|
John Wylde (lawyer)
John Wylde (or Wild; – 6 February 1840) was a Scottish advocate, academic and antiquarian. He was Professor of Civil Law at the University of Edinburgh. Life He was born in Edinburgh the son of John Wild, a tobacconist on the Royal Mile at the head of Fleshmarket Close. He was educated at the Edinburgh High School (then south of the Cowgate). He then studied law at the University of Edinburgh. He qualified as an advocate in 1785. In 1788 he was elected a Fellow of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. His proposers were Andrew Dalzell, John Hill, and John Clerk, Lord Eldin John Clerk, Lord Eldin FRSE FSA (1757– 30 May1832) was a Scottish judge based in Edinburgh. Life He was the eldest son of Susannah Adam, the sister of John Adam and Robert Adam, and John Clerk of Eldin. He was born in April 1757 in Edinburgh .... In 1790 he was living at North Castle Street in Edinburgh's New Town, then a newly built townhouse. In 1792 he became Joint Professor of Civil Law at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Edinburgh
The University of Edinburgh ( sco, University o Edinburgh, gd, Oilthigh Dhùn Èideann; abbreviated as ''Edin.'' in post-nominals) is a public research university based in Edinburgh, Scotland. Granted a royal charter by King James VI in 1582 and officially opened in 1583, it is one of Scotland's four ancient universities and the sixth-oldest university in continuous operation in the English-speaking world. The university played an important role in Edinburgh becoming a chief intellectual centre during the Scottish Enlightenment and contributed to the city being nicknamed the " Athens of the North." Edinburgh is ranked among the top universities in the United Kingdom and the world. Edinburgh is a member of several associations of research-intensive universities, including the Coimbra Group, League of European Research Universities, Russell Group, Una Europa, and Universitas 21. In the fiscal year ending 31 July 2021, it had a total income of £1.176 billion, of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
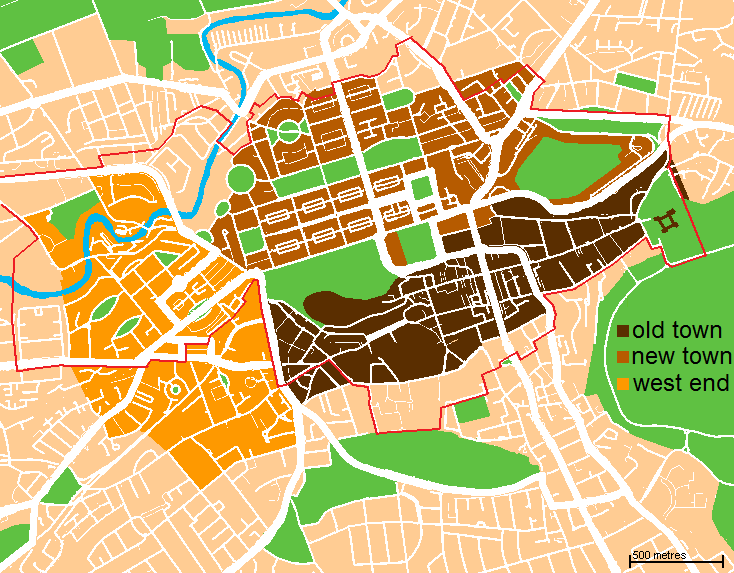
Royal Mile
The Royal Mile () is a succession of streets forming the main thoroughfare of the Old Town of the city of Edinburgh in Scotland. The term was first used descriptively in W. M. Gilbert's ''Edinburgh in the Nineteenth Century'' (1901), describing the city "with its Castle and Palace and the royal mile between", and was further popularised as the title of a guidebook by R. T. Skinner published in 1920, "''The Royal Mile (Edinburgh) Castle to Holyrood(house)''". The Royal Mile runs between two significant locations in the royal history of Scotland: Edinburgh Castle and Holyrood Palace. The name derives from it being the traditional processional route of monarchs, with a total length of approximately one Scots mile, a now obsolete measurement measuring 1.81km. The streets which make up the Royal Mile are (west to east) Castlehill, the Lawnmarket, the High Street, the Canongate and Abbey Strand. The Royal Mile is the busiest tourist street in the Old Town, rivalled only ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal High School, Edinburgh
The Royal High School (RHS) of Edinburgh is a co-educational school administered by the City of Edinburgh Council. The school was founded in 1128 and is one of the oldest schools in Scotland. It serves 1,200 pupils drawn from four feeder primaries in the north-west of the city: Blackhall primary school, Clermiston primary school, Cramond and Davidson's Mains. The school's profile has given it a flagship role in education, piloting such experiments as the introduction of the Certificate of Secondary Education, the provision of setting in English and mathematics, and the curricular integration of European Studies and the International Baccalaureate. The Royal High School was last inspected by HMIE in April 2007. The rector is Pauline Walker who replaced Jane Frith, the first woman to head the school. History The Royal High School is, by one reckoning, the 18th- oldest school in the world, with a history of almost 900 years. Historians associate its birth with the flowering o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Society Of Edinburgh
The Royal Society of Edinburgh is Scotland's national academy of science and letters. It is a registered charity that operates on a wholly independent and non-partisan basis and provides public benefit throughout Scotland. It was established in 1783. , there are around 1,800 Fellows. The Society covers a broader selection of fields than the Royal Society of London, including literature and history. Fellowship includes people from a wide range of disciplines – science & technology, arts, humanities, medicine, social science, business, and public service. History At the start of the 18th century, Edinburgh's intellectual climate fostered many clubs and societies (see Scottish Enlightenment). Though there were several that treated the arts, sciences and medicine, the most prestigious was the Society for the Improvement of Medical Knowledge, commonly referred to as the Medical Society of Edinburgh, co-founded by the mathematician Colin Maclaurin in 1731. Maclaurin was unhappy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andrew Dalzell
Andrew Dalzell (sometimes shown as Andrew Dalzel or Andrew Dalziel) FRSE (1742–1806) was a Scottish scholar and prominent figure during the Scottish Enlightenment. In 1783 he was a co-founder of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Life He was born in Gateside, Newliston near Linlithgow on 6 October 1742 the youngest son of William Dalzell, a carpenter, and his wife Alice Linn. His father died in 1751 and the young Dalzell then fell into the financial care of his namesake and uncle, the Rev Andrew Dalzell of Stoneykirk but remaining in Newliston under the supervision of Rev John Drysdale of Kirkliston. His early education was at Kirkliston Parish School, and then he attended Edinburgh University studying to be a minister in the footsteps of his uncle and adoptive father, but he was never licensed to preach. Instead (around 1765) he became the personal tutor of the Lauderdale family teaching in particular the young James (1758–1839), Thomas and Robert, later Lord Liston, the l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Hill (classicist)
John Hill FRSE (27 April 1747–7 December 1805) was a Scottish minister and classicist. In 1783 he was one of the joint founders of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Life He was born in St Andrews on 27 April 1747 the son of Rev John Hill (d. 1764), minister of St Andrews, and his wife Elizabeth Gowdie, daughter of John Gowdie. His mother died at or soon after his birth. His father remarried and had more children, including George Hill. He attended St Andrews Grammar School then the University of St Andrews where he graduated MA around 1767. From 1775 until 1793 he was joint Professor of Humanity at the University of St Andrews. The University of Edinburgh awarded him an honorary doctorate (LLD) in 1787. He then moved to the University of Edinburgh as the sole Professor of Humanity. His final years were spent at Brown Square in Edinburgh where he died on 7 December 1805. He is buried in Greyfriars Kirkyard against the western wall of the original area, north-west of the Adam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Clerk, Lord Eldin
John Clerk, Lord Eldin FRSE FSA (1757– 30 May1832) was a Scottish judge based in Edinburgh. Life He was the eldest son of Susannah Adam, the sister of John Adam and Robert Adam, and John Clerk of Eldin. He was born in April 1757 in Edinburgh. Though originally intended for the Indian Civil Service, he was apprenticed to a Writer to the Signet. After serving his articles he practised for a year or two as an accountant, and eventually was admitted a member of the Faculty of Advocates on 3 December 1785. He had an extensive practice at the bar. A keen Whig, on 11 March 1806 he was appointed Solicitor General for Scotland in the Grenville administration, an office which he held during the year that the ministry lasted. His practice at the bar had been for some time falling off, and his health had already begun to fail, when, on 10 November 1823, he was appointed an ordinary Lord of Session in place of William Bannatyne, Lord Bannatyne. Assuming the title of Lord Eldin, he took ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Town, Edinburgh
The New Town is a central area of Edinburgh, the capital of Scotland. It was built in stages between 1767 and around 1850, and retains much of its original neo-classical and Georgian period architecture. Its best known street is Princes Street, facing Edinburgh Castle and the Old Town across the geological depression of the former Nor Loch. Together with the West End, the New Town was designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site alongside the Old Town in 1995. The area is also famed for the New Town Gardens, a heritage designation since March 2001. Proposal and planning The idea of a New Town was first suggested in the late 17th century when the Duke of Albany and York (later King James VII and II), when resident Royal Commissioner at Holyrood Palace, encouraged the idea of having an extended regality to the north of the city and a North Bridge. He gave the city a grant:That, when they should have occasion to enlarge their city by purchasing ground without the town, or to build ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Dick
Robert Dick (January 1811 – 24 December 1866), was a Scottish geologist and botanist. Life He was born at Tullibody, in Clackmannanshire. His father was an officer of excise in nearby Alloa. At the age of thirteen, after receiving a good elementary education at the parish school, Dick was apprenticed to a baker, and served for three years. In these early days he became interested in wildflowers—he made a collection of plants and gradually acquired some knowledge of their names from an old encyclopedia. When his time was up he left Tullibody and gained employment as a journeyman baker at Leith, Glasgow and Greenock. Meanwhile, his father, who in 1826 had been removed to Thurso, as supervisor of excise, advised his son to set up a baker's shop in that town. Dick went there in 1830, started a business as a baker, and worked laboriously until his death. Throughout this period he zealously devoted himself to studying and collecting the plants, mollusca and insects of a wide a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old College, University Of Edinburgh
Old College is a late 18th-century to early 19th-century building of the University of Edinburgh, Scotland. It is located on South Bridge, and presently houses parts of the University's administration, the University of Edinburgh School of Law, and the Talbot Rice Gallery. Originally called the "New College", it was designed by Robert Adam to replace a number of older buildings previously built on the site of the former Kirk o' Field, and after considerable delays was completed to a modified design by William Henry Playfair, except for the dome added later. It is a Category A listed building. History Efforts by Edinburgh Town Council to build a college led to James VI of Scotland granting a royal charter in 1582 for what became known as the "Tounis College". On a visit in 1617 he expressed a wish that it be called "King James's College" and this became its formal name, but the older title remained in use for the town's college, which was also called ''Academia'' and sometim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Irving, Lord Newton
Alexander Irving, Lord Newton FRSE (1766–1832) was a Scottish judge who served as professor of civil law at Edinburgh University from 1800 to 1826. He was a Senator of the College of Justice. Life He was born on 12 October 1766, the son of George Irving of Newton, by Elvanfoot (South Lanarkshire). The Irvings of Newton were a cadet branch of the Scottish family the Irvines of Drum. He was educated at Edinburgh High School 1773 to 1777 and then studied law at Edinburgh University. He was created an advocate in 1788. He became a professor of civil law at Edinburgh University in 1800 and in the same year took over as manager of the Scots Mining Company, then based at Leadhills. In the final six years of his life he left the university to concentrate on his practical legal skills, becoming a Senator of the College of Justice (a High Court judge). At this time he was living at 5 Buccleuch Place, a large flat in Edinburgh's South Side. He later lived at 27 Heriot Row, Edinburgh. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1840 Deaths
__NOTOC__ Year 184 ( CLXXXIV) was a leap year starting on Wednesday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Eggius and Aelianus (or, less frequently, year 937 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 184 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place China * The Yellow Turban Rebellion and Liang Province Rebellion break out in China. * The Disasters of the Partisan Prohibitions ends. * Zhang Jue leads the peasant revolt against Emperor Ling of Han of the Eastern Han Dynasty. Heading for the capital of Luoyang, his massive and undisciplined army (360,000 men), burns and destroys government offices and outposts. * June – Ling of Han places his brother-in-law, He Jin, in command of the imperial army and sends them to attack the Yellow Turban rebels. * Winter – Zha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |