|
Juan Antonio Álvarez De Arenales
Juan Antonio Álvarez de Arenales ( Reinoso, Spain, June 13, 1770 – Moraya, Bolivia, December 4, 1831) was an Argentine general of Spanish origin (considered also a Bolivian for his activities in Bolivia) that fought in the war for the United Provinces of the Río de la Plata, Chile and Peru. Early life It is believed he was born in Spain in the town called Villa de Reinoso, in Castile, in 1770, although others say that he could have been born in Salta. Son of Francisco Alvarez Arenales and Maria Gonzalez. In 1784 he came with his family to Buenos Aires, where he was educated to follow an ecclesiastical career. Arenales chose a military career. Fights in Upper Peru After completing his studies he was sent to Upper Peru, where he was part of the Chuquisaca Revolution of May 25, 1809, first movement against Spanish rule held in the Viceroyalty of the Río de la Plata. With the victory in the Battle of La Florida, he received many wounds and almost lost his life, protected th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reinoso
Reinoso is a municipality and town located in the province of Burgos, Castile and León, Spain. According to the 2004 census A census (from Latin ''censere'', 'to assess') is the procedure of systematically acquiring, recording, and calculating population information about the members of a given Statistical population, population, usually displayed in the form of stati ... ( INE), the municipality has a population of 22 inhabitants. References Municipalities in the Province of Burgos {{Burgos-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Martin Miguel De Guemes
Martin may refer to: Places Antarctica * Martin Peninsula, Marie Byrd Land * Port Martin, Adelie Land * Point Martin, South Orkney Islands Europe * Martin, Croatia, a village * Martin, Slovakia, a city * Martín del Río, Aragón, Spain * Martín River, a tributary of the Ebro river in Spain * Martin (Val Poschiavo), Switzerland England * Martin, Hampshire * Martin, Kent * Martin, East Lindsey, Lincolnshire, a hamlet and former parish * Martin, North Kesteven, Lincolnshire, a village and parish * Martin Hussingtree, Worcestershire * Martin Mere, a lake in Lancashire ** WWT Martin Mere, a wetland nature reserve that includes the lake and surrounding areas North America Canada * Rural Municipality of Martin No. 122, Saskatchewan, Canada * Martin Islands, Nunavut, Canada United States * Martin, Florida * Martin, Georgia * Martin, Indiana * Martin, Kentucky * Martin, Louisiana * Martin, Michigan * Martin, Nebraska * Martin, North Dakota * Martin, Ohio * Martin, South Carolina * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
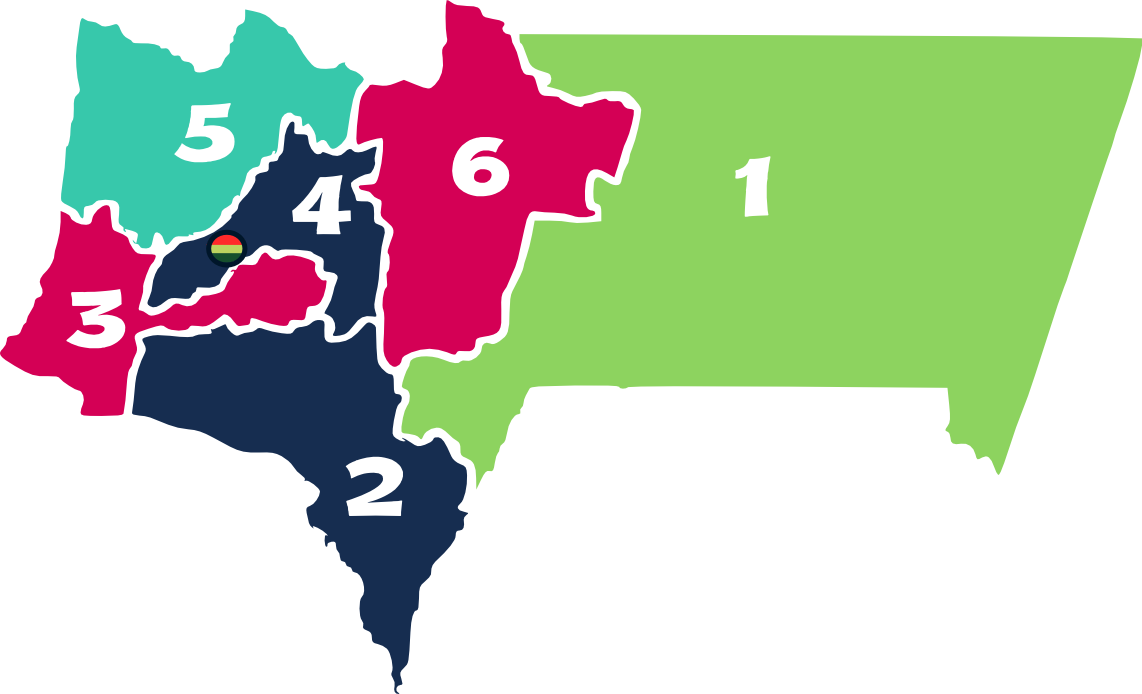
Tarija Department
Tarija () is a department in Bolivia. It is located in south-eastern Bolivia bordering with Argentina to the south and Paraguay to the east. According to the 2024 census, it has a population of 534,348 inhabitants. It has an area of . The city of Tarija is the capital of the department. Subdivisions The department is divided into five provinces and one autonomous region: # Gran Chaco Province (autonomous region) # Aniceto Arce Province # José María Avilés Province # Cercado Province # Eustaquio Méndez Province # Burdett O'Connor Province Notable places in Tarija include: * Villamontes in the department's oil-producing eastern scrubland. Villamontes has recorded the hottest temperature ever in Bolivia, , several times, most recently on 29 October 2010. * Bermejo, a border town adjoining Aguas Blancas, Argentina * Yacuiba, a border town with Argentina. The Department of Tarija is renowned for its mild, pleasant climate, and comprises one of the country's foremost ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pedro Antonio Olañeta
Pedro Antonio de Olañeta y Marquiegui (October 16, 1770 in Elgueta, Gipuzkoa, Spain – April 2, 1825 in Tumusla, Potosí Department, Bolivia) was a Royalist commander in the army of the Spanish Empire who fought against the South American insurgency led by Simón Bolívar. His support for Spanish absolutism and rebellion against the moderate Royalists created conflicts within the Royalist army that aided the rebels. After the defeat of the main Royalist armies, he continued the resistance, becoming one of the last Royalist commanders to hold out. Olañeta was the last Viceroy of the Río de la Plata. Early life Olañeta was born in a small mountain village in the Biscay province, Spain. His family actively engaged in the colonial trade, and several of his uncles and cousins established themselves in Chuquisaca, Tupiza and Cusco, creating a vast trade network. In 1789 he emigrated to South America with his uncle Pedro Marquegui, a merchant trading the route between Cádiz and L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
El Callao
Callao () is a Peruvian seaside city and Regions of Peru, region on the Pacific Ocean in the Lima metropolitan area. Callao is Peru's chief seaport and home to its main airport, Jorge Chávez International Airport. Callao municipality consists of the whole Callao region, which is also coterminous with the province of Callao. Founded in 1537 by the Spaniards, the city has a long naval history as one of the main ports in Latin America and the Pacific, as it was one of vital Spanish towns during the Spanish America, colonial era. Historic Centre of Callao, Central Callao is about west of the Historic Center of Lima. History El Callao was founded by Spanish colonists in 1537, just two years after Lima (1535). The origin of its name is unknown; both Amerindian (particularly Yunga language (Peru), Yunga, or Coastal Peruvian) and Spanish sources are credited, but it is certain that it was known by that name since 1550. Other sources point to the similarity with the Portuguese wor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bernardino Rivadavia
Bernardino de la Trinidad González Rivadavia (May 20, 1780 – September 2, 1845) was the first President of Argentina, then called the United Provinces of the Río de la Plata, from February 8, 1826 to June 27, 1827. He was educated at the Colegio Nacional de Buenos Aires, Royal College of San Carlos, but left without finishing his studies. During the British invasions of the River Plate, British Invasions he served as Third Lieutenant of the Galicia Volunteers. He participated in the Cabildo abierto del 22 de mayo de 1810, open Cabildo on May 22, 1810 voting for the deposition of the viceroy. He had a strong influence on the First Triumvirate (Argentina), First Triumvirate and shortly after he served as Minister of Government and Foreign Affairs of the Province of Buenos Aires. Although there was a General Congress intended to draft a constitution, the beginning of the Cisplatine War, War with Brazil led to the immediate establishment of the office of President of Argenti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huánuco
Huánuco (; ) is a city in central Peru. It had a population of 196,627 as of 2017 and in 2015 it had a population of 175,068. It is the capital of the Huánuco Region and the Huánuco District. It is the seat of the diocese of Huánuco. The metropolitan city of Huanuco is 170,000 hab (2011, urban pop, INEI). It has three districts, Huanuco (head), Amarilis, and Pillco Marca. In this city, the Higueras river meets the Huallaga river, one of the largest rivers in the country. History The city of Huánuco was founded by Spain, Spanish conquistador Gómez de Alvarado in 1539, in the Inca town of the Felipe Guaman Poma de Ayala#Biography, Yarowilca clan, Huánuco Pampa, Wanako. In 1541, the city was moved to its current location in the Pillco Valley. The indigenous chronicler Juan de Santa Cruz Pachacuti Yamqui Salcamaygua notes that during the Inca Empire, Pillco was a significant source of Aclla nuns for the capital city of Cusco, stating, "...there were maidens from all nati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diego O'Reilly
Diego is a Spanish masculine given name. The Portuguese equivalent is Diogo. The etymology of Diego is disputed, with two major origin hypotheses: ''Tiago'' and ''Didacus''. The name also has several patronymic derivations, listed below. Etymology ''Tiago'' hypothesis Diego has long been interpreted as variant of ''Tiago'' (also spelled as '' Thiago''), an abbreviation of ''Santiago'', from the older ''Sant Yago'' "Saint Jacob", in English known as Saint James or as ''San-Tiago'' (cf. ''San Diego''). This has been the standard interpretation of the name since at least the 19th century, as it was reported by Robert Southey in 1808 and by Apolinar Rato y Hevia (1891). The suggestion that this identification may be a folk etymology, i.e. that ''Diego'' (and ''Didacus''; see below) may be of another origin and only later identified with ''Jacobo'', is made by Buchholtz (1894), though this possibility is judged as improbable by the author. ''Didacus'' hypothesis In the la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Pasco
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force commitment. An engagement with only limited commitment between the forces and without decisive results is sometimes called a skirmish. The word "battle" can also be used infrequently to refer to an entire operational campaign, although this usage greatly diverges from its conventional or customary meaning. Generally, the word "battle" is used for such campaigns if referring to a protracted combat encounter in which either one or both of the combatants had the same methods, resources, and strategic objectives throughout the encounter. Some prominent examples of this would be the Battle of the Atlantic, Battle of Britain, and the Battle of France, all in World War II. Wars and military campaigns are guided by military strategy, whereas batt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pisco, Peru
Pisco () is a city located in the Department of Ica of Peru, the capital of the Pisco Province. The city is around 9 metres (28 feet) above sea level. Pisco was founded in 1640, close to the indigenous emplacement of the same name. Pisco originally prospered because of its nearby vineyards and became noted for its grape brandy or pisco which was exported from its port. Pisco has an estimated population of 104,656 (est. 2015). History Mid 16th Century: Pisco is Born The town of Santa Maria Magdalena, which was founded in 1572, had a port named Pisco, after the name of the valley in which it was located. This port became an important route for distribution of the liqueur throughout Peru. Demand for the product grew as sailors from around the world who called into the Port of Pisco created an important international trade link and further demand for the product. Over time, the town of Santa Maria Magdalena became simply known as ' Pisco' with the same name adopted for the grape ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Freedom Expedition Of Peru
The Liberating Expedition of Peru () was a naval and land military force created in 1820 by the government of Chile in continuation of the plan of the Argentine General José de San Martín to achieve the independence of Peru, and thus consolidate the independence of all former Spanish-American colonies. It was vital to defeat the Viceroyalty of Peru—the center of royalist power in South America—from where royalist expeditions were sent to reconquer the territories lost to the independence fighters. Following the independence of Chile, achieved at the Battle of Maipú, General San Martín determined to achieve the independence of Peru. Accordingly, on February 5, 1819, a treaty was signed between the new Chile, Republic of Chile and the United Provinces of the Río de la Plata. The treaty was to create an amphibious, naval, and land military expeditionary force promoted by the government of Chile, with the mission of making Peru independent of the Spanish Empire and consolida ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |