|
Joseph Ephraim Casely Hayford
Joseph Ephraim Casely Hayford, (29 September 1866 – 11 August 1930), also known as Ekra-Agyeman, was a prominent Fante Ghanaian people, Gold Coast journalist, editor, author, lawyer, educator, and politician who supported pan-Africanism, pan-African nationalism. His 1911 novel ''Ethiopia Unbound'' is one of the earliest novels published in English by an African. Biography Joseph Ephraim Casely Hayford was born on 29 September 1866 in Cape Coast, in the British Gold Coast (British colony), Gold Coast colony, now Ghana. His family, part of the Fante people, Fante Anona clan and descendants of a dynasty of ''omanhenes'' and ''Akan Chieftaincy#Okyeame, okyeames'', was part of the Fante coastal elite. His father, Joseph de Graft Hayford (1840–1919), was educated and ordained as a minister in the Methodist church, and was a prominent figure in Ghanaian politics. His mother was from the Brew family, descended from the 18th-century Irish trader Richard Brew and his African concubin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Order Of The British Empire
The Most Excellent Order of the British Empire is a British order of chivalry, rewarding contributions to the arts and sciences, work with charitable and welfare organisations, and public service outside the civil service. It was established on 4 June 1917 by King George V and comprises five classes across both civil and military divisions, the most senior two of which make the recipient either a knight if male or dame if female. There is also the related British Empire Medal, whose recipients are affiliated with, but not members of, the order. Recommendations for appointments to the Order of the British Empire were originally made on the nomination of the United Kingdom, the self-governing Dominions of the Empire (later Commonwealth) and the Viceroy of India. Nominations continue today from Commonwealth countries that participate in recommending British honours. Most Commonwealth countries ceased recommendations for appointments to the Order of the British Empire when they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph De Graft Hayford
Joseph de Graft Hayford (1840–1919) was a Wesleyan Methodist minister who was a prominent figure in Fante politics and society in the Gold Coast. He was one of the founders of the Fante Confederation of 1867 and one of the first political detainees in Ghanaian history. Background Rev. Joseph de Graft Hayford has been described as "one of the greatest politicians of his day, and the most active member of the Fanti Confederacy of 1867". When the Confederacy was declared illegal, he was one of the four leaders to be arrested on a charge of conspiracy, the others being James Hutton Brew, James F. Amissah and George Kunto Blankson. Family Of the Anona clan of Cape Coast, he was the son of Rev. James Hayford and Elizabeth de Graft. He was the husband of Mary Ewuraba Brew (daughter of the prominent Gold Coast trader Samuel Collins Brew and Adjuah Esson) and his children were: Rev. Josiah Hayford, Isaac Hayford, Ibinijah Hayford, Rev. Dr Ernest James Hayford Ernest James Hayford, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accra
Accra (; tw, Nkran; dag, Ankara; gaa, Ga or ''Gaga'') is the capital and largest city of Ghana, located on the southern coast at the Gulf of Guinea, which is part of the Atlantic Ocean. As of 2021 census, the Accra Metropolitan District, , had a population of 284,124 inhabitants, and the larger Greater Accra Region, , had a population of 5,455,692 inhabitants. In common usage, the name "Accra" often refers to the territory of the Accra Metropolitan District as it existed before 2008, when it covered .Sum of the land areas of Accra Metropolitan District, Ablekuma Central Municipal District, Ablekuma North Municipal District, Ablekuma West Municipal District, Ayawaso Central Municipal District, Ayawaso East Municipal District, Ayawaso North Municipal District, Ayawaso West Municipal District, Korle Klottey Municipal District, Krowor Municipal District, La Dadekotopon Municipal District, Ledzokuku Municipal District, and Okaikoi North Municipal District, as per the 2021 ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
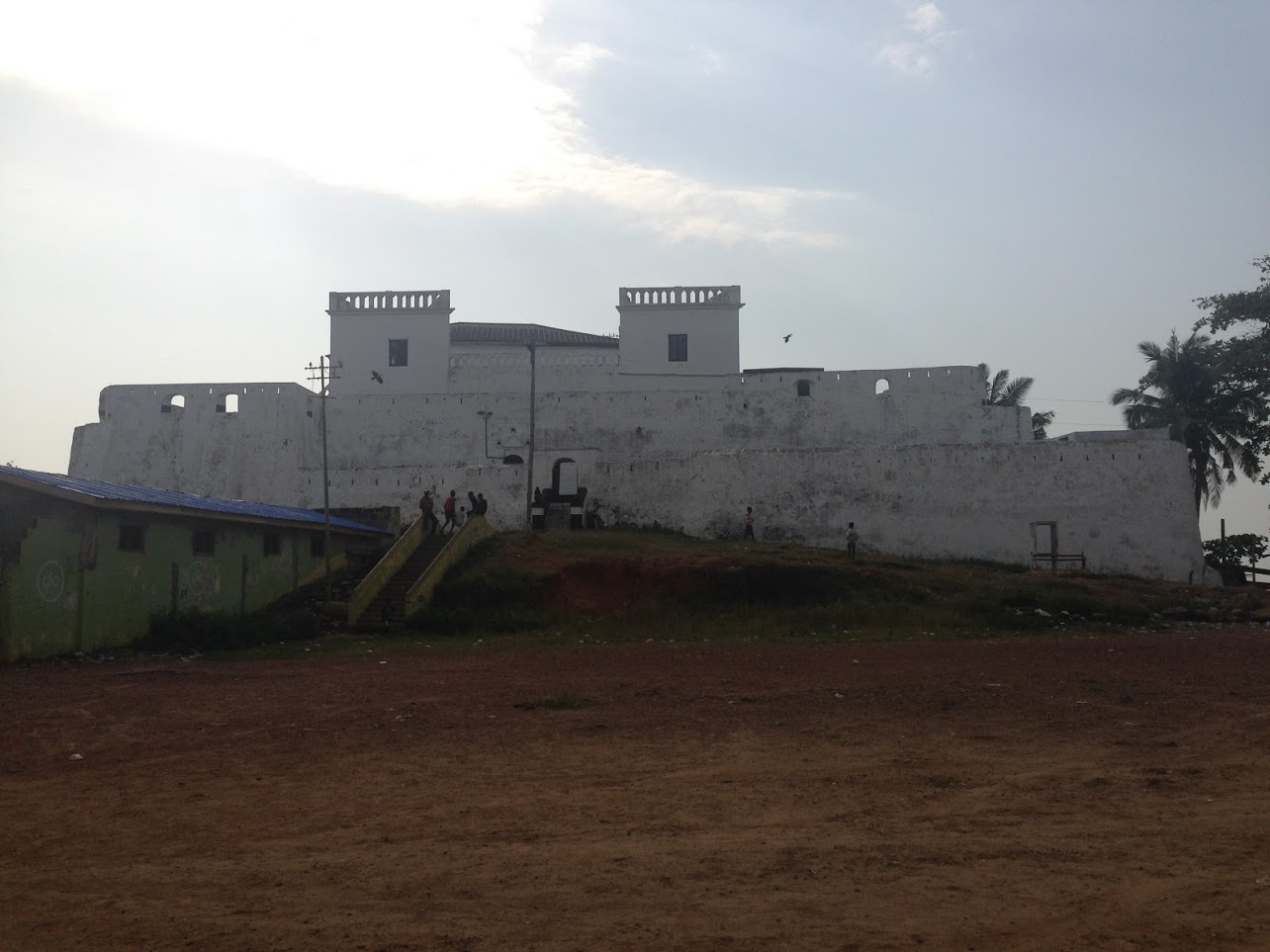
Sekondi
Sekondi-Takoradi is a city in Ghana comprising the twin cities of Sekondi and Takoradi. It is the capital of Sekondi – Takoradi Metropolitan Assembly and the Western Region of Ghana. Sekondi-Takoradi is the region's largest city and an industrial and commercial centre, with a population of 445,205 people (2012). The chief industries in Sekondi-Takoradi are timber, cocoa processing, plywood, shipbuilding, its harbour and railway repair, and recently, sweet crude oil and crude oil. The fundamental job in Sekondi-Takoradi is fishing. Sekondi-Takoradi lies on the main railway lines to Kumasi and Accra. History Sekondi, an older and larger Ahanta town, was the site of Dutch Fort Orange (1642) and English Fort Sekondi (1682). It prospered from a railroad built in 1903 to hinterland mineral and timber resources. Takoradi, also an Ahanta town, was the site of Dutch Fort Witsen (1665) and has an important deepwater seaport, Ghana's first, built in 1928. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Axim
Axim is a coastal town and the capital of Nzema East Municipal district, a district in Western Region of South Ghana. Axim lies 64 kilometers west of the port city of Sekondi-Takoradi in the Western Region, west of Cape Three Points. Axim has a 2013 settlement population of 27,719 people. History This area was occupied by the Nzema people. The Portuguese arrived by the early 16th century as traders. They built a prominent seaside fort, Fort Santo Antonio, in 1515. They exported some Africans as slaves to Europe and the Americas. Between 1642 and 1872, the fort was expanded and altered by the Dutch, who "ruled" during that period. The fort, now property of Ghana, is open to the public. Off-shore are some picturesque islands, including one with a lighthouse. Axim structure The town of Axim is divided into two parts: Upper Axim and Lower Axim. Fort Santo Antonio lies roughly on the division between the two parts, but closest to the centre of Upper Axim, the original European ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Called To The Bar
The call to the bar is a legal term of art in most common law jurisdictions where persons must be qualified to be allowed to argue in court on behalf of another party and are then said to have been "called to the bar" or to have received "call to the bar". "The bar" is now used as a collective noun for barristers, but literally referred to the wooden barrier in old courtrooms, which separated the often crowded public area at the rear from the space near the judges reserved for those having business with the court. Barristers would sit or stand immediately behind it, facing the judge, and could use it as a table for their briefs. Like many other common law terms, the term originated in England in the Middle Ages, and the ''call to the bar'' refers to the summons issued to one found fit to speak at the "bar" of the royal courts. In time, English judges allowed only legally qualified men to address them on the law and later delegated the qualification and admission of barristers t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
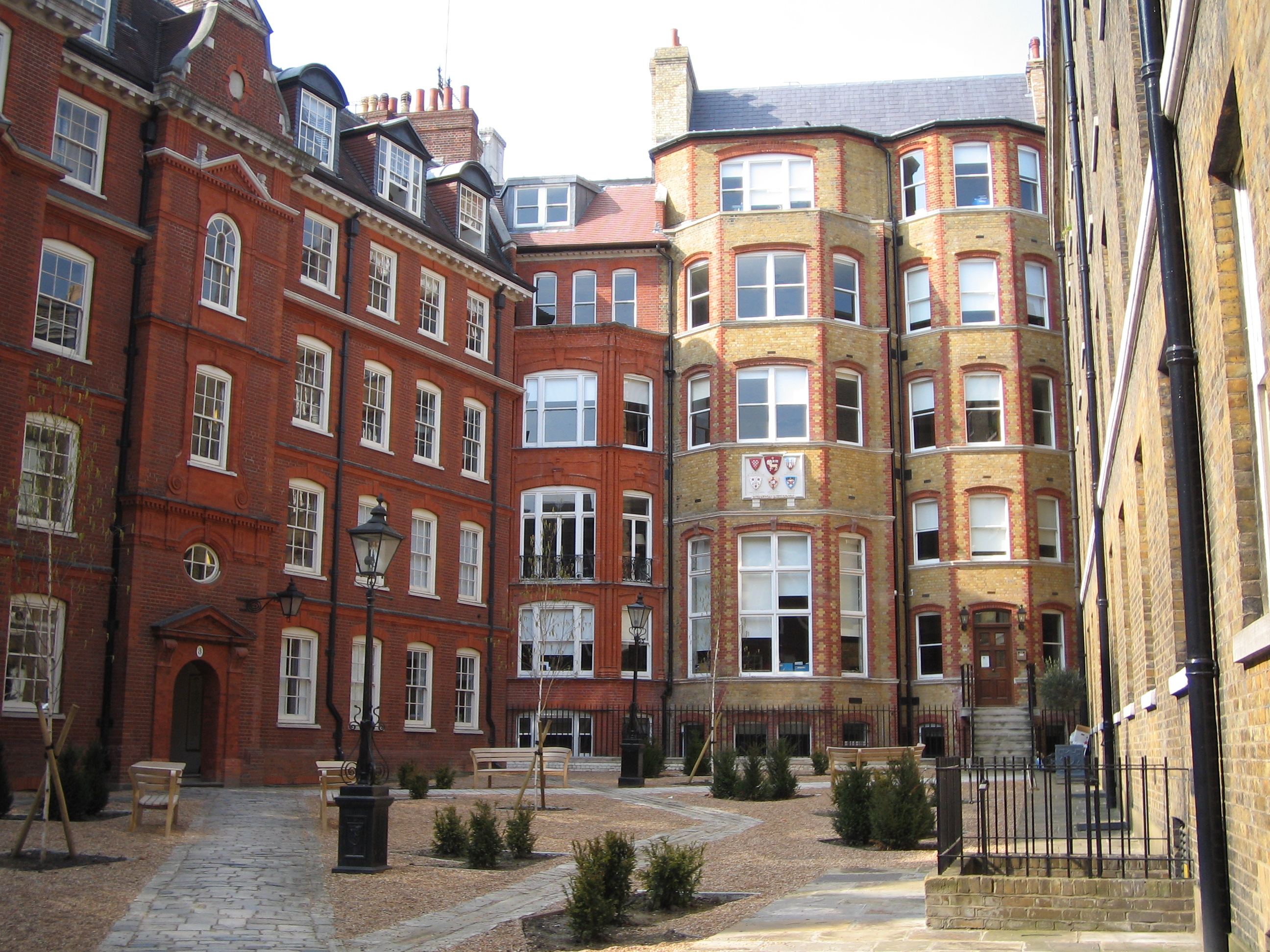
Fitzwilliam College, Cambridge
Fitzwilliam College is a constituent college of the University of Cambridge. The college traces its origins back to 1869 and the foundation of the Non-Collegiate Students Board, a venture intended to offer academically excellent students of all backgrounds a chance to study at the university. The institution was originally based at Fitzwilliam Hall (later renamed Fitzwilliam House), opposite the Fitzwilliam Museum in south-west Cambridge. Having moved to its present site in the north of the city, Fitzwilliam attained collegiate status in 1966. Female undergraduates were first admitted in 1978, around the time most colleges were first admitting women. Fitzwilliam is now home to around 475 undergraduates, 500 graduate students and 90 fellows. By overall student numbers, it is the seventh-largest college in Cambridge as of 2018/19. Notable alumni of Fitzwilliam College include six Nobel Laureates, a large number of prominent academics, public officials, businesspeople, clergy and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peterhouse, Cambridge
Peterhouse is the oldest constituent college of the University of Cambridge in England, founded in 1284 by Hugh de Balsham, Bishop of Ely. Today, Peterhouse has 254 undergraduates, 116 full-time graduate students and 54 fellows. It is quite often erroneously referred to as ''Peterhouse College'', although the correct name is simply ''Peterhouse''. Peterhouse alumni are notably eminent within the natural sciences, including scientists Lord Kelvin, Henry Cavendish, Charles Babbage, James Clerk Maxwell, James Dewar, Frank Whittle, and five Nobel prize winners in science: Sir John Kendrew, Sir Aaron Klug, Archer Martin, Max Perutz, and Michael Levitt. Peterhouse alumni also include the Archbishop of Canterbury John Whitgift, Lord Chancellors, Lord Chief Justices, as well as Oscar-winning film director Sam Mendes, and comedian David Mitchell. British Prime Minister Augustus FitzRoy, 3rd Duke of Grafton, and Elijah Mudenda, second prime minister of Zambia, also studied at t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inner Temple
The Honourable Society of the Inner Temple, commonly known as the Inner Temple, is one of the four Inns of Court and is a professional associations for barristers and judges. To be called to the Bar and practise as a barrister in England and Wales, a person must belong to one of these Inns. It is located in the wider Temple area, near the Royal Courts of Justice, and within the City of London. The Inn is a professional body that provides legal training, selection, and regulation for members. It is ruled by a governing council called "Parliament", made up of the Masters of the Bench (or "Benchers"), and led by the Treasurer, who is elected to serve a one-year term. The Temple takes its name from the Knights Templar, who originally (until their abolition in 1312) leased the land to the Temple's inhabitants (Templars). The Inner Temple was a distinct society from at least 1388, although as with all the Inns of Court its precise date of founding is not known. After a disrupted early ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Negro
In the English language, ''negro'' is a term historically used to denote persons considered to be of Black African heritage. The word ''negro'' means the color black in both Spanish and in Portuguese, where English took it from. The term can be construed as offensive, inoffensive, or completely neutral, largely depending on the region or country where it is used, as well as the context in which it is applied. It has various equivalents in other languages of Europe. In English Around 1442, the Portuguese first arrived in Southern Africa while trying to find a sea route to India. The term ', literally meaning "black", was used by the Spanish and Portuguese as a simple description to refer to the Bantu peoples that they encountered. ''Negro'' denotes "black" in Spanish and Portuguese, derived from the Latin word ''niger'', meaning ''black'', which itself is probably from a Proto-Indo-European root ''*nekw-'', "to be dark", akin to ''*nokw-'', "night". ''Negro'' was also used of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward Wilmot Blyden
Edward Wilmot Blyden (3 August 1832 – 7 February 1912) was a Liberian educator, writer, diplomat, and politician who was primarily active in West Africa. Born in the Danish West Indies, he joined the waves of black immigrants from the Americas who migrated to the country. Blyden became a teacher for five years in the British West African colony of Sierra Leone in the early twentieth century. His writings on pan-Africanism became influential throughout West Africa, attracting attention in countries such as the United States as well. He believed that Zionism was a model for what he termed Ethiopianism, and that African Americans could return to Africa and help in the rebuilding of the continent. Blyden was recognised in his youth for his talents and drive; he was educated and mentored by John Knox, an American Protestant minister in Sankt Thomas who encouraged him to continue his education in the United States. In 1850 Blyden was refused admission to three Northern theo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Freetown
Freetown is the capital and largest city of Sierra Leone. It is a major port city on the Atlantic Ocean and is located in the Western Area of the country. Freetown is Sierra Leone's major urban, economic, financial, cultural, educational and political centre, as it is the seat of the Government of Sierra Leone. The population of Freetown was 1,055,964 at the 2015 census. The city's economy revolves largely around its harbour, which occupies a part of the estuary of the Sierra Leone River in one of the world's largest natural deep water harbours. Although the city has traditionally been the homeland of the Sierra Leone Creole people, the population of Freetown is ethnically, culturally, and religiously diverse. The city is home to a significant population of all of Sierra Leone's ethnic groups, with no single ethnic group forming more than 27% of the city's population. As in virtually all parts of Sierra Leone, the Krio language of the Sierra Leone Creole people is Freetown's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)
