|
JrMan
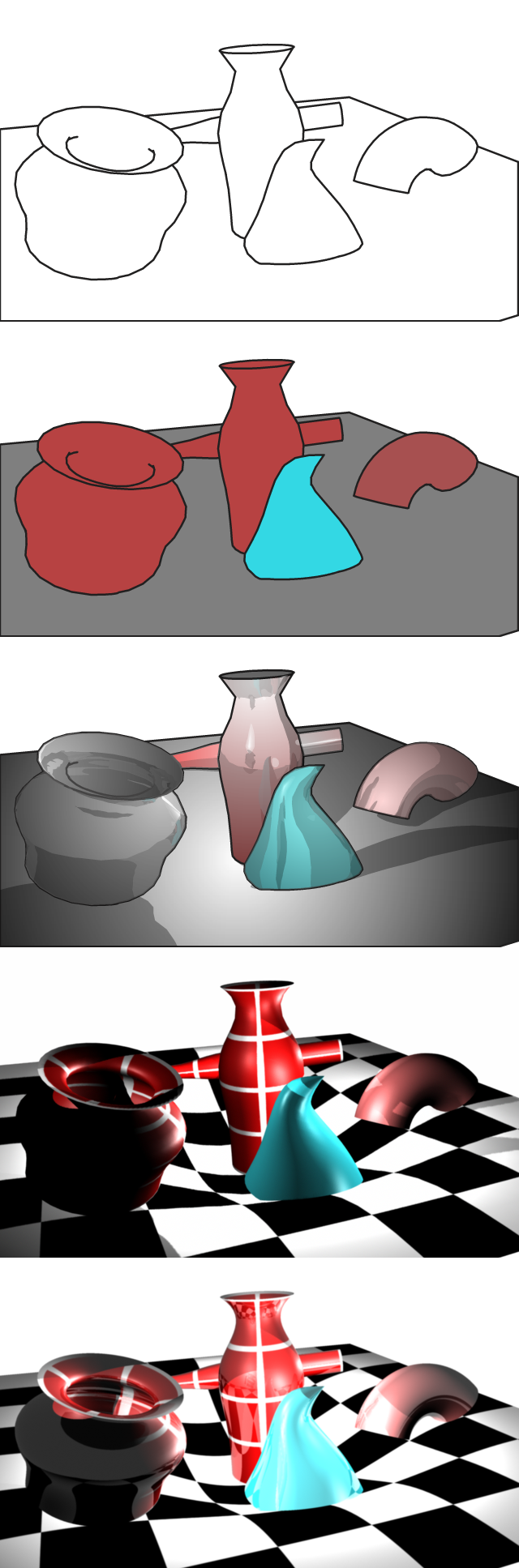
jrMan renderer is an open-source version of the Reyes rendering algorithm used by Pixar's PhotoRealistic RenderMan, implemented in Java by Gerardo Horvilleur, Jorge Vargas, Elmer Garduno and Alessandro Falappa. jrMan is available under the GNU General Public License (GPL) Current version Release 0.4 Features Shadows, texture mapping, surface shaders, light shaders, volume shaders, displacement shaders, all pixel filters, generate image to file (RGB & RGBA), delayed Read Archive. Supported primitives Sphere, Torus, Cone, Disk, Cylinder, Paraboloid, Hyperboloid, Points, Patch "bilinear" and "bicubic" (all basis & rational), Polygon, PointsPolygon, ObjectInstance, PatchMesh, NuPatch, Curves "linear" and "cubic" (also rational). Features not yet implemented Shading language compiler, Motion blur, Depth of field, Level of detail, CSG, Trim curves, Subdivision surfaces, General Polygons. See also *RenderMan Interface Specification The RenderMan Interface Spe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rendering (computer Graphics)
Rendering or image synthesis is the process of generating a photorealistic or non-photorealistic image from a 2D or 3D model by means of a computer program. The resulting image is referred to as the render. Multiple models can be defined in a ''scene file'' containing objects in a strictly defined language or data structure. The scene file contains geometry, viewpoint, texture, lighting, and shading information describing the virtual scene. The data contained in the scene file is then passed to a rendering program to be processed and output to a digital image or raster graphics image file. The term "rendering" is analogous to the concept of an artist's impression of a scene. The term "rendering" is also used to describe the process of calculating effects in a video editing program to produce the final video output. Rendering is one of the major sub-topics of 3D computer graphics, and in practice it is always connected to the others. It is the last major step in the gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cross-platform
In computing, cross-platform software (also called multi-platform software, platform-agnostic software, or platform-independent software) is computer software that is designed to work in several computing platforms. Some cross-platform software requires a separate build for each platform, but some can be directly run on any platform without special preparation, being written in an interpreted language or compiled to portable bytecode for which the interpreters or run-time packages are common or standard components of all supported platforms. For example, a cross-platform application may run on Microsoft Windows, Linux, and macOS. Cross-platform software may run on many platforms, or as few as two. Some frameworks for cross-platform development are Codename One, Kivy, Qt, Flutter, NativeScript, Xamarin, Phonegap, Ionic, and React Native. Platforms ''Platform'' can refer to the type of processor (CPU) or other hardware on which an operating system (OS) or application runs, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GNU General Public License
The GNU General Public License (GNU GPL or simply GPL) is a series of widely used free software licenses that guarantee end users the Four Freedoms (Free software), four freedoms to run, study, share, and modify the software. The license was the first copyleft for general use and was originally written by the founder of the Free Software Foundation (FSF), Richard Stallman, for the GNU Project. The license grants the recipients of a computer program the rights of the Free Software Definition. These GPL series are all copyleft licenses, which means that any derivative work must be distributed under the same or equivalent license terms. It is more restrictive than the GNU Lesser General Public License, Lesser General Public License and even further distinct from the more widely used permissive software licenses BSD licenses, BSD, MIT License, MIT, and Apache License, Apache. Historically, the GPL license family has been one of the most popular software licenses in the free and open ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Java (programming Language)
Java is a high-level, class-based, object-oriented programming language that is designed to have as few implementation dependencies as possible. It is a general-purpose programming language intended to let programmers ''write once, run anywhere'' ( WORA), meaning that compiled Java code can run on all platforms that support Java without the need to recompile. Java applications are typically compiled to bytecode that can run on any Java virtual machine (JVM) regardless of the underlying computer architecture. The syntax of Java is similar to C and C++, but has fewer low-level facilities than either of them. The Java runtime provides dynamic capabilities (such as reflection and runtime code modification) that are typically not available in traditional compiled languages. , Java was one of the most popular programming languages in use according to GitHub, particularly for client–server web applications, with a reported 9 million developers. Java was originally developed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Open-source Software
Open-source software (OSS) is computer software that is released under a license in which the copyright holder grants users the rights to use, study, change, and distribute the software and its source code to anyone and for any purpose. Open-source software may be developed in a collaborative public manner. Open-source software is a prominent example of open collaboration, meaning any capable user is able to participate online in development, making the number of possible contributors indefinite. The ability to examine the code facilitates public trust in the software. Open-source software development can bring in diverse perspectives beyond those of a single company. A 2008 report by the Standish Group stated that adoption of open-source software models has resulted in savings of about $60 billion per year for consumers. Open source code can be used for studying and allows capable end users to adapt software to their personal needs in a similar way user scripts an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reyes Rendering
Reyes rendering is a computer software architecture used in 3D computer graphics to render photo-realistic images. It was developed in the mid-1980s by Loren Carpenter and Robert L. Cook at Lucasfilm's Computer Graphics Research Group, which is now Pixar. It was first used in 1982 to render images for the ''Genesis effect'' sequence in the movie ''Star Trek II: The Wrath of Khan''. Pixar's RenderMan (software), RenderMan was one implementation of the Reyes algorithm, until its removal in 2016. According to the original paper describing the algorithm, the Reyes image rendering system is "An architecture for fast high-quality rendering of complex images." Reyes was proposed as a collection of algorithms and data processing systems. However, the terms "algorithm" and "architecture" have come to be used synonymously in this context and are used interchangeably in this article. Name ''Reyes'' is an acronym for ''Renders Everything You Ever Saw'' (the name is also a pun on Point Reye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pixar
Pixar Animation Studios (commonly known as Pixar () and stylized as P I X A R) is an American computer animation studio known for its critically and commercially successful computer animated feature films. It is based in Emeryville, California, United States. Since 2006, Pixar has been a subsidiary of Walt Disney Studios, which is another studio owned by The Walt Disney Company. Pixar started in 1979 as part of the Lucasfilm computer division, known as the Graphics Group, before its spin-off as a corporation in 1986, with funding from Apple co-founder Steve Jobs, who became its majority shareholder. Disney purchased Pixar in January 2006 at a valuation of $7.4+ billion by converting each share of Pixar stock to 2.3 shares of Disney stock. Pixar is best known for its feature films, technologically powered by RenderMan, the company's own implementation of the industry-standard RenderMan Interface Specification image-rendering API. The studio's mascot is Luxo Jr., a desk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PhotoRealistic RenderMan
Pixar RenderMan (formerly PhotoRealistic RenderMan) is proprietary photorealistic 3D rendering software produced by Pixar Animation Studios. Pixar uses RenderMan to render their in-house 3D animated movie productions and it is also available as a commercial product licensed to third parties. In 2015, a free non-commercial version of RenderMan became available. Name To speed up rendering, Pixar engineers performed experiments with parallel rendering computers using Transputer chips inside a Pixar Image Computer. The name comes from the nickname of a small circuit board (2.5 × 5 inches or 6.4 × 13 cm) containing one Transputer that engineer Jeff Mock could put in his pocket. During that time the Sony Walkman was very popular and Jeff Mock called his portable board Renderman, leading to the software name. Technology RenderMan defines cameras, geometry, materials, and lights using the RenderMan Interface Specification. This specification facilitates communication between 3D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Level Of Detail (computer Graphics)
In computer graphics, level of detail (LOD) refers to the complexity of a 3D model representation. LOD can be decreased as the model moves away from the viewer or according to other metrics such as object importance, viewpoint-relative speed or position. LOD techniques increase the efficiency of rendering by decreasing the workload on graphics pipeline stages, usually vertex transformations. The reduced visual quality of the model is often unnoticed because of the small effect on object appearance when distant or moving fast. Although most of the time LOD is applied to geometry detail only, the basic concept can be generalized. Recently, LOD techniques also included shader management to keep control of pixel complexity. A form of level of detail management has been applied to texture maps for years, under the name of mipmapping, also providing higher rendering quality. It is commonplace to say that "an object has been ''LOD-ed''" when the object is simplified by the underlying ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constructive Solid Geometry
Constructive solid geometry (CSG; formerly called computational binary solid geometry) is a technique used in solid modeling. Constructive solid geometry allows a modeler to create a complex surface or object by using Boolean operators to combine simpler objects,, potentially generating visually complex objects by combining a few primitive ones.. In 3D computer graphics and CAD, CSG is often used in procedural modeling. CSG can also be performed on polygonal meshes, and may or may not be procedural and/or parametric. Contrast CSG with polygon mesh modeling and box modeling. Workings The simplest solid objects used for the representation are called ''geometric primitives''. Typically they are the objects of simple shape: cuboids, cylinders, prisms, pyramids, spheres, cones. The set of allowable primitives is limited by each software package. Some software packages allow CSG on curved objects while other packages do not. An object is ''constructed'' from primitives by means ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subdivision Surface
In the field of 3D computer graphics, a subdivision surface (commonly shortened to SubD surface) is a curved surface represented by the specification of a coarser polygon mesh and produced by a recursive algorithmic method. The curved surface, the underlying ''inner mesh'', can be calculated from the coarse mesh, known as the ''control cage'' or ''outer mesh'', as the functional limit of an iterative process of subdividing each polygonal face into smaller faces that better approximate the final underlying curved surface. Less commonly, a simple algorithm is used to add geometry to a mesh by subdividing the faces into smaller ones without changing the overall shape or volume. Overview A subdivision surface algorithm is recursive in nature. The process starts with a base level polygonal mesh. A refinement scheme is then applied to this mesh. This process takes that mesh and subdivides it, creating new vertices and new faces. The positions of the new vertices in the mesh are compu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RenderMan Interface Specification
The RenderMan Interface Specification, or RISpec in short, is an open API developed by Pixar Animation Studios to describe three-dimensional scenes and turn them into digital photorealistic images. It includes the RenderMan Shading Language. As Pixar's technical specification for a standard communications protocol (or interface) between modeling programs and rendering programs capable of producing photorealistic-quality images, RISpec is a similar concept to PostScript but for describing 3D scenes rather than 2D page layouts. Thus, modelling programs which understand the RenderMan Interface protocol can send data to rendering software which implements the RenderMan Interface, without caring what rendering algorithms are utilized by the latter. The interface was first published in 1988 (version 3.0) and was designed to be sufficiently future proof to encompass advances in technology for a significant number of years. The current revision is 3.2.1, released in November 2005. Wha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




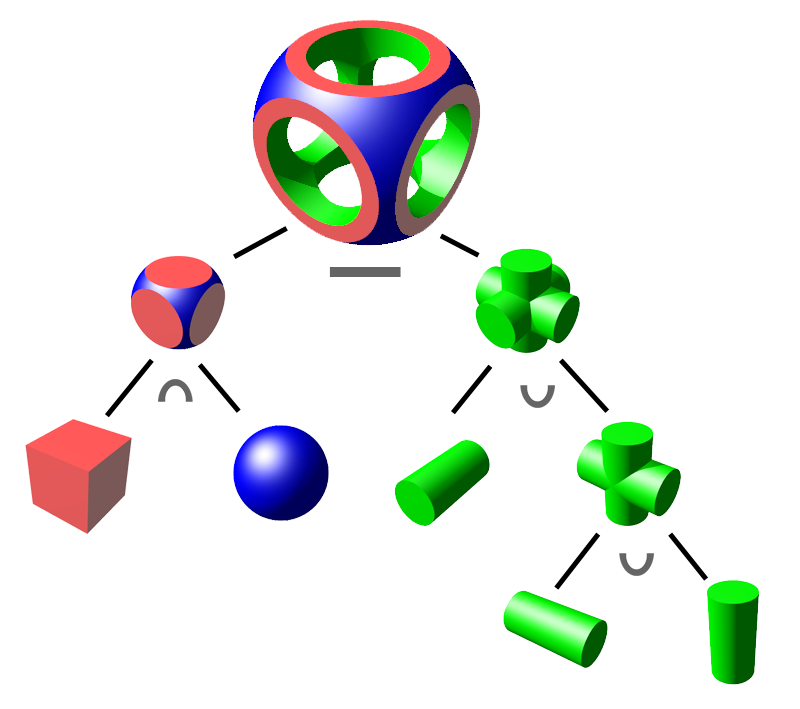
.png)