|
Jos Van Der Meer
Jos W.M. van der Meer (born April 15, 1947) is emeritus professor and former chairman at the department of internal medicine of the Radboud University Nijmegen Medical Centre in Nijmegen, Netherlands. He is a member of the Royal Netherlands Academy of Arts and Sciences (since 2003), of which he was vice president and chairman of the division of natural sciences (2006-2012). He is a member of Academia Europaea. Between 2014 and 2016 he was president of European Academies Science Advisory Council (EASAC). He performs research on cytokines and host defence, chronic fatigue syndrome and Hyper-IgD syndrome, hyper-immunoglobulinemia D syndrome (HIDS). He is also active in graphic art and makes cartoons, for example for the Dutch science journal ''Mediator''. History In 1984, van der Meer published the first paper about HIDS, the new "periodic fever" syndrome he had discovered. This was the start of his research on interleukin-1 (IL-1) and his collaboration with Dr. Charles A. Dinar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Hague
The Hague ( ; nl, Den Haag or ) is a city and municipality of the Netherlands, situated on the west coast facing the North Sea. The Hague is the country's administrative centre and its seat of government, and while the official capital of the Netherlands is Amsterdam, The Hague has been described as the country's de facto capital. The Hague is also the capital of the province of South Holland, and the city hosts both the International Court of Justice and the International Criminal Court. With a population of over half a million, it is the third-largest city in the Netherlands, after Amsterdam and Rotterdam. The Hague is the core municipality of the Greater The Hague urban area, which comprises the city itself and its suburban municipalities, containing over 800,000 people, making it the third-largest urban area in the Netherlands, again after the urban areas of Amsterdam and Rotterdam. The Rotterdam–The Hague metropolitan area, with a population of approximately ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
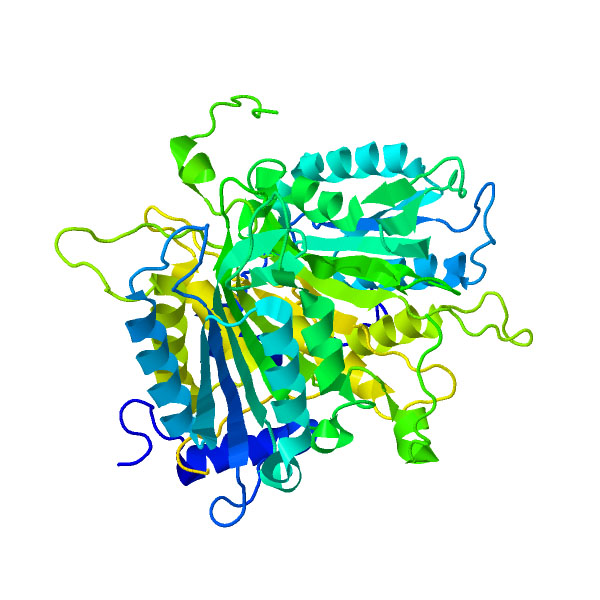
Mevalonate Kinase
Mevalonate kinase is an enzyme (specifically a kinase) that in humans is encoded by the ''MVK'' gene. Mevalonate kinases are found in a wide variety of organisms from bacteria to mammals. This enzyme catalyzes the following reaction: . Function Mevalonate is a key intermediate, and mevalonate kinase a key early enzyme, in isoprenoid and sterol synthesis. As the second enzyme in the Mevalonate pathway, it catalyzes the phosphorylation of Mevalonic acid to produce Mevalonate-5-phosphate. A 5-10% reduction in mevalonate kinase activity is associated with the mevalonate kinase deficiency (MVD) resulting in accumulation of intermediate mevalonic acid. Clinical significance Defects can be associated with hyperimmunoglobulinemia D with recurrent fever. Mevalonate kinase deficiency caused by mutation of this gene results in mevalonic aciduria, a disease characterized psychomotor retardation, failure to thrive, hepatosplenomegaly, anemia and recurrent febrile crises. Defects in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epstein Barr Virus
The surname Epstein ( yi, עפּשטײן, Epshteyn) is one of the oldest Ashkenazi Jewish family names. It is probably derived from the German town of Eppstein, in Hesse; the place-name was probably derived from Gaulish ''apa'' ("water", in the sense of a river) and German '' -stein'' ("stone", in the sense of a hill). Some people with this name include: Arts * Alex Epstein, Israeli writer * Barbara Epstein, literary editor * Brian Epstein (1934–1967), businessman, manager of the Beatles * Daniel Epstein (pianist) * Daniel Mark Epstein, biographer and poet * Deborah Epstein, French-American singer-songwriter more commonly known as SoShy * Dena Epstein (1916–2013), American music librarian, writer, and musicologist * Edward Jay Epstein, author and early critic of the Warren Commission * Howie Epstein, bass guitarist * Jacob Epstein, sculptor * Jake Epstein, Canadian actor * Jason Epstein, publisher who popularized the trade paperback * Jean Epstein, film director * Joseph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reactive Oxygen Species
In chemistry, reactive oxygen species (ROS) are highly reactive chemicals formed from diatomic oxygen (). Examples of ROS include peroxides, superoxide, hydroxyl radical, singlet oxygen, and alpha-oxygen. The reduction of molecular oxygen () produces superoxide (), which is the precursor to most other reactive oxygen species: :O2 + e^- -> \ ^\bullet O2- Dismutation of superoxide produces hydrogen peroxide (): :2 H+ + \ ^\bullet O2^- + \ ^\bullet O2^- -> H2O2 + O2 Hydrogen peroxide in turn may be partially reduced, thus forming hydroxide ions and hydroxyl radicals (), or fully reduced to water: :H2O2 + e^- -> HO^- + \ ^\bullet OH :2 H+ + 2 e- + H2O2 -> 2 H2O In a biological context, ROS are byproducts of the normal metabolism of oxygen. ROS have roles in cell signaling and homeostasis. ROS are intrinsic to cellular functioning, and are present at low and stationary levels in normal cells. In plants, ROS are involved in metabolic processes related to photoprotection and toleran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Out Of Africa
''Out of Africa'' is a memoir by the Danish author Karen Blixen. The book, first published in 1937, recounts events of the seventeen years when Blixen made her home in Kenya, then called British East Africa. The book is a lyrical meditation on Blixen's life on her coffee plantation, as well as a tribute to some of the people who touched her life there. It provides a vivid snapshot of African colonial life in the last decades of the British Empire. Blixen wrote the book in English and then rewrote it in Danish. The book has sometimes been published under the author's pen name, Isak Dinesen. Background Karen Blixen moved to British East Africa in late 1913, at the age of 28, to marry her second cousin, the Swedish Baron Bror von Blixen-Finecke, and make a life in the British colony known today as Kenya. The young Baron and Baroness bought farmland below the Ngong Hills about ten miles (16 km) southwest of Nairobi, which at the time was still shaking off its rough origins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monocytes
Monocytes are a type of leukocyte or white blood cell. They are the largest type of leukocyte in blood and can differentiate into macrophages and conventional dendritic cells. As a part of the vertebrate innate immune system monocytes also influence adaptive immune responses and exert tissue repair functions. There are at least three subclasses of monocytes in human blood based on their phenotypic receptors. Structure Monocytes are amoeboid in appearance, and have nongranulated cytoplasm. Thus they are classified as agranulocytes, although they might occasionally display some azurophil granules and/or vacuoles. With a diameter of 15–22 μm, monocytes are the largest cell type in peripheral blood. Monocytes are mononuclear cells and the ellipsoidal nucleus is often lobulated/indented, causing a bean-shaped or kidney-shaped appearance. Monocytes compose 2% to 10% of all leukocytes in the human body. Development Monocytes are produced by the bone marrow from precursors c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caspase-1
Caspase-1/Interleukin-1 converting enzyme (ICE) is an evolutionarily conserved enzyme that proteolysis, proteolytically cleaves other proteins, such as the Protein precursor, precursors of the inflammatory cytokines Interleukin 1 beta, interleukin 1β and interleukin 18 as well as the pyroptosis inducer Gasdermin D, into active mature peptides. It plays a central role in cell immunity as an inflammatory response initiator. Once activated through formation of an inflammasome complex, it initiates a proinflammatory response through the cleavage and thus activation of the two inflammatory cytokines, Interleukin 1 beta, interleukin 1β (IL-1β) and interleukin 18 (IL-18) as well as pyroptosis, a programmed lytic cell death pathway, through cleavage of Gasdermin D. The two inflammatory cytokines activated by Caspase-1 are excreted from the cell to further induce the inflammatory response in neighboring cells. Cellular expression Caspase-1 is evolutionarily conserved in many eukaryot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mannose Receptor
The mannose receptor (Cluster of Differentiation 206, CD206) is a C-type lectin primarily present on the surface of macrophages, immature dendritic cells and liver sinusoidal endothelial cells, but is also expressed on the surface of skin cells such as human dermal fibroblasts and keratinocytes. It is the first member of a family of endocytic receptors that includes Endo180 (CD280), M-type PLA2R, and DEC-205 (CD205). The receptor recognises terminal mannose, ''N''-acetylglucosamine and fucose residues on glycans attached to proteins found on the surface of some microorganisms, playing a role in both the innate and adaptive immune systems. Additional functions include clearance of glycoproteins from circulation, including sulphated glycoprotein hormones and glycoproteins released in response to pathological events. The mannose receptor recycles continuously between the plasma membrane and endosomal compartments in a clathrin-dependent manner. Structure Domain organisat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Candida Albicans
''Candida albicans'' is an opportunistic pathogenic yeast that is a common member of the human gut flora. It can also survive outside the human body. It is detected in the gastrointestinal tract and mouth in 40–60% of healthy adults. It is usually a commensal organism, but it can become pathogenic in immunocompromised individuals under a variety of conditions. It is one of the few species of the genus '' Candida'' that causes the human infection candidiasis, which results from an overgrowth of the fungus. Candidiasis is, for example, often observed in HIV-infected patients. ''C. albicans'' is the most common fungal species isolated from biofilms either formed on (permanent) implanted medical devices or on human tissue. ''C. albicans'', ''C. tropicalis'', ''C. parapsilosis'', and ''C. glabrata'' are together responsible for 50–90% of all cases of candidiasis in humans. A mortality rate of 40% has been reported for patients with systemic candidiasis due to ''C. albicans' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
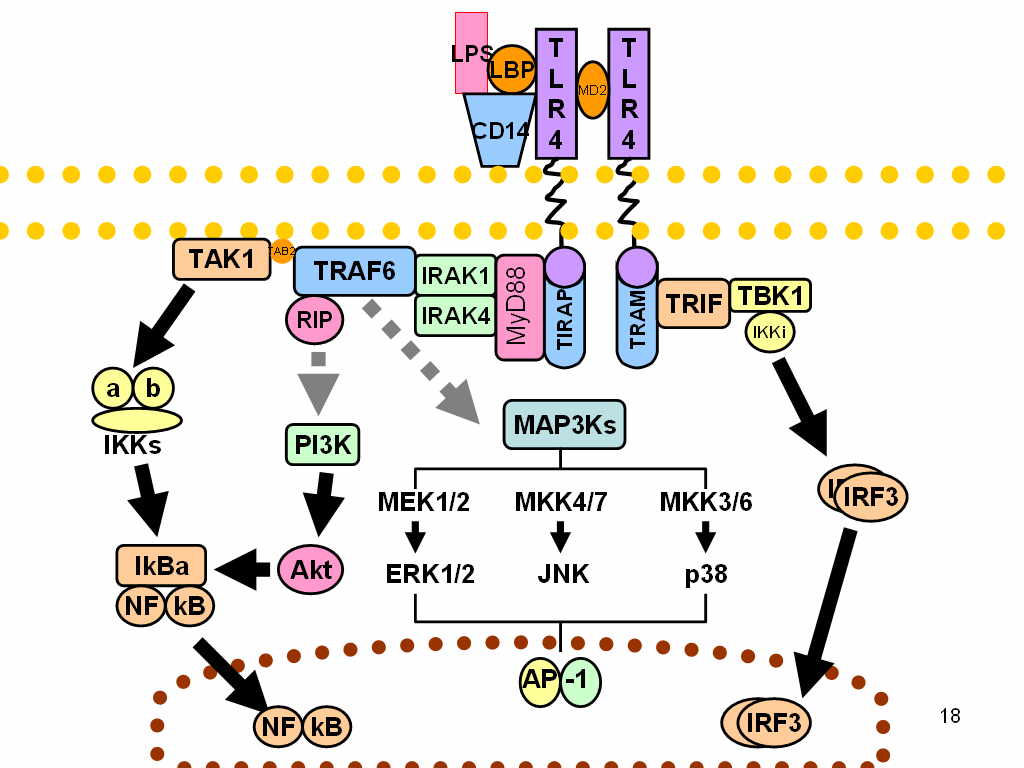
Toll-like Receptor 4
Toll-like receptor 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TLR4'' gene. TLR4 is a transmembrane protein, member of the toll-like receptor family, which belongs to the pattern recognition receptor (PRR) family. Its activation leads to an intracellular signaling pathway NF-κB and inflammatory cytokine production which is responsible for activating the innate immune system. TLR4 expressing cells are myeloid (erythrocytes, granulocytes, macrophages) rather than lymphoid (T-cells, B-cells, NK cells). Most myeloid cells also express high levels of CD14, which facilitates activation of TLR4 by LPS. It is most well known for recognizing lipopolysaccharide (LPS), a component present in many Gram-negative bacteria (e.g. ''Neisseria'' spp.) and selected Gram-positive bacteria. Its ligands also include several viral proteins, polysaccharide, and a variety of endogenous proteins such as low-density lipoprotein, beta-defensins, and heat shock protein. Palmitic acid and lauric acid ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lipopolysaccharide
Lipopolysaccharides (LPS) are large molecules consisting of a lipid and a polysaccharide that are bacterial toxins. They are composed of an O-antigen, an outer core, and an inner core all joined by a covalent bond, and are found in the outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria. Today, the term ''endotoxin'' is often used synonymously with LPS, although there are a few endotoxins (in the original sense of toxins that are inside the bacterial cell that are released when the cell disintegrates) that are not related to LPS, such as the so-called delta endotoxin proteins produced by '' Bacillus thuringiensis''. Lipopolysaccharides can have substantial impacts on human health, primarily through interactions with the immune system. LPS is a potent activator of the immune system and pyrogen (agent that causes fever). In severe cases, LPS can play a role in causing septic shock. In lower levels and over a longer time period, there is evidence LPS may play an important and harmful rol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bartonella
''Bartonella'' is a genus of Gram-negative bacteria. It is the only genus in the family Bartonellaceae. Facultative intracellular parasites, ''Bartonella'' species can infect healthy people, but are considered especially important as opportunistic pathogens. ''Bartonella'' species are transmitted by vectors such as ticks, fleas, sand flies, and mosquitoes. At least eight ''Bartonella'' species or subspecies are known to infect humans. '' Bartonella henselae'' is the organism responsible for cat scratch disease. History ''Bartonella'' species have been infecting humans for thousands of years, as demonstrated by ''Bartonella quintana'' DNA in a 4000-year-old tooth. The genus is named for Alberto Leonardo Barton Thompson (1871–October 26, 1950), a Peruvian scientist. Infection cycle The currently accepted model explaining the infection cycle holds that the transmitting vectors are blood-sucking arthropods and the reservoir hosts are mammals. Immediately after infection, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.png)