|
Jonathan Haidt
Jonathan David Haidt (; born October 19, 1963) is an American social psychologist and author. He is the Thomas Cooley Professor of Ethical Leadership at New York University Stern School of Business. His main areas of study are the psychology of morality and moral emotions. Haidt's main scientific contributions come from the psychological field of moral foundations theory, which attempts to explain the evolutionary origins of human moral reasoning on the basis of innate, gut feelings rather than logic and reason. The theory was later extended to explain the different moral reasoning and how they relate to political ideology, with different political orientations prioritizing different sets of morals. The research served as a foundation for future books on various topics. Haidt has written three books for general audiences: '' The Happiness Hypothesis: Finding Modern Truth in Ancient Wisdom'' (2006) explores the relationship between ancient philosophies and modern science; '' The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the List of United States cities by population, most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the List of United States cities by population density, most densely populated major city in the United States, and is more than twice as populous as second-place Los Angeles. New York City lies at the southern tip of New York (state), New York State, and constitutes the geographical and demographic center of both the Northeast megalopolis and the New York metropolitan area, the largest metropolitan area in the world by urban area, urban landmass. With over 20.1 million people in its metropolitan statistical area and 23.5 million in its combined statistical area as of 2020, New York is one of the world's most populous Megacity, megacities, and over 58 million people live within of the city. New York City is a global city, global Culture of New ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jonathan Baron
Jonathan Baron is an American psychologist. He is a professor emeritus of psychology at the University of Pennsylvania in the science of decision-making. Life and career Baron was born in Boston, Massachusetts, in 1944, and received a B.A. in psychology from Harvard in 1966 and a Ph.D. from Michigan in 1970 for thesis titled ''The threshold for successiveness''. He married Judith Baron in 1967, and has one son, David, born in 1980. Baron is the founding editor of the open-access journal ''Judgment and Decision Making'' and has been on the editorial boards of several other journals. He is a Fellow of the American Association for the Advancement of Science and of the Association for Psychological Science, and was the President of the Society for Judgment and Decision Making for 2006–2007. Notable contributions Baron's work has occurred primarily within the field of judgment and decision making, a multi-disciplinary area that applies psychology to problems in economics, law, busin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Why Good People Are Divided By Politics And Religion
Why may refer to: * Causality, a consequential relationship between two events * Reason (argument), a premise in support of an argument, for what reason or purpose * Grounding (metaphysics), a topic in metaphysics regarding how things exist in virtue of more fundamental things. * Why?, one of the Five Ws used in journalism Music Artists * Why? (American band), a hip hop/indie rock band formed in Oakland, California, in 2004 ** Yoni Wolf, formerly known by the stage name Why? * Why (Canadian band), a rock band formed in Winnipeg, Manitoba, in 1993 * Why?, a 1990s UK folk band, two members of which formed Quench in 2001 Albums * ''Why'' (Baby V.O.X album) or the title song, 2000 * ''Why?'' (Ginger Baker album) or the title song, 2014 * ''Why'' (Prudence Liew album) or the title song, 1987 * ''Why?'' (They Might Be Giants album), 2015 * ''Why?'', by Jacob Whitesides, 2016 * ''Why'', by Moahni Moahna, 1996 * ''Why?'', by the MonaLisa Twins, 2022 EPs * ''Why'' (Discharge EP) o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finding Modern Truth In Ancient Wisdom
Find, FIND or Finding may refer to: Computing * find (Unix), a command on UNIX platforms * find (Windows), a command on DOS/Windows platforms Books * ''The Find'' (2010), by Kathy Page * ''The Find'' (2014), by William Hope Hodgson Film and television * "The Find", an episode of '' Beyond Belief: Fact or Fiction'' * "The Find", an episode of reality TV show ''The Curse of Oak Island'' Music * ''Find'' (Hidden in Plain View EP), 2001 * ''Find'' (SS501 EP) * '' The Find'', a 2005 hip hop album by Ohmega Watts People * Áed Find (died 778), king of Dál Riata (modern-day Scotland) * Caittil Find, Norse-Gaelic warrior contingent leader * Cumméne Find (died 669), seventh abbot of Iona, Scotland Other uses * Find, in archaeology * Finding (jewelcrafting), jewellery components * Meteorite find, a found meteorite not observed to have fallen * Foundation for Innovative New Diagnostics, a not-for-profit organisation * Facial Images National Database See also * Discovery (observation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moral Reasoning
Moral reasoning is the study of how people think about right and wrong and how they acquire and apply moral rules. It is a subdiscipline of moral psychology that overlaps with moral philosophy, and is the foundation of descriptive ethics. Description Starting from a young age, people can make moral decisions about what is right and wrong. Moral reasoning, however, is a part of morality that occurs both within and between individuals. Prominent contributors to this theory include Lawrence Kohlberg and Elliot Turiel. The term is sometimes used in a different sense: reasoning under conditions of uncertainty, such as those commonly obtained in a court of law. It is this sense that gave rise to the phrase, "To a moral certainty;" however, this idea is now seldom used outside of charges to juries. Moral reasoning is an important and often daily process that people use when trying to do the right thing. For instance, every day people are faced with the dilemma of whether to lie in a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
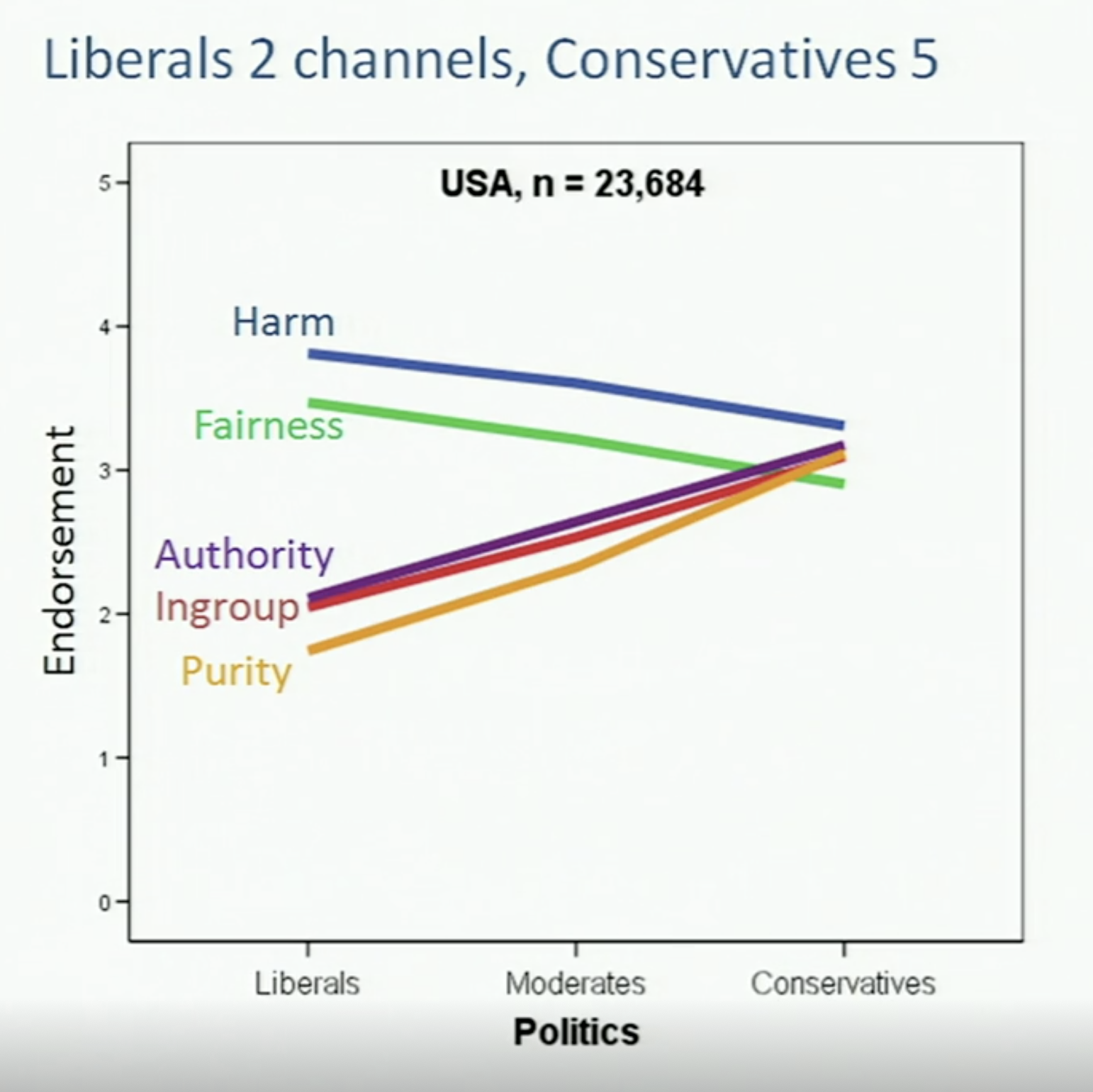
Moral Foundations Theory
Moral foundations theory is a social psychological theory intended to explain the origins of and variation in human moral reasoning on the basis of innate, modular foundations. It was first proposed by the psychologists Jonathan Haidt, Craig Joseph, and Jesse Graham, building on the work of cultural anthropologist Richard Shweder. It has been subsequently developed by a diverse group of collaborators and popularized in Haidt's book ''The Righteous Mind''. The theory proposes six foundations: Care/Harm, Fairness/Cheating, Loyalty/Betrayal, Authority/Subversion, Sanctity/Degradation, and Liberty/Oppression. Its authors remain open to the addition, subtraction, or modification of the set of foundations. Although the initial development of moral foundations theory focused on cultural differences, subsequent work with the theory has largely focused on political ideology. Various scholars have offered moral foundations theory as an explanation of differences among political progressives ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moral Emotions
Moral emotions are a variety of social emotion that are involved in forming and communicating moral judgments and decisions, and in motivating behavioral responses to one's own and others' moral behavior. Background Moral reasoning has been the focus of most study of morality dating all the way back to Plato and Aristotle. The emotive side of morality, worked by Adam Smith's ''The Theory of Moral Sentiments'', has been looked upon with disdain, as subservient to the higher, rational, moral reasoning, with scholars like Immanuel Kant, Piaget and Kohlberg touting moral reasoning as the key forefront of morality. However, in the last 30–40 years, there has been a rise in a new front of research: moral emotions as the basis for moral behavior. This development began with a focus on empathy and guilt, but has since moved on to encompass new emotional scholarship on emotions such as anger, shame, disgust, awe, and elevation. With the new research, theorists have begun to question wheth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New York University Stern School Of Business
The New York University Leonard N. Stern School of Business (commonly referred to as NYU Stern, The Stern School of Business, or simply Stern) is the business school of New York University, a private research university based in New York City. It was founded in 1900. It is located on Gould Plaza next to the Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences and the economics department of the College of Arts and Sciences. Stern is a founding member of the Association to Advance Collegiate Schools of Business. Established as the School of Commerce, Accounts and Finance, the school changed its name in 1988 in honor of Leonard N. Stern, an alumnus and benefactor of the school. The school offers Bachelor of Science in Business at the undergraduate level and Master of Business Administration degrees at the postgraduate level. Consistently ranked among the best business schools, Stern was ranked 1st among US schools for careers in finance on Wall Street in 2018, accounting for 3.9% of hires ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kahneman
Daniel Kahneman (; he, דניאל כהנמן; born March 5, 1934) is an Israeli-American psychologist and economist notable for his work on the psychology of judgment and decision-making, as well as behavioral economics, for which he was awarded the 2002 Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences (shared with Vernon L. Smith). His empirical findings challenge the assumption of human rationality prevailing in modern economic theory. With Amos Tversky and others, Kahneman established a cognitive basis for common human errors that arise from heuristics and biases, and developed prospect theory. In 2011 he was named by ''Foreign Policy'' magazine in its list of top global thinkers. In the same year his book ''Thinking, Fast and Slow'', which summarizes much of his research, was published and became a best seller. In 2015, ''The Economist'' listed him as the seventh most influential economist in the world. He is professor emeritus of psychology and public affairs at Princeton Unive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cultural Psychology
Cultural psychology is the study of how cultures reflect and shape the psychological processes of their members.Heine, S. J. (2011). ''Cultural Psychology. ''New York: W. W. Norton & Company. It is based on the premise that mind and culture are inseparable and mutually constitutive, meaning that people are shaped by their culture and their culture is also shaped by them.Fiske, A.; Kitayama, S.; Markus, H.R.; & Nisbett, R.E. (1998)The cultural matrix of social psychology In D. Gilbert & S. Fiske & G. Lindzey (Eds.), The Handbook of Social Psychology (4th ed., pp. 915–81). San Francisco: McGraw-Hill. Cultural psychology aims to define culture, its nature and function, specifically in relation to psychological phenomena. Gerd Baumann has argued: "Culture is not a real thing, but an abstract and purely analytical notion. In itself «it» does not «cause» behavior, but denotes an abstraction from it, and is thus neither normative nor predictive but a heuristic means towards explain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Positive Psychology
Positive psychology is the scientific study of what makes life most worth living, focusing on both individual and societal well-being. It studies "positive subjective experience, positive individual traits, and positive institutions...it aims to improve quality of life." It is a field of study that has been growing steadily throughout the years as individuals and researchers look for common ground on better well-being. Positive psychology began as a new domain of psychology in 1998 when Martin Seligman chose it as the theme for his term as president of the American Psychological Association. It is a reaction against past practices, which have tended to focus on mental illness and emphasized maladaptive behavior and negative thinking. It builds on the humanistic movement by Abraham Maslow, Rollo May, James Bugental, and Carl Rogers, which encourages an emphasis on happiness, well-being, and positivity, thus creating the foundation for what is now known as positive psychology. P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)

cropped.jpg)