|
Joseph C. Abbott
Joseph Carter Abbott (July 15, 1825October 8, 1881) was a Union Army colonel during the American Civil War who was awarded the grade of brevet brigadier general of volunteers and a Republican United States Senator from the state of North Carolina between 1868 and 1871. During his career in private life he was a lawyer, newspaper editor and businessman. He also served as collector of the port of Wilmington, inspector of posts along the eastern line of the southern coast during the Rutherford B. Hayes Administration, and special agent of the United States Treasury Department. Early life Abbott was born in Concord, New Hampshire to farmer Aaron Carter Abbott and Nancy Badger, and graduated from Phillips Academy in Andover, Massachusetts, in 1846, having studied there and under private auspices. He studied law at Concord, and was admitted to the bar in 1852. From 1852 to 1857, Abbott was the owner and editor of the ''Daily American'' newspaper, in Manchester, New Hampshire. His suc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Carolina
North Carolina () is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States. The state is the 28th largest and 9th-most populous of the United States. It is bordered by Virginia to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, Georgia and South Carolina to the south, and Tennessee to the west. In the 2020 census, the state had a population of 10,439,388. Raleigh is the state's capital and Charlotte is its largest city. The Charlotte metropolitan area, with a population of 2,595,027 in 2020, is the most-populous metropolitan area in North Carolina, the 21st-most populous in the United States, and the largest banking center in the nation after New York City. The Raleigh-Durham-Cary combined statistical area is the second-largest metropolitan area in the state and 32nd-most populous in the United States, with a population of 2,043,867 in 2020, and is home to the largest research park in the United States, Research Triangle Park. The earliest evidence of human occupation i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Olustee
The Battle of Olustee or Battle of Ocean Pond was fought in Baker County, Florida on February 20, 1864, during the American Civil War. It was the largest battle fought in Florida during the war. Union General Truman Seymour had landed troops at Jacksonville, aiming chiefly to disrupt Confederate food supply. Meeting little resistance, he proceeded towards the state capital of Tallahassee, against orders, assuming that he would face only the small Florida militia. Confederates in Charleston sent reinforcements under General Alfred H. Colquitt and the two armies collided near Ocean Pond in Olustee. The Union forces were repulsed and retreated to Jacksonville. Some were garrisoned there to occupy territory. Other troops were transferred to other, more active, areas where they were needed. Background In February 1864, Major General Quincy A. Gillmore, commander of the Union's Department of the South at Hilton Head, South Carolina, ordered an expedition into Florida to secure Un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Treasury Department
The Department of the Treasury (USDT) is the Treasury, national treasury and finance department of the federal government of the United States, where it serves as an United States federal executive departments, executive department. The department oversees the Bureau of Engraving and Printing and the U.S. Mint. These two agencies are responsible for printing all paper currency and United States coinage, coins, while the treasury executes its Circulation (currency), circulation in the domestic fiscal system. The USDT Tax collector, collects all taxation in the United States, federal taxes through the Internal Revenue Service; manages United States Treasury security, U.S. government debt instruments; Bank regulation#Licensing and supervision, licenses and supervises banks and Savings and loan association, thrift institutions; and advises the Federal government of the United States#Legislative branch, legislative and Federal government of the United States#Executive branch, executive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rutherford B
Rutherford may refer to: Places Australia * Rutherford, New South Wales, a suburb of Maitland * Rutherford (Parish), New South Wales, a civil parish of Yungnulgra County Canada * Mount Rutherford, Jasper National Park * Rutherford, Edmonton, neighbourhood * Rutherford House, in Edmonton, Alberta * Rutherford Library, University of Alberta United Kingdom * Rutherford Appleton Laboratory, Oxfordshire United States * Rutherford, California, in Napa County * East Rutherford, New Jersey * Rutherford, New Jersey * Rutherford, Pennsylvania * Rutherford, Virginia * Rutherford, West Virginia * Rutherford County, North Carolina * Rutherford County, Tennessee People * Rutherford (name), people with the surname or given name ** Ernest Rutherford (1871–1937), 1st Baron Rutherford of Nelson, known as the father of nuclear physics ** Rutherford B. Hayes (1822–1893), 19th president of the United States (1877–1881) Fiction * Rutherford the Brave, a character from Game ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Senator
The United States Senate is the Upper house, upper chamber of the United States Congress, with the United States House of Representatives, House of Representatives being the Lower house, lower chamber. Together they compose the national Bicameralism, bicameral legislature of the United States. The composition and powers of the Senate are established by Article One of the United States Constitution. The Senate is composed of #Membership, senators, each of whom represents a single U.S. state, state in its entirety. Each of the 50 states is equally represented by two senators who serve Classes of United States senators, staggered terms of six years, for a total of 100 senators. The Vice President of the United States, vice president of the United States serves as presiding officer and president of the Senate by Ex officio member, virtue of that office, despite not being a senator, and has a vote only if the Senate is equally divided. In the vice president's absence, the Presiden ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Republican Party
The Republican Party, also referred to as the GOP ("Grand Old Party"), is one of the Two-party system, two Major party, major contemporary political parties in the United States. The GOP was founded in 1854 by Abolitionism in the United States, anti-slavery activists who opposed the Kansas–Nebraska Act, which allowed for the potential expansion of Slavery#Chattel slavery, chattel slavery into the western territories. Since Ronald Reagan's Presidency of Ronald Reagan, presidency in the 1980s, Conservatism in the United States, conservatism has been the dominant ideology of the GOP. It has been the main political rival of the Democratic Party (United States), Democratic Party since the mid-1850s. The Republican Party's intellectual predecessor is considered to be Northern United States, Northern members of the Whig Party (United States), Whig Party, with Republican presidents Abraham Lincoln, Rutherford B. Hayes, Chester A. Arthur, and Benjamin Harrison all being Whigs before ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brigadier General (United States)
In the United States Armed Forces, a brigadier general is a one-star general officer in the United States Army, Marine Corps, Air Force, and Space Force. A brigadier general ranks above a colonel and below a major general. The pay grade of brigadier general is O-7. It is equivalent to the rank of rear admiral (lower half) in the other United States uniformed services which use naval ranks. It is abbreviated as BG in the Army, BGen in the Marine Corps, and Brig Gen in the Air Force and Space Force. History The rank of brigadier general has existed in the U.S. military since the inception of the Continental Army in June 1775. To prevent mistakes in recognizing officers, a general order was issued on July 14, 1775, establishing that brigadier generals would wear a ribbon, worn across the breast, between coat and waistcoat, pink in color. Later, on June 18, 1780, it was prescribed that brigadier generals would instead wear a single silver star on each epaulette. At first, briga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brevet (military)
In many of the world's military establishments, a brevet ( or ) was a warrant giving a commissioned officer a higher rank title as a reward for gallantry or meritorious conduct but may not confer the authority, precedence, or pay of real rank. An officer so promoted was referred to as being brevetted (for example, "he was brevetted major general"). The promotion would be noted in the officer's title (for example, "Bvt. Maj. Gen. Joshua L. Chamberlain" or "Bvt. Col. Arthur MacArthur"). It is not to be confused with a ''Brevet d'état-major'' in Francophone European military circles, where it is an award, nor should it be confused with temporary commissions. France In France, ''brevet'' is a word with a very broad meaning, which includes every document giving a capacity to a person. For instance, the various military speciality courses, such as military parachutism, are ended by the award of a brevet. The more important brevet in the French military is the one of the Écol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
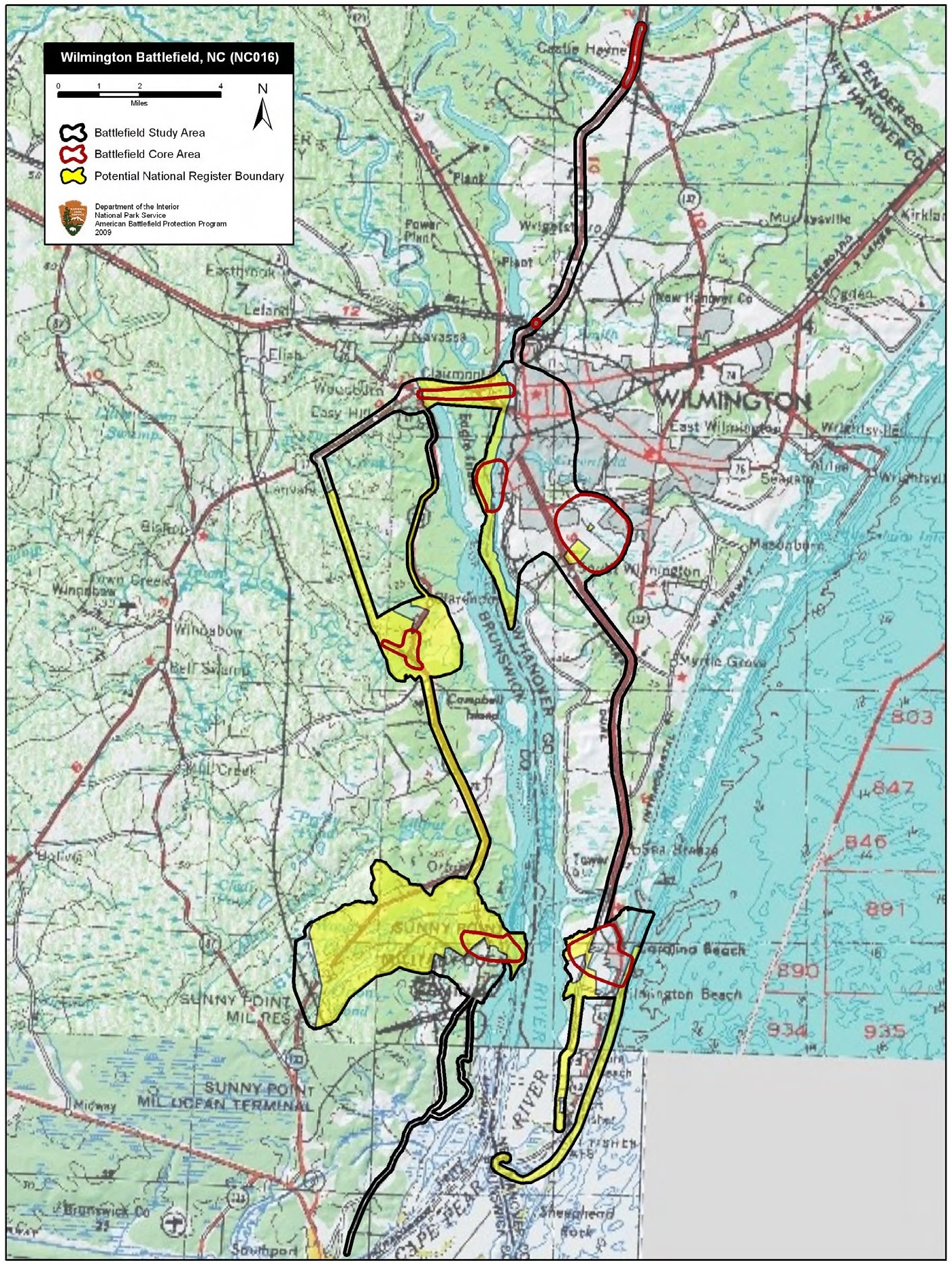
Battle Of Wilmington
The Battle of Wilmington was fought February 11–22, 1865, during the American Civil War, mostly outside the city of Wilmington, North Carolina, between the opposing Union and Confederate Departments of North Carolina. The Union victory in January in the Second Battle of Fort Fisher meant that Wilmington, 30 miles upriver, could no longer be used by the Confederacy as a port. It fell to Union troops after they overcame Confederate defenses along the Cape Fear River south of the city. The Confederate General Braxton Bragg burned stores of tobacco and cotton, among other supplies and equipment, before leaving the city, to prevent the Union from seizing them. Background After the fall of Fort Fisher, the port city of Wilmington was sealed to any further blockade runners; the Confederates had no remaining major ports along the Atlantic seaboard. Confederate forces evacuated the other defensive works near the mouth of the Cape Fear River; they were forced to disable and abandon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Battle Of Fort Fisher
The Second Battle of Fort Fisher was a successful assault by the Union Army, Navy and Marine Corps against Fort Fisher, south of Wilmington, North Carolina, near the end of the American Civil War in January 1865. Sometimes referred to as the "Gibraltar of the South" and the last major coastal stronghold of the Confederacy, Fort Fisher had tremendous strategic value during the war, providing a port for blockade runners supplying the Army of Northern Virginia.Kennedy, p. 402. Background Wilmington was the last major port open to the Confederacy on the Atlantic seacoast. Ships leaving Wilmington via the Cape Fear River and setting sail for the Bahamas, Bermuda or Nova Scotia to trade cotton and tobacco for needed supplies from the British were protected by the fort. Based on the design of the Malakoff redoubt in Sevastopol, Russian Empire, Fort Fisher was constructed mostly of earth and sand. This made it better able to absorb the pounding of heavy fire from Union ships than older ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilmington Campaign
The Wilmington campaigns were part of a Union effort to take Wilmington, North Carolina, from the Confederates. Wilmington was the last major port on the Atlantic seacoast available to the Confederacy. Fort Fisher guarded the Cape Fear River and in order to capture Wilmington, Fort Fisher had to fall. First campaign On December 7, 1864, Union troops under command of General Benjamin Butler were sent to take the fort. Before the troops arrived, Admiral David D. Porter sent the USS Wyalusing and two escort ships on an expedition to try to capture Rainbow Bluff and a Confederate Ram. But Porter didn't know that there were Water mines in the river and both of the escorts were sunk by the mines and the expedition abandoned. Colonel William Lamb was charged with defending Fort Fisher. The Union troops numbered about 6,500 men, and the Confederates had about 7,000. Due to a number of delays caused by storms, the attack didn't begin until December 23, and in the interim, General B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Darbytown And New Market Roads
The Battle of Darbytown and New Market Roads ( or Johnson's Farm or Four Mile Creek) was an engagement between Union and Confederate forces during the American Civil War, which took place on October 7, 1864, in Henrico County, Virginia, as part of the Richmond-Petersburg Campaign. Background The Richmond-Petersburg Campaign (June 15, 1864 – March 25, 1865) was a Union effort to capture the city of Petersburg, Virginia, from Confederate forces under the command of Confederate General Robert E. Lee. During the Battle of Chaffin's Farm, Union forces captured Fort Harrison from the Confederates on September 30. This prompted Lee to order an offensive on the right flank of the Union forces, which were under the command of Lt. Gen. Ulysses S. Grant, on October 7. Opposing forces Union Confederate Battle The Union defensive lines, commanded by Brig. Gen. August V. Kautz and Maj. Gen. David B. Birney, were positioned along the length of New Market Road, with further Uni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |