|
Jparc
J-PARC (Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex) is a high intensity proton accelerator facility. It is a joint project between KEK and JAEA and is located at the Tokai campus of JAEA. J-PARC aims for the frontier in materials and life sciences, and nuclear and particle physics. J-PARC uses high intensity proton beams to create high intensity secondary beams of neutrons, hadrons, and neutrinos. Components J-PARC includes three main parts: the 400 MeV proton linear accelerator, the 3 GeV Rapid Cycling Synchrotron (RCS), and the 30 GeV Main Ring (MR) synchrotron. There are two main experimental areas: the Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF), where the proton beam from the RCS is used to create beams of either neutrons or muons for further study, and the Hadron Facility (HD), where the beam from the main ring is used to create heavy hadronic particles such as pions and kaons. The main ring beam is also used to create neutrino beams for analysis at the Kam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proton
A proton is a stable subatomic particle, symbol , Hydron (chemistry), H+, or 1H+ with a positive electric charge of +1 ''e'' (elementary charge). Its mass is slightly less than the mass of a neutron and approximately times the mass of an electron (the proton-to-electron mass ratio). Protons and neutrons, each with a mass of approximately one Dalton (unit), dalton, are jointly referred to as ''nucleons'' (particles present in atomic nuclei). One or more protons are present in the Atomic nucleus, nucleus of every atom. They provide the attractive electrostatic central force which binds the atomic electrons. The number of protons in the nucleus is the defining property of an element, and is referred to as the atomic number (represented by the symbol ''Z''). Since each chemical element, element is identified by the number of protons in its nucleus, each element has its own atomic number, which determines the number of atomic electrons and consequently the chemical characteristi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Transmutation
Nuclear transmutation is the conversion of one chemical element or an isotope into another chemical element. Nuclear transmutation occurs in any process where the number of protons or neutrons in the nucleus of an atom is changed. A transmutation can be achieved either by nuclear reactions (in which an outside particle reacts with a nucleus) or by radioactive decay, where no outside cause is needed. Natural transmutation by stellar nucleosynthesis in the past created most of the heavier chemical elements in the known existing universe, and continues to take place to this day, creating the vast majority of the most common elements in the universe, including helium, oxygen and carbon. Most stars carry out transmutation through fusion reactions involving hydrogen and helium, while much larger stars are also capable of fusing heavier elements up to iron late in their evolution. Elements heavier than iron, such as gold or lead, are created through elemental transmutations that can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soft Matter
Soft matter or soft condensed matter is a type of matter that can be deformed or structurally altered by thermal or mechanical stress which is of similar magnitude to thermal fluctuations. The science of soft matter is a subfield of condensed matter physics. Soft materials include liquids, colloids, polymers, foams, gels, granular materials, liquid crystals, flesh, and a number of biomaterials. These materials share an important common feature in that predominant physical behaviors occur at an energy scale comparable with room temperature thermal energy (of order of kT), and that entropy is considered the dominant factor. At these temperatures, quantum aspects are generally unimportant. When soft materials interact favorably with surfaces, they become squashed without an external compressive force. Pierre-Gilles de Gennes, who has been called the "founding father of soft matter," received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1991 for discovering that methods developed f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reptation
A peculiarity of thermal motion of very long linear macromolecules in ''entangled'' polymer melts or concentrated polymer solutions is reptation. Derived from the word reptile, reptation suggests the movement of entangled polymer chains as being analogous to snakes slithering through one another. Pierre-Gilles de Gennes introduced (and named) the concept of reptation into polymer physics in 1971 to explain the dependence of the mobility of a macromolecule on its length. Reptation is used as a mechanism to explain viscous flow in an amorphous polymer. Sir Sam Edwards and Masao Doi later refined reptation theory. Similar phenomena also occur in proteins. Two closely related concepts are reptons and entanglement. A repton is a mobile point residing in the cells of a lattice, connected by bonds. Entanglement means the topological restriction of molecular motion by other chains. Theory and mechanism Reptation theory describes the effect of polymer chain entanglements on the rela ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
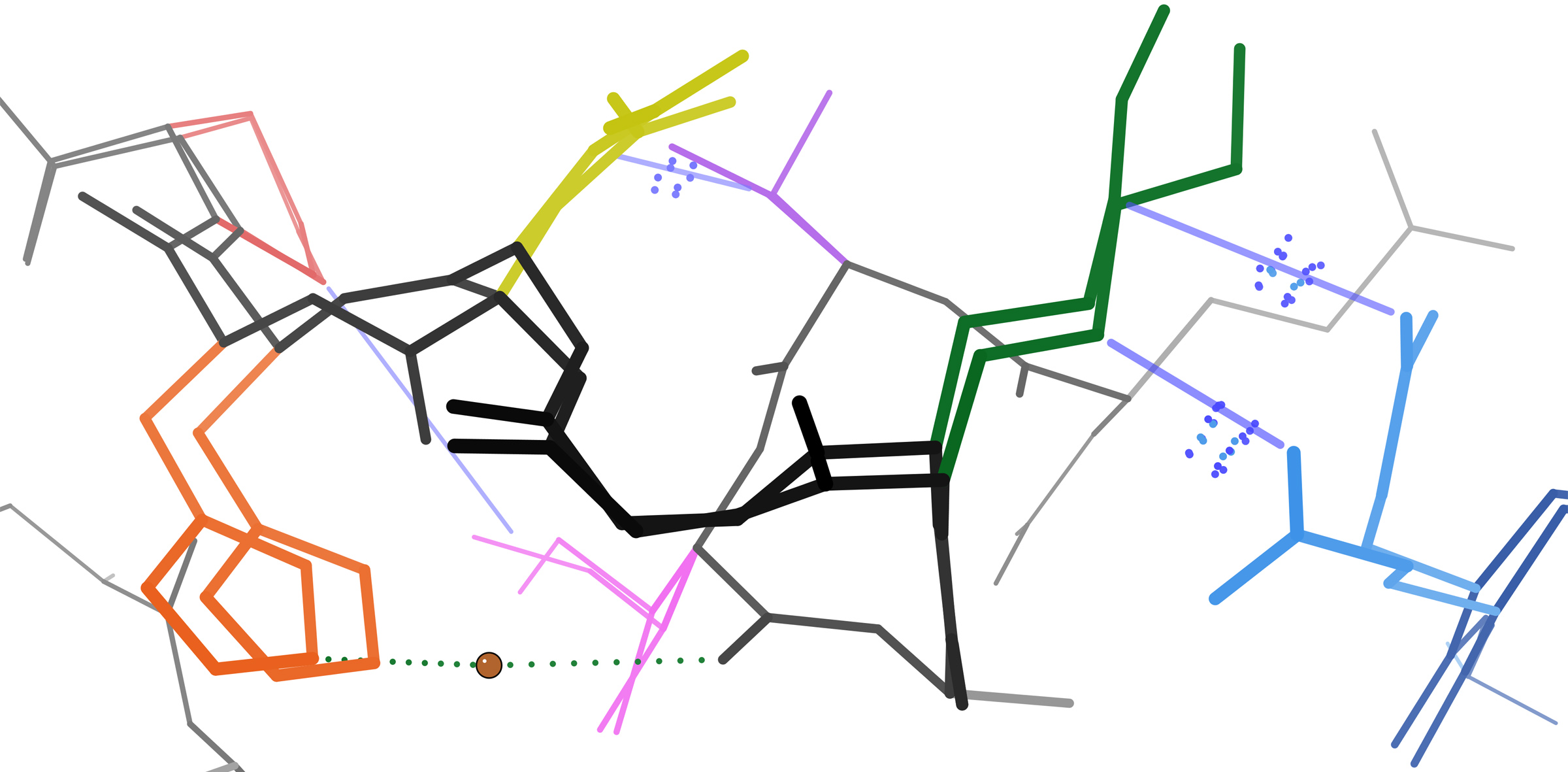
Protein Dynamics
In molecular biology, proteins are generally thought to adopt unique structures determined by their amino acid sequences. However, proteins are not strictly static objects, but rather populate ensembles of (sometimes similar) conformations. Transitions between these states occur on a variety of length scales (tenths of angstroms to nm) and time scales (ns to s), and have been linked to functionally relevant phenomena such as allosteric signaling and enzyme catalysis. The study of protein dynamics is most directly concerned with the transitions between these states, but can also involve the nature and equilibrium populations of the states themselves. These two perspectives— kinetics and thermodynamics, respectively—can be conceptually synthesized in an " energy landscape" paradigm: highly populated states and the kinetics of transitions between them can be described by the depths of energy wells and the heights of energy barriers, respectively. Local flexibility: atoms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polymer Physics
Polymer physics is the field of physics that studies polymers, their fluctuations, mechanical properties, as well as the kinetics of reactions involving degradation of polymers and polymerisation of monomers.P. Flory, ''Principles of Polymer Chemistry'', Cornell University Press, 1953. .Pierre Gilles De Gennes, ''Scaling Concepts in Polymer Physics'' CORNELL UNIVERSITY PRESS Ithaca and London, 1979M. Doi and S. F. Edwards, ''The Theory of Polymer Dynamics'' Oxford University Inc NY, 1986 While it focuses on the perspective of condensed matter physics, polymer physics was originally a branch of statistical physics. Polymer physics and polymer chemistry are also related to the field of polymer science, which is considered to be the applicative part of polymers. Polymers are large molecules and thus are very complicated for solving using a deterministic method. Yet, statistical approaches can yield results and are often pertinent, since large polymers (i.e., polymers with many ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
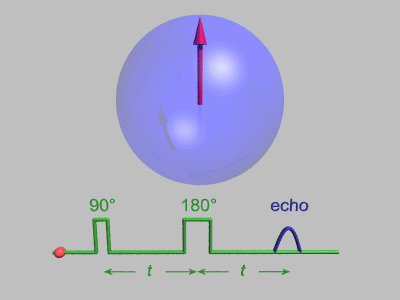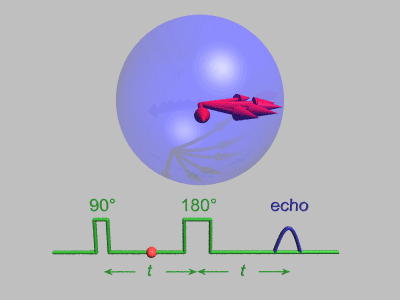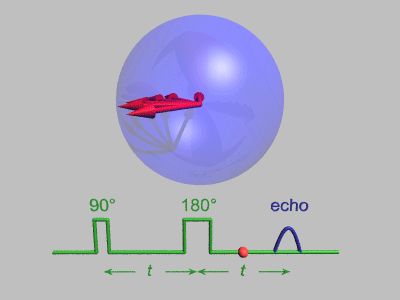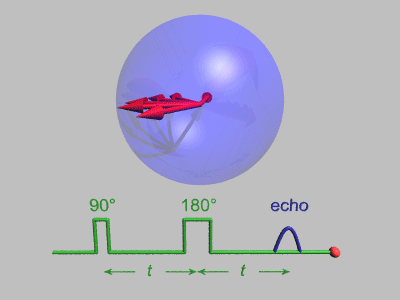
Neutron Spin Echo
Neutron spin echo spectroscopy is an inelastic neutron scattering technique invented by Ferenc Mezei in the 1970s and developed in collaboration with John Hayter. In recognition of his work and in other areas, Mezei was awarded the first Walter Haelg Prize in 1999. In magnetic resonance, a spin echo is the refocusing of spin magnetisation by a pulse of resonant electromagnetic radiation. The spin echo spectrometer possesses an extremely high energy resolution (roughly one part in 100,000). Additionally, it measures the density-density correlation (or intermediate scattering function) F(Q,t) as a function of momentum transfer Q and time. Other neutron scattering techniques measure the dynamic structure factor S(Q,ω), which can be converted to F(Q,t) by a Fourier transform, which may be difficult in practice. For weak inelastic features S(Q,ω) is better suited, however, for (slow) relaxations the natural representation is given by F(Q,t). Because of its extraordina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neutron Diffraction
Neutron diffraction or elastic neutron scattering is the application of neutron scattering to the determination of the atomic and/or magnetic structure of a material. A sample to be examined is placed in a beam of Neutron temperature, thermal or cold neutron radiation, neutrons to obtain a diffraction pattern that provides information of the structure of the material. The technique is similar to X-ray diffraction but due to their different scattering properties, neutrons and X-rays provide complementary information: X-Rays are suited for superficial analysis, strong x-rays from synchrotron radiation are suited for shallow depths or thin specimens, while neutrons having high penetration depth are suited for bulk samples.Measurement of residual stress in materials using neutrons IAEA, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inelastic Neutron Scattering
Neutron scattering, the irregular dispersal of free neutrons by matter, can refer to either the naturally occurring physical process itself or to the man-made experimental techniques that use the natural process for investigating materials. The natural/physical phenomenon is of elemental importance in nuclear engineering and the nuclear sciences. Regarding the experimental technique, understanding and manipulating neutron scattering is fundamental to the applications used in crystallography, physics, physical chemistry, biophysics, and materials research. Neutron scattering is practiced at research reactors and spallation neutron sources that provide neutron radiation of varying intensities. Neutron diffraction (elastic scattering) techniques are used for analyzing structures; where inelastic neutron scattering is used in studying atomic vibrations and other excitations. Scattering of fast neutrons "Fast neutrons" (see neutron temperature) have a kinetic energy above 1& ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Spallation Source
The European Spallation Source ERIC (ESS) is a multi-disciplinary research facility currently under construction in Lund, Sweden. Its Data Management and Software Centre (DMSC) is co-located with DTU in Lyngby, Denmark. Its 13 European contributor countries are partners in the construction and operation of the ESS. The ESS is scheduled to begin its scientific user program in 2027, when the construction phase is set to be completed. The ESS will assist scientists in the tasks of observing and understanding basic atomic structures and forces, which are more challenging to do with other neutron sources in terms of lengths and time scales. The research facility is located near the MAX IV Laboratory, which conducts synchrotron radiation research. The construction of the facility began in the summer of 2014 and the first science results are planned for 2027. During operation, the ESS will use nuclear spallation, a process in which neutrons are liberated from heavy elements by hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
China Spallation Neutron Source
The China Spallation Neutron Source is an accelerator-based neutron source, operated by the Institute of High Energy Physics, under construction at Dongguan in Guangdong province - the first major scientific facility in south China. The project was approved by Chinese central government in 2005. Construction began 20 October 2011, with commissioning planned for 2016, and operation in 2018. The source contains a proton synchrotron fed by a linear accelerator; short (<500ns) pulses of 1.6 GeV protons are extracted from the synchrotron 25 times a second; these pulses strike a tungsten-metal target (cooled with heavy water) to produce energetic neutrons, which are reduced to scientifically interesting energies by a variety of moderators. The intended budget for the project is 1.5 billion CNY;http://accelconf.web.cern.ch/AccelConf/a07/PAPERS/WEZMA02.PDF this limits the initial power of the machine to about 120 kW, but it has been designed so that its power can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biological Small-angle Scattering
Biological small-angle scattering is a small-angle scattering method for structure analysis of biological materials. Small-angle scattering is used to study the structure of a variety of objects such as solutions of biological macromolecules, nanocomposites, alloys, and synthetic polymers. Small-angle X-ray scattering ( SAXS) and small-angle neutron scattering ( SANS) are the two complementary techniques known jointly as small-angle scattering (SAS). SAS is an analogous method to X-ray and neutron diffraction, wide angle X-ray scattering, as well as to static light scattering. In contrast to other X-ray and neutron scattering methods, SAS yields information on the sizes and shapes of both crystalline and non-crystalline particles. When used to study biological materials, which are very often in aqueous solution, the scattering pattern is orientation averaged. SAS patterns are collected at small angles of a few degrees. SAS is capable of delivering structural information in the r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |