|
John Trumbull (poet)
John Trumbull (April 24, 1750 – May 11, 1831) was an American poet. Biography Trumbull was born in what is now Watertown, Connecticut, where his father was a Congregational preacher. At the age of seven he passed his entrance examinations at Yale, but did not enter until 1763; he graduated in 1767, studied law there, and in 1771–1773 was a tutor (taking part in teaching and supervising the undergraduates). While studying at Yale he had contributed in 1769–1770 ten essays, called "The Meddler", imitating ''The Spectator,'' to the ''Boston Chronicle,'' and in 1770 similar essays, signed " The Correspondent" to the '' Connecticut Journal and New Haven Post Boy.'' While a tutor he wrote his first satire in verse, '' The Progress of Dulness'' (1772–1773), an attack in three poems on educational methods of his time. His great poem, which ranks him with Philip Freneau and Francis Hopkinson as an American political satirist of the period of the War of Independence, was '' M'Fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
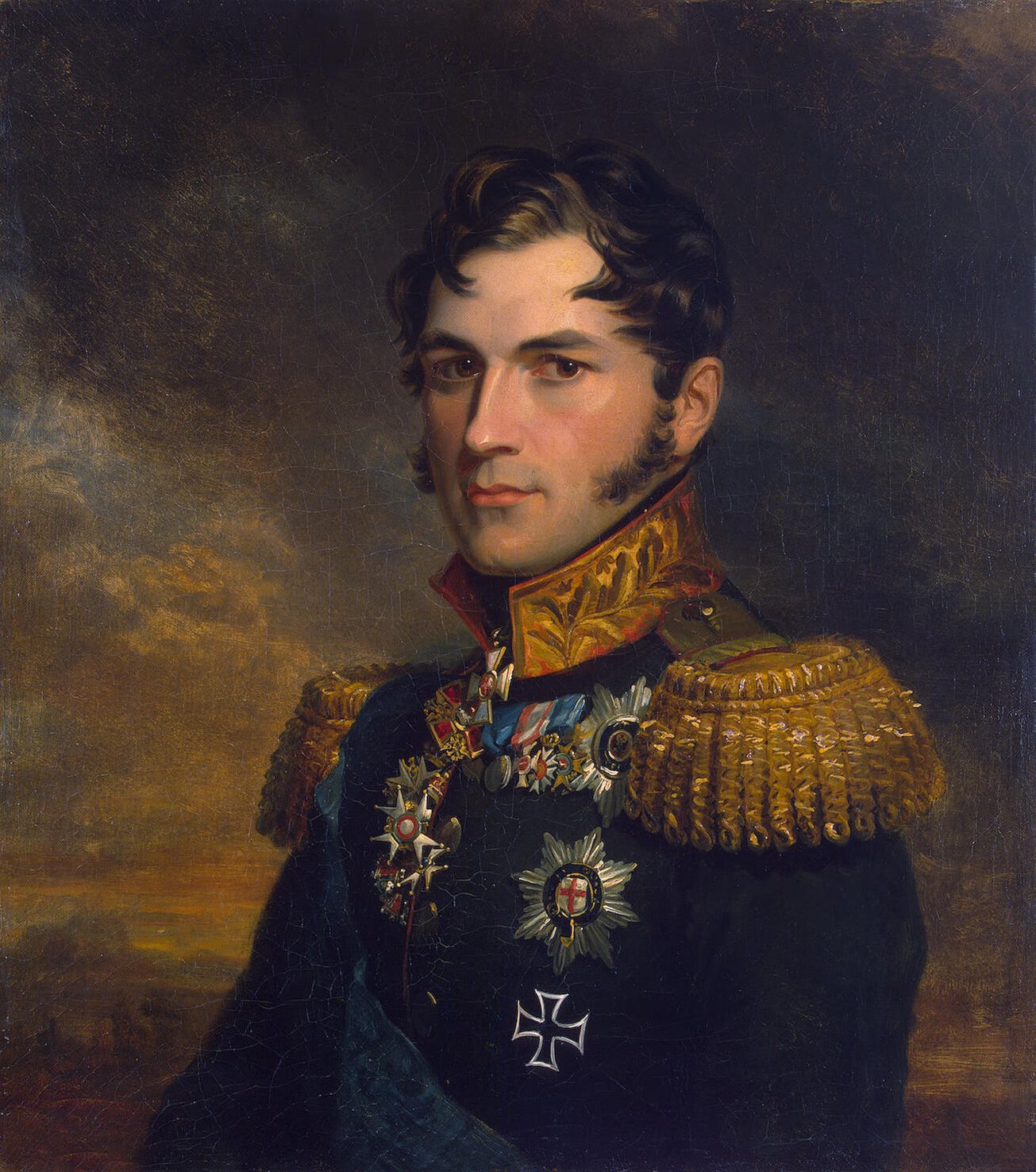
John Trumbull Painter John Trumbull Poet 1793
John is a common English name and surname: * John (given name) * John (surname) John may also refer to: New Testament Works * Gospel of John, a title often shortened to John * First Epistle of John, often shortened to 1 John * Second Epistle of John, often shortened to 2 John * Third Epistle of John, often shortened to 3 John People * John the Baptist (died c. AD 30), regarded as a prophet and the forerunner of Jesus Christ * John the Apostle (lived c. AD 30), one of the twelve apostles of Jesus * John the Evangelist, assigned author of the Fourth Gospel, once identified with the Apostle * John of Patmos, also known as John the Divine or John the Revelator, the author of the Book of Revelation, once identified with the Apostle * John the Presbyter, a figure either identified with or distinguished from the Apostle, the Evangelist and John of Patmos Other people with the given name Religious figures * John, father of Andrew the Apostle and Saint Peter * Pope John ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Federalism (United States)
Federalism in the United States is the constitutional division of power between U.S. state governments and the federal government of the United States. Since the founding of the country, and particularly with the end of the American Civil War, power shifted away from the states and toward the national government. The progression of federalism includes dual, cooperative, and new federalism. Early federalism Federalism is a form of political organization that seeks to distinguish states and unites them, which assigns different types of decision-making power at different levels to allow a degree of political independence in an overarching structure. Federalism was a political solution for the problems with the Articles of Confederation which gave little practical authority to the federal government. For example, the Articles allowed the Continental Congress the power to sign treaties and declare war, but it could not raise taxes to pay for an army and all major decisions requ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
18th-century American Male Writers
The 18th century lasted from January 1, 1701 ( MDCCI) to December 31, 1800 ( MDCCC). During the 18th century, elements of Enlightenment thinking culminated in the American, French, and Haitian Revolutions. During the century, slave trading and human trafficking expanded across the shores of the Atlantic, while declining in Russia, China, and Korea. Revolutions began to challenge the legitimacy of monarchical and aristocratic power structures, including the structures and beliefs that supported slavery. The Industrial Revolution began during mid-century, leading to radical changes in human society and the environment. Western historians have occasionally defined the 18th century otherwise for the purposes of their work. For example, the "short" 18th century may be defined as 1715–1789, denoting the period of time between the death of Louis XIV of France and the start of the French Revolution, with an emphasis on directly interconnected events. To historians who expan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
18th-century American Poets
The 18th century lasted from January 1, 1701 (Roman numerals, MDCCI) to December 31, 1800 (Roman numerals, MDCCC). During the 18th century, elements of Age of Enlightenment, Enlightenment thinking culminated in the American Revolution, American, French Revolution, French, and Haitian Revolution, Haitian Revolutions. During the century, History of slavery, slave trading and human trafficking expanded across the shores of the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, while declining in Russian Empire, Russia, Qing dynasty, China, and Joseon, Korea. Revolutions began to challenge the legitimacy of monarchical and aristocratic power structures, including the structures and beliefs that Proslavery, supported slavery. The Industrial Revolution began during mid-century, leading to radical changes in Society, human society and the Natural environment, environment. Western historians have occasionally defined the 18th century otherwise for the purposes of their work. For example, the "short" 18th cen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fellows Of The American Academy Of Arts And Sciences
{{disambiguation ...
Fellows may refer to Fellow, in plural form. Fellows or Fellowes may also refer to: Places *Fellows, California, USA *Fellows, Wisconsin, ghost town, USA Other uses *Fellows Auctioneers, established in 1876. *Fellowes, Inc., manufacturer of workspace products *Fellows, a partner in the firm of English canal carriers, Fellows Morton & Clayton *Fellows (surname) See also *North Fellows Historic District, listed on the National Register of Historic Places in Wapello County, Iowa *Justice Fellows (other) Justice Fellows may refer to: * Grant Fellows (1865–1929), associate justice of the Michigan Supreme Court * Raymond Fellows (1885–1957), associate justice of the Maine Supreme Judicial Court {{disambiguation, tndis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1831 Deaths
Events January–March * January 1 – William Lloyd Garrison begins publishing '' The Liberator'', an anti-slavery newspaper, in Boston, Massachusetts. * January 10 – Japanese department store, Takashimaya in Kyoto established. * February–March – Revolts in Modena, Parma and the Papal States are put down by Austrian troops. * February 2 – Pope Gregory XVI succeeds Pope Pius VIII, as the 254th pope. * February 5 – Dutch naval lieutenant Jan van Speyk blows up his own gunboat in Antwerp rather than strike his colours on the demand of supporters of the Belgian Revolution. * February 7 – The Belgian Constitution of 1831 is approved by the National Congress. *February 8 - Aimé Bonpland leaves Paraguay. * February 14 – Battle of Debre Abbay: Ras Marye of Yejju marches into Tigray, and defeats and kills the warlord Sabagadis. * February 25 – Battle of Olszynka Grochowska (Grochów): Polish rebel forces divide a Ru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1750 Births
Year 175 ( CLXXV) was a common year starting on Saturday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Piso and Iulianus (or, less frequently, year 928 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 175 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Roman Empire * Marcus Aurelius suppresses a revolt of Avidius Cassius, governor of Syria, after the latter proclaims himself emperor. * Avidius Cassius fails in seeking support for his rebellion and is assassinated by Roman officers. They send his head to Aurelius, who persuades the Senate to pardon Cassius's family. * Commodus, son of Marcus Aurelius and his wife Faustina, is named Caesar. * M. Sattonius Iucundus, decurio in Colonia Ulpia Traiana, restores the Thermae of Coriovallum (modern Heerlen) there are sources that state this happe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Detroit
Detroit ( , ; , ) is the largest city in the U.S. state of Michigan. It is also the largest U.S. city on the United States–Canada border, and the seat of government of Wayne County. The City of Detroit had a population of 639,111 at the 2020 census, making it the 27th-most populous city in the United States. The metropolitan area, known as Metro Detroit, is home to 4.3 million people, making it the second-largest in the Midwest after the Chicago metropolitan area, and the 14th-largest in the United States. Regarded as a major cultural center, Detroit is known for its contributions to music, art, architecture and design, in addition to its historical automotive background. ''Time'' named Detroit as one of the fifty World's Greatest Places of 2022 to explore. Detroit is a major port on the Detroit River, one of the four major straits that connect the Great Lakes system to the Saint Lawrence Seaway. The City of Detroit anchors the second-largest regional economy in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Academy Of Arts And Sciences
The American Academy of Arts and Sciences (abbreviation: AAA&S) is one of the oldest learned societies in the United States. It was founded in 1780 during the American Revolution by John Adams, John Hancock, James Bowdoin, Andrew Oliver, and other Founding Fathers of the United States. It is headquartered in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Membership in the academy is achieved through a thorough petition, review, and election process. The academy's quarterly journal, ''Dædalus'', is published by MIT Press on behalf of the academy. The academy also conducts multidisciplinary public policy research. History The Academy was established by the Massachusetts legislature on May 4, 1780, charted in order "to cultivate every art and science which may tend to advance the interest, honor, dignity, and happiness of a free, independent, and virtuous people." The sixty-two incorporating fellows represented varying interests and high standing in the political, professional, and commercial secto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Anarchiad
''The Anarchiad'' (1786–87) is an American mock-epic poem that reflected Federalist concerns during the formation of the United States. ''The Anarchiad, or American Antiquities: A Poem on the Restoration of Chaos and Substantial Night'' was penned by four members of the Hartford Wits: David Humphreys, John Trumbull, Joel Barlow, and Lemuel Hopkins. It was serialized in 12 parts in ''The New Haven Gazette and Connecticut Magazine'' between October 26, 1786 and September 13, 1787. ''The Anarchiad'' drew inspiration from Alexander Pope's satiric epics like ''The Dunciad'' and James MacPherson's forged Ossian cycle of epic poems, which inspired the pseudo-classical setting as a vehicle for satire. The poem purported to be fragments of an ancient heroic poem unearthed in ruined fortifications to the west. As a literary counterpart to ''The Federalist Papers'', the poem criticized the dysfunctional Articles of Confederation, demanded a stronger central government, and rebuked the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lemuel Hopkins
Lemuel Hopkins (June 19, 1750 – April 14, 1801) was an American poet and physician who was a member of the Hartford Wits, a group of literary satirists active in the late eighteenth century. A politically conservative Federalist, he coauthored '' The Anarchiad'' (1786–1787), a lengthy satiric poem critical of popular democracy and of the Articles of Confederation. His fellow authors on the poem were three other leading Wits: David Humphreys, Joel Barlow, and John Trumbull. Hopkins practiced medicine in Litchfield and Hartford and received an honorary Master of Arts degree from Yale University in 1784. Hopkins died of pneumonia and was interred at Hartford's Ancient Burying Ground. References External links * ''The Anarchiad: A New England Poem'' - full text via the Internet Archive The Internet Archive is an American digital library with the stated mission of "universal access to all knowledge". It provides free public access to collections of digitized ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joel Barlow
Joel Barlow (March 24, 1754 – December 26, 1812) was an American poet, and diplomat, and politician. In politics, he supported the French Revolution and was an ardent Jeffersonian republican. He worked as an agent for American speculator William Duer to set up the Scioto Company in Paris in 1788, and to sell worthless deeds to land in the Northwest Territory which it did not own. Scholars believe that he did not know the transactions were fraudulent. He stayed in Paris, becoming involved in the French Revolution. He was elected to the Assembly and given French citizenship in 1792. In his own time, Barlow was known especially for the epic poem '' The Columbiad'', a later version of the ''Vision of Columbus'' (1807),Brian PelandaDeclarations of Cultural Independence: The Nationalistic Imperative Behind the Passage of Early American Copyright Laws, 1783-1787 '' Journal of the Copyright Society of the U.S.A.'' Vol. 58 (2011), pp. 431, 442-448 . though modern readers rank '' The H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |