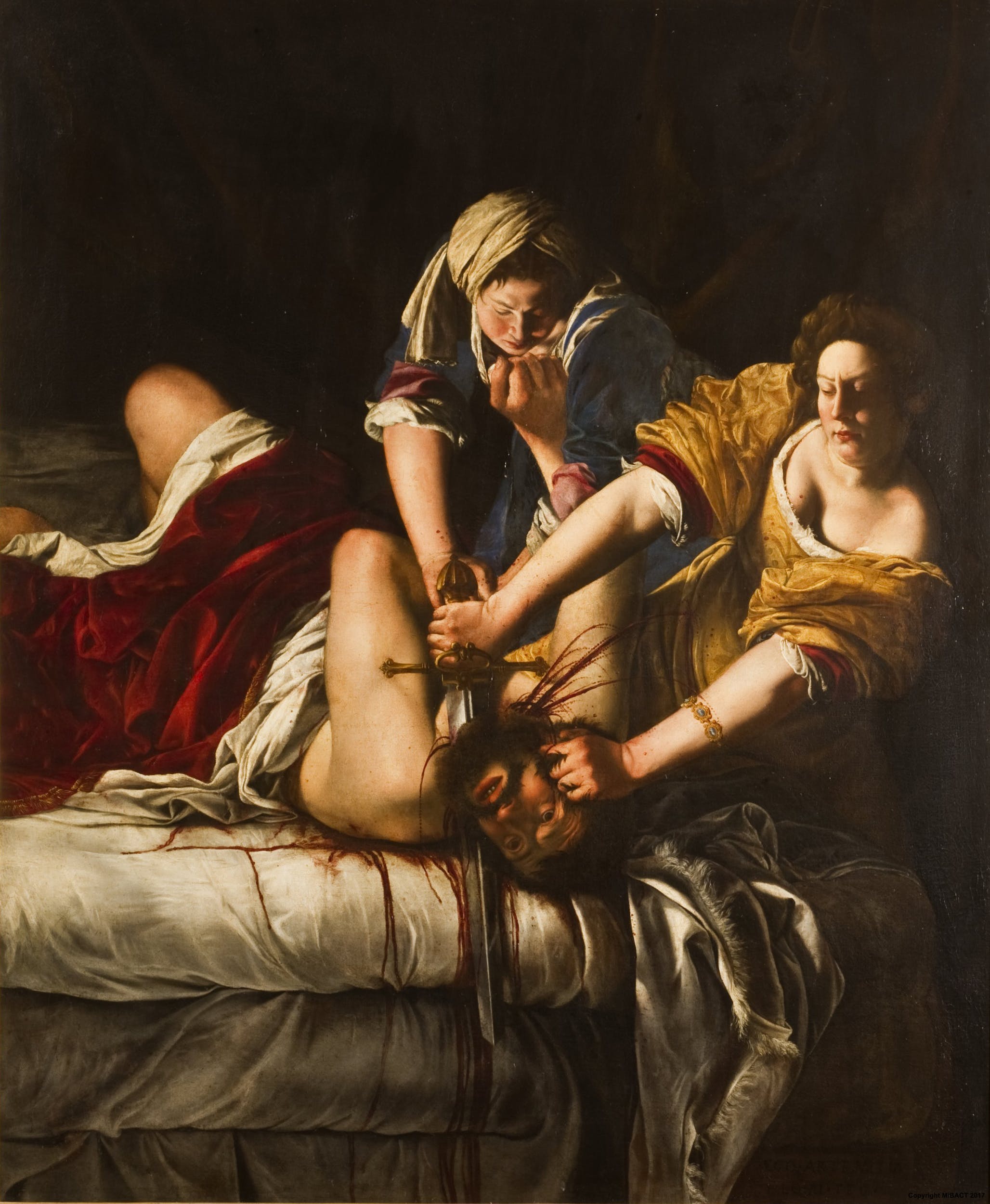
Judith Beheading Holofernes
The account of the beheading of Holofernes by Judith is given in the deuterocanonical ''Book of Judith'', and is the subject of many paintings and sculptures from the Renaissance and Baroque periods. In the story, Judith, a beautiful widow, is able to enter the tent of Holofernes because of his desire for her. Holofernes was an Assyrian general who was about to destroy Judith's home, the city of Bethulia. Overcome with drink, he passes out and is decapitated by Judith; his head is taken away in a basket (often depicted as being carried by an elderly female servant). Artists have mainly chosen one of two possible scenes (with or without the servant): the decapitation, with Holofernes supine on the bed, or the heroine holding or carrying the head, often assisted by her maid. In European art, Judith is very often accompanied by her maid at her shoulder, which helps to distinguish her from Salome, who also carries her victim's head on a silver charger (plate). However, a Northern tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Judit Decapitando A Holofernes, Por Artemisia Gentileschi (born 1930), Hungarian swimmer and Olympic champion
* Judit Varga (born ...
Judit is a feminine given name related to Judith. Notable people with the name include: *Judit Bar-Ilan (1958–2019), Israeli computer scientist *Judit Elek (born 1937), Hungarian film director and screenwriter *Judit Földing-Nagy (born 1965), Hungarian runner who specializes in the marathon * Judit Gófitz (1701–1723), Hungarian conjoined twins *Judit Kovács (born 1969), Hungarian retired high jumper *Judit Mascó (born 1969), Spanish model, television host and writer *Judit Polgár (born 1976), Hungarian chess Grandmaster *Judit Temes Judit Temes (; 10 October 1930 – 11 August 2013)"El ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clement Of Rome
Pope Clement I ( la, Clemens Romanus; Greek: grc, Κλήμης Ῥώμης, Klēmēs Rōmēs) ( – 99 AD) was bishop of Rome in the late first century AD. He is listed by Irenaeus and Tertullian as the bishop of Rome, holding office from 88 AD to his death in 99 AD. He is considered to be the first Apostolic Father of the Church, one of the three chief ones together with Polycarp and Ignatius of Antioch. Few details are known about Clement's life. Clement was said to have been consecrated by Peter the Apostle, and he is known to have been a leading member of the church in Rome in the late 1st century. Early church lists place him as the second or third bishop of Rome after Peter. The '' Liber Pontificalis'' states that Clement died in Greece in the third year of Emperor Trajan's reign, or 101 AD. Clement's only genuine extant writing is his letter to the church at Corinth (1 Clement) in response to a dispute in which certain presbyters of the Corinthian church had been deposed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jonathan Jones (journalist)
Jonathan Jones is a British art critic who has written for ''The Guardian ''The Guardian'' is a British daily newspaper. It was founded in 1821 as ''The Manchester Guardian'', and changed its name in 1959. Along with its sister papers ''The Observer'' and ''The Guardian Weekly'', ''The Guardian'' is part of the Gu ...'' since 1999. He has appeared in the BBC television series ''Private Life of a Masterpiece'' and in 2009 was a judge for the Turner Prize. He has also been a judge for the BP Portrait Award. Early life Jones was born in Wales, and brought up in North Wales. Both his parents were school teachers and the family visited Italy in the summer holidays which kindled his interest in art. He studied history at the University of Cambridge and, at one time, wanted to be a professional historian. Jones developed an interest in modern art while living in the United States, where his wife was an academic at Brown University. On his return to the United Kingdom he wrote f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lucas Cranach The Elder
Lucas Cranach the Elder (german: Lucas Cranach der Ältere ; – 16 October 1553) was a German Renaissance painter and printmaker in woodcut and engraving. He was court painter to the Electors of Saxony for most of his career, and is known for his portraits, both of German princes and those of the leaders of the Protestant Reformation, whose cause he embraced with enthusiasm. He was a close friend of Martin Luther. Cranach also painted religious subjects, first in the Catholic tradition, and later trying to find new ways of conveying Lutheran religious concerns in art. He continued throughout his career to paint nude subjects drawn from mythology and religion. Cranach had a large workshop and many of his works exist in different versions; his son Lucas Cranach the Younger and others continued to create versions of his father's works for decades after his death. He has been considered the most successful German artist of his time. Early life He was born at Kronach in uppe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sistine Chapel
The Sistine Chapel (; la, Sacellum Sixtinum; it, Cappella Sistina ) is a chapel in the Apostolic Palace, the official residence of the pope in Vatican City. Originally known as the ''Cappella Magna'' ('Great Chapel'), the chapel takes its name from Pope Sixtus IV, who had it built between 1473 and 1481. Since that time, the chapel has served as a place of both religious and functionary papal activity. Today, it is the site of the papal conclave, the process by which a new pope is selected. The fame of the Sistine Chapel lies mainly in the frescoes that decorate the interior, most particularly the Sistine Chapel ceiling and ''The Last Judgment (Michelangelo), The Last Judgment'', both by Michelangelo. During the reign of Sixtus IV, a team of Italian Renaissance painting, Renaissance painters that included Sandro Botticelli, Pietro Perugino, Pinturicchio, Domenico Ghirlandaio and Cosimo Rosselli, created a series of frescos depicting the ''Life of Moses'' and the ''Life of Christ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michelangelo
Michelangelo di Lodovico Buonarroti Simoni (; 6 March 1475 – 18 February 1564), known as Michelangelo (), was an Italian sculptor, painter, architect, and poet of the High Renaissance. Born in the Republic of Florence, his work was inspired by models from classical antiquity and had a lasting influence on Western art. Michelangelo's creative abilities and mastery in a range of artistic arenas define him as an archetypal Renaissance man, along with his rival and elder contemporary, Leonardo da Vinci. Given the sheer volume of surviving correspondence, sketches, and reminiscences, Michelangelo is one of the best-documented artists of the 16th century. He was lauded by contemporary biographers as the most accomplished artist of his era. Michelangelo achieved fame early; two of his best-known works, the ''Pietà'' and ''David'', were sculpted before the age of thirty. Although he did not consider himself a painter, Michelangelo created two of the most influential frescoes i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Judith And Holofernes (Mantegna)
Judith and Holofernes may refer to: * Judith beheading Holofernes, a Biblical account in the deuterocanonical ''Book of Judith'', often shown in art * ''Judith and Holofernes'' (Donatello), a c. 1460 sculpture by Donatello * ''Judith with the Head of Holofernes'' (Mantegna, Montreal), a painting of the 1490s by Andrea Mantegna * ''Judith with the Head of Holofernes'' (Mantegna, Washington), a c. 1495 painting by Andrea Mantegna * ''Judith with the Head of Holofernes'' (Mantegna, Dublin), a c. 1495 glue tempera on canvas painting in the grisaille style * ''Judith with the Head of Holofernes'' (Titian), a c. 1570 painting by Titian * ''Judith with the Head of Holofernes'' (Veronese), a c. 1575–1580 oil-on-canvas painting by Paolo Veronese * ''Judith and Holofernes'' (studio of Tintoretto), a c. 1577 oil painting on canvas by the studio of Jacopo Tintoretto * ''Judith Beheading Holofernes'' (Caravaggio), a 1598–1599 painting by Caravaggio * ''Judith with the Head of Hol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andrea Mantegna
Andrea Mantegna (, , ; September 13, 1506) was an Italian painter, a student of Roman archeology, and son-in-law of Jacopo Bellini. Like other artists of the time, Mantegna experimented with perspective, e.g. by lowering the horizon in order to create a sense of greater monumentality. His flinty, metallic landscapes and somewhat stony figures give evidence of a fundamentally sculptural approach to painting. He also led a workshop that was the leading producer of prints in Venice before 1500. Biography Youth and education Mantegna was born in Isola di Carturo, Venetian Republic close to Padua (now Italy), second son of a carpenter, Biagio. At the age of 11, he became the apprentice of Paduan painter Francesco Squarcione. Squarcione, whose original profession was tailoring, appears to have had a remarkable enthusiasm for ancient art, and a faculty for acting. Like his famous compatriot Petrarca, Squarcione was an ancient Rome enthusiast: he traveled in Italy, and perhaps a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sandro Botticelli
Alessandro di Mariano di Vanni Filipepi ( – May 17, 1510), known as Sandro Botticelli (, ), was an Italian Renaissance painting, Italian painter of the Early Renaissance. Botticelli's posthumous reputation suffered until the late 19th century, when he was rediscovered by the Pre-Raphaelite Brotherhood, Pre-Raphaelites who stimulated a reappraisal of his work. Since then, his paintings have been seen to represent the linear grace of late Italian Gothic and some Early Renaissance painting, even though they date from the latter half of the Italian Renaissance period. In addition to the mythological subjects for which he is best known today, Botticelli painted a wide range of religious subjects (including dozens of renditions of the ''Madonna and Child'', many in the round tondo (art), tondo shape) and also some portraits. His best-known works are ''The Birth of Venus'' and ''Primavera (painting), Primavera'', both in the Uffizi in Florence, which holds many of Botticelli’s w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mary (mother Of Jesus)
Mary; arc, ܡܪܝܡ, translit=Mariam; ar, مريم, translit=Maryam; grc, Μαρία, translit=María; la, Maria; cop, Ⲙⲁⲣⲓⲁ, translit=Maria was a first-century Jewish woman of Nazareth, the wife of Joseph and the mother of Jesus. She is a central figure of Christianity, venerated under various titles such as virgin or queen, many of them mentioned in the Litany of Loreto. The Eastern and Oriental Orthodox, Church of the East, Catholic, Anglican, and Lutheran churches believe that Mary, as mother of Jesus, is the Mother of God. Other Protestant views on Mary vary, with some holding her to have considerably lesser status. The New Testament of the Bible provides the earliest documented references to Mary by name, mainly in the canonical Gospels. She is described as a young virgin who was chosen by God to conceive Jesus through the Holy Spirit. After giving birth to Jesus in Bethlehem, she raised him in the city of Nazareth in Galilee, and was in Jerusal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gazette Des Beaux-Arts
The ''Gazette des Beaux-Arts'' was a French art review, founded in 1859 by Édouard Houssaye, with Charles Blanc as its first chief editor. Assia Visson Rubinstein was chief editorial secretary under the direction of George Wildenstein from 1936 until 1960. Her papers, which include all editions of the ''Gazette'' from this period, are intact at the Cantonal and University Library of Lausanne in Dorigny university campus, Dorigny. The ''Gazette'' was a world reference work on art history for nearly 100 years - one other editor in chief, from 1955 to 1987, was Jean Adhémar. It was bought in 1928 by the Wildenstein family, whose last representative was Daniel Wildenstein, its director from 1963 until his death in 2001. The magazine was published monthly and was headquartered in Paris. The review closed in 2002. List of directors *1859-1863: Édouard Houssaye *1863-1872: Émile Galichon *1872-1875: Maurice Cottier, Édouard André (art collector), Édouard André and Ernest Hosche ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medieval Commune
Medieval communes in the European Middle Ages had sworn allegiances of mutual defense (both physical defense and of traditional freedoms) among the citizens of a town or city. These took many forms and varied widely in organization and makeup. Communes are first recorded in the late 11th and early 12th centuries, thereafter becoming a widespread phenomenon. They had greater development in central-northern Italy, where they became city-states based on partial democracy. At the same time in Germany they became free cities, independent from local nobility. Etymology The English and French word "commune" ( it, comune) appears in Latin records in various forms. They come from Medieval Latin , plural form of (that which is common, community, state), substantive noun from (common). Ultimately, the Proto-Indo-European root is ''*mey-'' (to change, exchange). When autonomy was won through violent uprising and overthrow, the commune was often called (a conspiracy) ( it, cospirazione ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |








.jpg)