|
Joseph Burke (botanist)
Joseph Burke (12 June 1812 in Bristol, England – 23 January 1873 in Harrisonville, USA) was a collector of plants and animals for Edward Smith-Stanley, 13th Earl of Derby, Lord Derby. 1839–1840 Burke was employed as a gardener for Lord Derby, an enthusiastic natural history collector with his own menagerie at Prescot, Lancashire. In 1839 Lord Derby commissioned Karl Ludwig Philipp Zeyher, Karl Zeyher to collect plants and animals in southern Africa, delegating Burke to organise the expedition. Burke left London on the vessel "Joanna" in December 1839 and arrived in Cape Town in March 1840. From here he went on to "Vygekraal" (about 3 km SE of Table Bay), the home of Rev. Fry and an agent of Lord Derby. Here he arranged for a wagon and oxen to transport him, and set out on 23 May to Uitenhage where he planned to meet up with Karl Zeyher for a joint expedition to the interior. A smallpox outbreak in Cape Town caused usually hospitable farmers along the way to bar their homes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bristol
Bristol () is a city, ceremonial county and unitary authority in England. Situated on the River Avon, it is bordered by the ceremonial counties of Gloucestershire to the north and Somerset to the south. Bristol is the most populous city in South West England. The wider Bristol Built-up Area is the eleventh most populous urban area in the United Kingdom. Iron Age hillforts and Roman villas were built near the confluence of the rivers Frome and Avon. Around the beginning of the 11th century, the settlement was known as (Old English: 'the place at the bridge'). Bristol received a royal charter in 1155 and was historically divided between Gloucestershire and Somerset until 1373 when it became a county corporate. From the 13th to the 18th century, Bristol was among the top three English cities, after London, in tax receipts. A major port, Bristol was a starting place for early voyages of exploration to the New World. On a ship out of Bristol in 1497, John Cabot, a Venetia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andries Potgieter
Andries Hendrik Potgieter, known as Hendrik Potgieter (19 December 1792 – 16 December 1852) was a Voortrekker leader and the last known Champion of the Potgieter family. He served as the first head of state of Potchefstroom from 1840 and 1845 and also as the first head of state of Zoutpansberg from 1845 to 1852. Beyond the Orange River Potgieter and his party moved inland to the present Free State, where they signed a treaty with the leader of the Barolong, Moroka. The treaty stipulated that Potgieter would protect the Baralong against the Matabele raiders, in exchange for land. The tract of land was from the Vet River to the Vaal River. The Matabele leader, Mzilikazi, was threatened by the white incursion into what he saw as his sphere of influence, which led to the Matabele's attack on the Potgieter laager in October 1836, at Vegkop, near the present-day town of Heilbron. The attack was beaten off, but the Matabele made off with most of the trekker oxen, crucial draught ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tswaing Crater
Tswaing is an impact crater in South Africa that is accompanied by a museum. It is situated 40 km to the north-west of Pretoria. This astrobleme is 1.13 km in diameter and 100 m deep and the age is estimated to be 220,000 ± 52,000 years (Pleistocene). The impactor is believed to have been a chondrite or stony meteorite some 30 to 50 m in diameter that was vapourised during the impact event. Morokweng impact structure, another crater of chondrite origin, lies north-west of Vryburg. Etymology The name ''Tswaing'' means "place of salt" in Tswana and the crater was also formerly known in English as ''Pretoria Saltpan crater'' and in Afrikaans as ''Soutpankrater''. History Stone tools from the Middle Stone Age show that the crater was regularly visited by people from as far back as 100,000 years ago in order to hunt and collect salt. Water in the crater comes from surface springs, ground water and rain water and is rich in dissolved carbonates and sodium chlorides. Tswan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nile Crocodile
The Nile crocodile (''Crocodylus niloticus'') is a large crocodilian native to freshwater habitats in Africa, where it is present in 26 countries. It is widely distributed throughout sub-Saharan Africa, occurring mostly in the central, eastern, and southern regions of the continent, and lives in different types of aquatic environments such as lakes, rivers, swamps, and marshlands. In West Africa, it occurs along with two other crocodilians. Although capable of living in saline environments, this species is rarely found in saltwater, but occasionally inhabits deltas and brackish lakes. The range of this species once stretched northward throughout the Nile, as far north as the Nile Delta. On average, the adult male Nile crocodile is between in length and weighs including stomach stones. However, specimens exceeding in length and weighing up to have been recorded. It is the largest freshwater predator in Africa, and may be considered the second-largest extant reptile in the w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tsessebe
The common tsessebe or sassaby (''Damaliscus lunatus lunatus'') is the southern, nominate subspecies of ''Damaliscus lunatus'', although some authorities have recognised it as an independent species. It is most closely related to the Bangweulu tsessebe, sometimes also seen as a separate species,''Damaliscus lunatus'' MSW3 less to the , , and [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wildebeest
Wildebeest ( , , ), also called gnu ( or ), are antelopes of the genus ''Connochaetes'' and native to Eastern and Southern Africa. They belong to the family Bovidae, which includes true antelopes, cattle, goats, sheep, and other even-toed horned ungulates. There are two species of wildebeest: the black wildebeest or white-tailed gnu (''C. gnou''), and the blue wildebeest or brindled gnu (''C. taurinus''). Fossil records suggest these two species diverged about one million years ago, resulting in a northern and a southern species. The blue wildebeest remained in its original range and changed very little from the ancestral species, while the black wildebeest changed more as adaptation to its open grassland habitat in the south. The most obvious ways of telling the two species apart are the differences in their colouring and in the way their horns are oriented. In East Africa, the blue wildebeest is the most abundant big-game species; some populations perform an annual mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waterbuck
The waterbuck (''Kobus ellipsiprymnus'') is a large antelope found widely in sub-Saharan Africa. It is placed in the genus '' Kobus'' of the family Bovidae. It was first described by Irish naturalist William Ogilby in 1833. Its 13 subspecies are grouped under two varieties: the common or ellipsiprymnus waterbuck and the defassa waterbuck. The head-and-body length is typically between and the typical height is between . In this sexually dimorphic antelope, males are taller and heavier than females. Males reach roughly at the shoulder, while females reach . Males typically weigh and females . Their coat colour varies from brown to grey. The long, spiral horns, present only on males, curve backward, then forward, and are long. Waterbucks are rather sedentary in nature. As gregarious animals, they may form herds consisting of six to 30 individuals. These groups are either nursery herds with females and their offspring or bachelor herds. Males start showing territorial behaviou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kudu
The kudus are two species of antelope of the genus ''Tragelaphus'': * Lesser kudu, ''Tragelaphus imberbis'', of eastern Africa * Greater kudu, ''Tragelaphus strepsiceros'', of eastern and southern Africa The two species look similar, though greaters are larger than lessers. A large adult male greater kudu stands over tall at the shoulder, and a large male lesser kudu stands about tall. Males of both species have long horns, which point upward and slightly back, curling in a corkscrew shape. Etymology The name of the animal was imported into English in the 18th century from isiXhosa ''iqhude'', via Afrikaans ''koedoe''. Kudu, or koodoo, is the Khoikhoi and seTswana name for this antelope. ''Tragos'' (Greek) denotes a he-goat and ''elaphos'' (Greek) a deer. ''Strepho'' (Greek) means "I twist", and ''strephis'' is "twisting". ''Keras'' (Greek) means "horn". Habitat Lesser kudus occupy savanna near '' Acacia'' and ''Commiphora'' shrubs. They rely on thickets for prote ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zebra
Zebras (, ) (subgenus ''Hippotigris'') are African equines with distinctive black-and-white striped coats. There are three living species: the Grévy's zebra (''Equus grevyi''), plains zebra (''E. quagga''), and the mountain zebra (''E. zebra''). Zebras share the genus ''Equus'' with horses and asses, the three groups being the only living members of the family Equidae. Zebra stripes come in different patterns, unique to each individual. Several theories have been proposed for the function of these stripes, with most evidence supporting them as a deterrent for biting flies. Zebras inhabit eastern and southern Africa and can be found in a variety of habitats such as savannahs, grasslands, woodlands, shrublands, and mountainous areas. Zebras are primarily grazers and can subsist on lower-quality vegetation. They are preyed on mainly by lions, and typically flee when threatened but also bite and kick. Zebra species differ in social behaviour, with plains and mountain zebra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Eland
The common eland (''Taurotragus oryx''), also known as the southern eland or eland antelope, is a savannah and plains antelope found in East and Southern Africa. It is a species of the family Bovidae and genus ''Taurotragus''. An adult male is around tall at the shoulder (females are shorter) and can weigh up to with a typical range of , for females). It is the second-largest antelope in the world, being slightly smaller on average than the giant eland. It was scientifically described by Peter Simon Pallas in 1766. Mainly a herbivore, its diet is primarily grasses and leaves. Common elands form herds of up to 500 animals, but are not territorial. The common eland prefers habitats with a wide variety of flowering plants such as savannah, woodlands, and open and montane grasslands; it avoids dense forests. It uses loud barks, visual and postural movements, and the flehmen response to communicate and warn others of danger. The common eland is used by humans for leather, meat, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
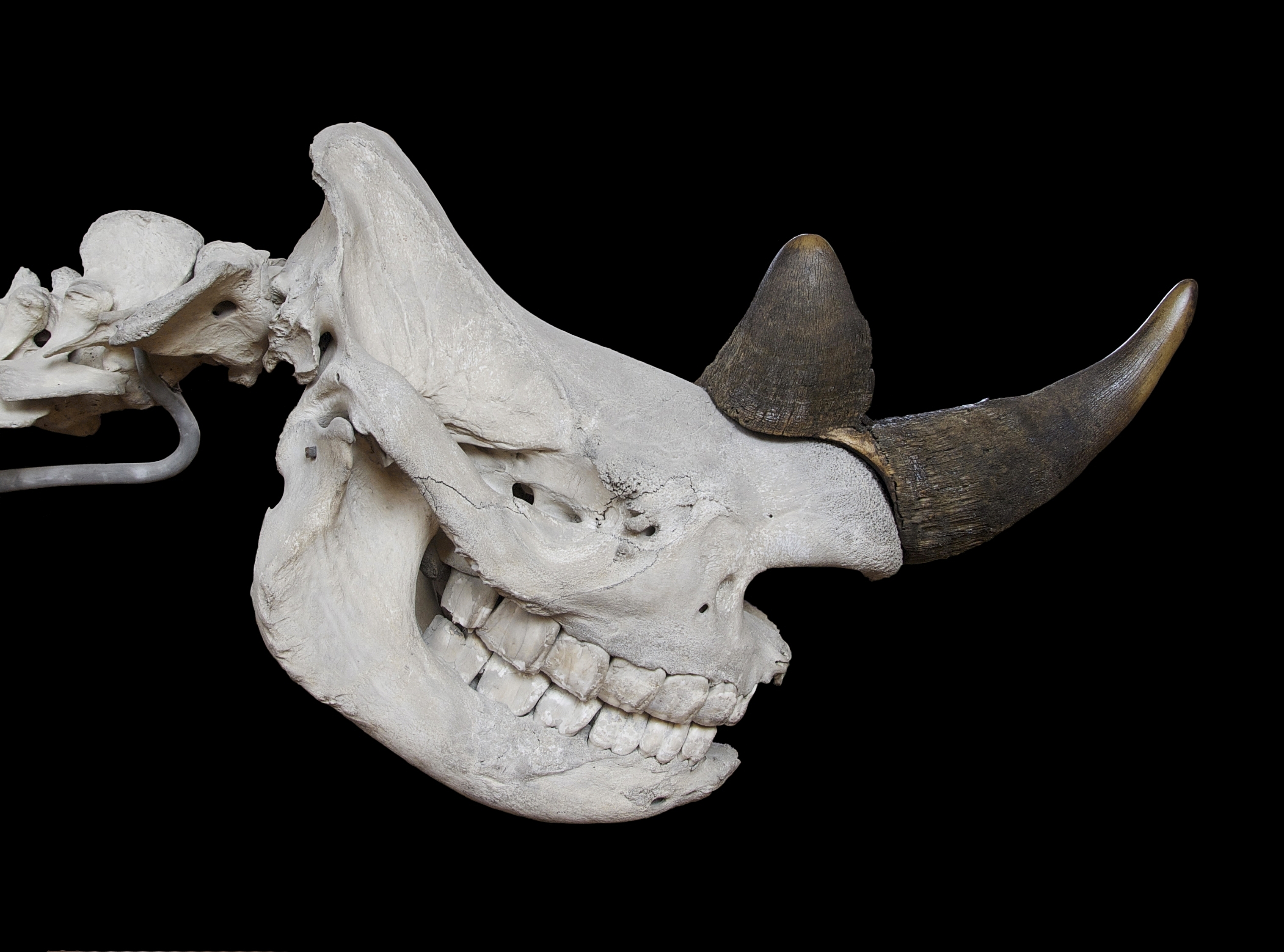
Black Rhino
The black rhinoceros, black rhino or hook-lipped rhinoceros (''Diceros bicornis'') is a species of rhinoceros, native to eastern and southern Africa including Angola, Botswana, Kenya, Malawi, Mozambique, Namibia, South Africa, Eswatini, Tanzania, Zambia, and Zimbabwe. Although the rhinoceros is referred to as ''black'', its colours vary from brown to grey. The other African rhinoceros is the white rhinoceros (''Ceratotherium simum''). The word "white" in the name "white rhinoceros" is often said to be a misinterpretation of the Afrikaans word ' ( Dutch ') meaning wide, referring to its square upper lip, as opposed to the pointed or hooked lip of the black rhinoceros. These species are now sometimes referred to as the square-lipped (for white) or hook-lipped (for black) rhinoceros. The species overall is classified as critically endangered (even though the south-western black rhinoceros is classified as near threatened). Three subspecies have been declared extinct, including ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)

.jpg)