|
John Spratt Rainier
John Spratt Rainier (sometimes spelt Sprat; 1777 – 13 November 1822) was an officer in the Royal Navy, rising to the rank of Rear-Admiral, and Member of Parliament for Sandwich from 1808 to 1812. Life John Spratt Rainier was born in Sandwich, Kent in 1777, the second son of Daniel Rainier, a wine merchant who had served as mayor of Sandwich, and his wife Margaret, . His family were of Huguenot origin. Naval career His family had strong naval connections, and a number of John Rainier's relatives, including his uncle, Admiral Peter Rainier, and later his cousin, Captain Peter Rainier, had distinguished naval careers. After joining the Royal Navy and serving as a midshipman, John Rainier was promoted lieutenant in May 1794 and was posted to in 1795. This was the East Indies Station flagship of his uncle, Peter Rainier, whose patronage ensured his nephew's rapid promotion. By February 1796 John Rainier had been promoted locally to the rank of commander, with command of the 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sandwich (UK Parliament Constituency)
Sandwich was a parliamentary constituency in Kent, which elected two Members of Parliament (MPs) to the House of Commons from 1366 until 1885, when it was disfranchised for corruption. History Sandwich like most of the other Cinque Ports, was first enfranchised in the 14th century. As a Cinque Port it was technically of different status from a parliamentary borough, but the difference was in most respects purely a nominal one. (The writ for election was directed to the Lord Warden of the Cinque Ports, rather than the sheriff of the county, and its MPs were termed "barons" rather than "burgesses" as in boroughs.) Until 1832, the constituency consisted of the three parishes making up the town of Sandwich; it had once been a flourishing port but by the 19th century the harbour had silted up and there was only a limited maritime trade. The right to vote was reserved to the freemen of the town, whether or not they were resident within the borough. In 1831 this amounted to 955 qual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
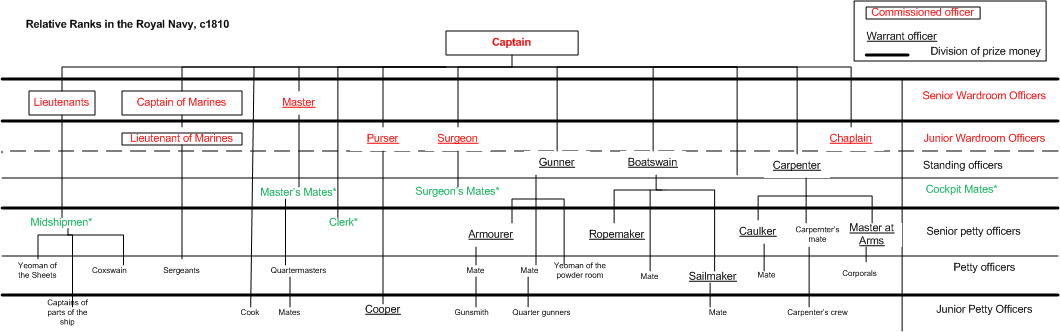
Commander (Royal Navy)
Commander (Cdr) is a senior officer rank of the Royal Navy of the United Kingdom. It is immediately junior to captain and immediately senior to the rank of lieutenant commander. Officers holding the junior rank of lieutenant commander are not considered to be commanders. History The title (originally 'master and commander') originated in around 1670 to describe Royal Navy officers who commanded ships of war too large to be commanded by a lieutenant, but too small to warrant the assignment of a post-captain, or (before about 1770) a sailing-master who was in charge of a ship's navigation. These ships were usually unrated sloops-of-war of no more than 20 guns, fireships, hospital ships and store ships. The commanding officer of this type of ship was responsible for both sailing and fighting the ship and was thus its 'master and commander'. Before 1750, the rank was broadly considered as the limit of advancement for those without patronage, especially those who had been promot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Museums Greenwich
Royal Museums Greenwich is an organisation comprising four museums in Greenwich, east London, illustrated below. The Royal Museums Greenwich Foundation is a Private Limited Company by guarantee without share capital use of 'Limited' exemption, company number 08002287, incorporated on 22 March 2012. It is Charity Commission for England and Wales, registered as charity number 1147279. For a year between 2016 and 2017 the Museum reported 2.41 million visitors to the National Maritime Museum. References External links * Museums in the Royal Borough of Greenwich, *Royal Museums Greenwich Musical instrument museums Non-departmental public bodies of the United Kingdom government Museums sponsored by the Department for Digital, Culture, Media and Sport {{UK-museum-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Half-pay
Half-pay (h.p.) was a term used in the British Army and Royal Navy of the 18th, 19th and early 20th centuries to refer to the pay or allowance an officer received when in retirement or not in actual service. Past usage United Kingdom In the English Army the option of half-pay developed during the late 17th and early 18th centuries, at the same time as the system of purchasing commissions and promotions by officers took hold. Serving officers could go on half-pay voluntarily, or be obliged to do so if their services were not required. In both cases, they could be summoned back to their regiments if there was a sudden need for their services. As an example, during the Jacobite rising of 1715, all listed half-pay officers were recalled to the army. In the long period of peace that the reduced British Army experienced after the Napoleonic Wars, the half-pay system became a means by which arduous overseas service could be avoided. Well-to-do officers who were promoted through the pu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Vizagapatam
The Battle of Vizagapatam was a minor naval engagement fought in the approaches to Vizagapatam harbour in the Coastal Andhra region of British India on the Bay of Bengal on 15 September 1804 during the Napoleonic Wars. A French squadron under Contre-Admiral Charles-Alexandre Léon Durand Linois in the ship of the line ''Marengo'' attacked the British Royal Navy fourth rate ship HMS ''Centurion'' and two East Indiaman merchant ships anchored in the harbour roads. Linois was engaged in an extended raiding campaign, which had already involved operations in the South China Sea, in the Mozambique Channel, off Ceylon and along the Indian coast of the Bay of Bengal. The French squadron had fought one notable engagement, at the Battle of Pulo Aura on 15 February 1804, in which Linois had attacked the Honourable East India Company's (HEIC) China Fleet, a large convoy of well-armed merchant ships carrying cargo worth £8 million. Linois failed to press the attack and withdrew with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prize Money
Prize money refers in particular to naval prize money, usually arising in naval warfare, but also in other circumstances. It was a monetary reward paid in accordance with the prize law of a belligerent state to the crew of a ship belonging to the state, either a warship of its navy or a privateer vessel commissioned by the state. Prize money was most frequently awarded for the capture of enemy ships or of cargoes belonging to an enemy in time of war, either arrested in port at the outbreak of war or captured during the war in international waters or other waters not the territorial waters of a neutral state. Goods carried in neutral ships that are classed as contraband, being shipped to enemy-controlled territory and liable to be useful to it for making war, were also liable to be taken as prizes, but non-contraband goods belonging to neutrals were not. Claims for the award of prize money were usually heard in a prize court, which had to adjudicate the claim and condemn the priz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Jakarta
Jakarta is Indonesia's capital and largest city. Located on an estuary of the Ciliwung River, on the northwestern part of Java, the area has long sustained human settlement. Historical evidence from Jakarta dates back to the 4th century CE, when it was a Hindu settlement and port. The city has been sequentially claimed by the Indianized kingdom of Tarumanegara, the Hindu Kingdom of Sunda, the Muslim Sultanate of Banten, and by Dutch, Japanese and Indonesian administrations. The Dutch East Indies built up the area before it was taken during World War II by the Empire of Japan and finally became independent as part of Indonesia. Jakarta has been known by several names. It was called Sunda Kelapa during the Kingdom of Sunda period and Jayakarta, Djajakarta or Jacatra during the short period of the Banten Sultanate. Thereafter, Jakarta evolved in three stages. The " old city", close to the sea in the north, developed between 1619 and 1799 during the era of the VOC. The "new city" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
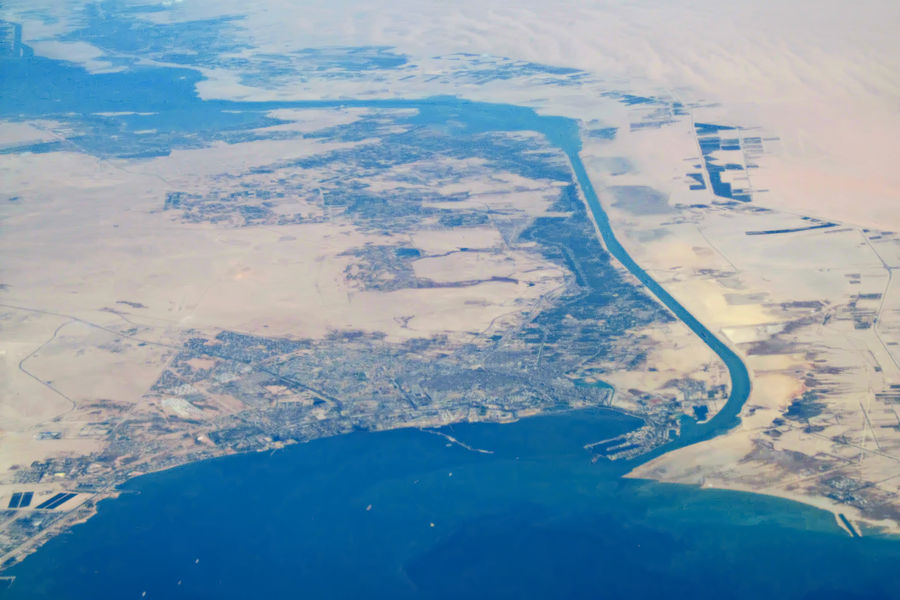
Suez
Suez ( ar, السويس '; ) is a seaport city (population of about 750,000 ) in north-eastern Egypt, located on the north coast of the Gulf of Suez (a branch of the Red Sea), near the southern terminus of the Suez Canal, having the same boundaries as Suez Governorate. It has three harbours, Adabiya, Ain Sokhna and Port Tawfiq, and extensive port facilities. Together they form a metropolitan area, located mostly in Africa with a small portion in Asia. Railway lines and highways connect the city with Cairo, Port Said, and Ismailia. Suez has a petrochemical plant, and its oil refineries have pipelines carrying the finished product to Cairo. These are represented in the flag of the governorate: the blue background refers to the sea, the gear refers to Suez's status as an industrial governorate, and the flame refers to the petroleum firms of Suez. The modern city of Suez is a successor of the ancient city of Clysma (, meaning "surf, waves that break"; ; ), a major Red Sea por ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Sea
The Red Sea ( ar, البحر الأحمر - بحر القلزم, translit=Modern: al-Baḥr al-ʾAḥmar, Medieval: Baḥr al-Qulzum; or ; Coptic: ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϩⲁϩ ''Phiom Enhah'' or ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϣⲁⲣⲓ ''Phiom ǹšari''; Tigrinya: ቀይሕ ባሕሪ ''Qeyih Bahri''; ) is a seawater inlet of the Indian Ocean, lying between Africa and Asia. Its connection to the ocean is in the south, through the Bab el Mandeb strait and the Gulf of Aden. To its north lie the Sinai Peninsula, the Gulf of Aqaba, and the Gulf of Suez (leading to the Suez Canal). It is underlain by the Red Sea Rift, which is part of the Great Rift Valley. The Red Sea has a surface area of roughly 438,000 km2 (169,100 mi2), is about 2250 km (1398 mi) long, and — at its widest point — 355 km (220.6 mi) wide. It has an average depth of 490 m (1,608 ft), and in the central ''Suakin Trough'' it reaches its maximum depth of . The Red Sea also has exten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dutch Cape Colony
The Cape Colony ( nl, Kaapkolonie) was a Dutch United East India Company (VOC) colony in Southern Africa, centered on the Cape of Good Hope, from where it derived its name. The original colony and its successive states that the colony was incorporated into occupied much of modern South Africa. Between 1652 and 1691 it was a Commandment, and between 1691 and 1795 a Governorate of the United East India Company (VOC). Jan van Riebeeck established the colony as a re-supply and layover port for vessels of the VOC trading with Asia. The Cape came under VOC rule from 1652 to 1795 and from 1803 to 1806 was ruled by the Batavian Republic. Much to the dismay of the shareholders of the VOC, who focused primarily on making profits from the Asian trade, the colony rapidly expanded into a settler colony in the years after its founding. As the only permanent settlement of the Dutch United East India Company not serving as a trading post, it proved an ideal retirement place for employees ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capitulation Of Saldanha Bay
The Capitulation of Saldanha Bay was the surrender in 1796 to the British Royal Navy of a Dutch expeditionary force sent to recapture the Dutch Cape Colony. In 1794, early in the French Revolutionary Wars, the army of the French Republic overran the Dutch Republic which then became a French client state, the Batavian Republic. Great Britain was concerned by the threat the Dutch Cape Colony in Southern Africa posed to its trade routes to British India. It therefore sent an expeditionary force that landed at Simon's Town in June 1795 and forced the surrender of the colony in a short campaign. The British commander, Vice-Admiral Sir George Elphinstone, then reinforced the garrison and stationed a naval squadron at the Cape to protect the captured colony. The Batavian government, not yet aware of the capture of the Cape Colony, but worried by rumors of the loss of this and other colonies of the Dutch East India Company (which was about to be nationalized by the Batavian Republic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Post-captain
Post-captain is an obsolete alternative form of the rank of Captain (Royal Navy), captain in the Royal Navy. The term served to distinguish those who were captains by rank from: * Officers in command of a naval vessel, who were (and still are) addressed as captain regardless of rank; * Commander (Royal Navy), Commanders, who received the title of captain as a courtesy, whether they currently had a command or not (e.g. the fictional Captain Jack Aubrey in ''Aubrey-Maturin series#Master and Commander, Master and Commander'' or the fictional Captain Horatio Hornblower in ''Hornblower and the Hotspur''); this custom is now defunct. In the Royal Navy of the 18th and 19th centuries, an officer might be promoted from commander to captain, but not have a command. Until the officer obtained a command, he was "on the beach" and on half-pay. An officer "took post" or was "made post" when he was first commissioned to command a vessel. Usually this was a rating system of the Royal Navy, ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |