|
John Mason (governor)
Captain John Mason (1586–1635) was a sailor and colonist who was instrumental to the establishment of various settlements in colonial America. Born in 1586 at King's Lynn, Norfolk, and educated at Peterhouse, Cambridge. In 1610, he was appointed by James I to help reclaim the Hebrides. As a reward, he was granted exclusive fishing rights in the North Sea. This was ignored by the Dutch and he was treated as a pirate by the Scots. In 1615, he was arrested, but soon released after the seizure of his ship. He was appointed the second Proprietary Governor of Newfoundland's Cuper's Cove colony in 1615, succeeding John Guy. Mason arrived on the island in 1616 and explored much of the territory. He compiled a map of the island and wrote and published a short tract (or "Discourse") of his findings. Mason drew up a map of the island of Newfoundland. Published in William Vaughan's Cambrensium Caroleia in 1625, the map included previously established placenames as well as new ones such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James I Of England
James VI and I (James Charles Stuart; 19 June 1566 – 27 March 1625) was King of Scotland as James VI from 24 July 1567 and King of England and King of Ireland, Ireland as James I from the Union of the Crowns, union of the Scottish and English crowns on 24 March 1603 until his death in 1625. The kingdoms of Kingdom of Scotland, Scotland and Kingdom of England, England were individual sovereign states, with their own parliaments, judiciaries, and laws, though both were ruled by James in personal union. James was the son of Mary, Queen of Scots, and a great-great-grandson of Henry VII of England, Henry VII, King of England and Lord of Ireland, and thus a potential successor to all three thrones. He succeeded to the Scottish throne at the age of thirteen months, after his mother was compelled to abdicate in his favour. Four different regents governed during his minority, which ended officially in 1578, though he did not gain full control of his government until 1583. In 1603, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subdivision 1I, Newfoundland And Labrador
Division No. 1, Subdivision I is an unorganized subdivision on the Avalon Peninsula in Newfoundland and Labrador, Canada. It is in Division 1 and contains the unincorporated community of Bristol's Hope. Bristol's Hope Bristol's Hope is the modern name of a community in the province of Newfoundland and Labrador, Canada. It is located on Conception Bay between Carbonear and Harbour Grace. The place names Musket's Cove and Mosquito have been used since about the 1630s to refer to the area now called Bristol's Hope (Seary 1971: 63). The community was renamed in 1904 to commemorate the 1617 outpost of that name, an offshoot of the John Guy colony established at Cupids, ten miles away, in 1610 (Dale 1981a). The Plantation of Bristol's Hope was the second English colony in Newfoundland established by the Bristol Society of Merchant Venturers. It was a "sister" colony to Cuper's Cove, established in 1618 with a land grant from King James I of England, and was settled by some of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Massachusetts
Massachusetts (Massachusett language, Massachusett: ''Muhsachuweesut [Massachusett writing systems, məhswatʃəwiːsət],'' English: , ), officially the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, is the most populous U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders on the Atlantic Ocean and Gulf of Maine to the east, Connecticut and Rhode Island to the south, New Hampshire and Vermont to the north, and New York (state), New York to the west. The state's capital and List of municipalities in Massachusetts, most populous city, as well as its cultural and financial center, is Boston. Massachusetts is also home to the urban area, urban core of Greater Boston, the largest metropolitan area in New England and a region profoundly influential upon American History of the United States, history, academia, and the Economy of the United States, research economy. Originally dependent on agriculture, fishing, and trade. Massachusetts was transformed into a manuf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Hampshire
New Hampshire is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the northeastern United States. It is bordered by Massachusetts to the south, Vermont to the west, Maine and the Gulf of Maine to the east, and the Canadian province of Quebec to the north. Of the 50 U.S. states, New Hampshire is the List of U.S. states and territories by area, fifth smallest by area and the List of U.S. states and territories by population, tenth least populous, with slightly more than 1.3 million residents. Concord, New Hampshire, Concord is the state capital, while Manchester, New Hampshire, Manchester is the largest city. New Hampshire's List of U.S. state mottos, motto, "Live Free or Die", reflects its role in the American Revolutionary War; its state nickname, nickname, "The Granite State", refers to its extensive granite formations and quarries. It is well known nationwide for holding New Hampshire primary, the first primary (after the Iowa caucus) in the United States presidential election ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
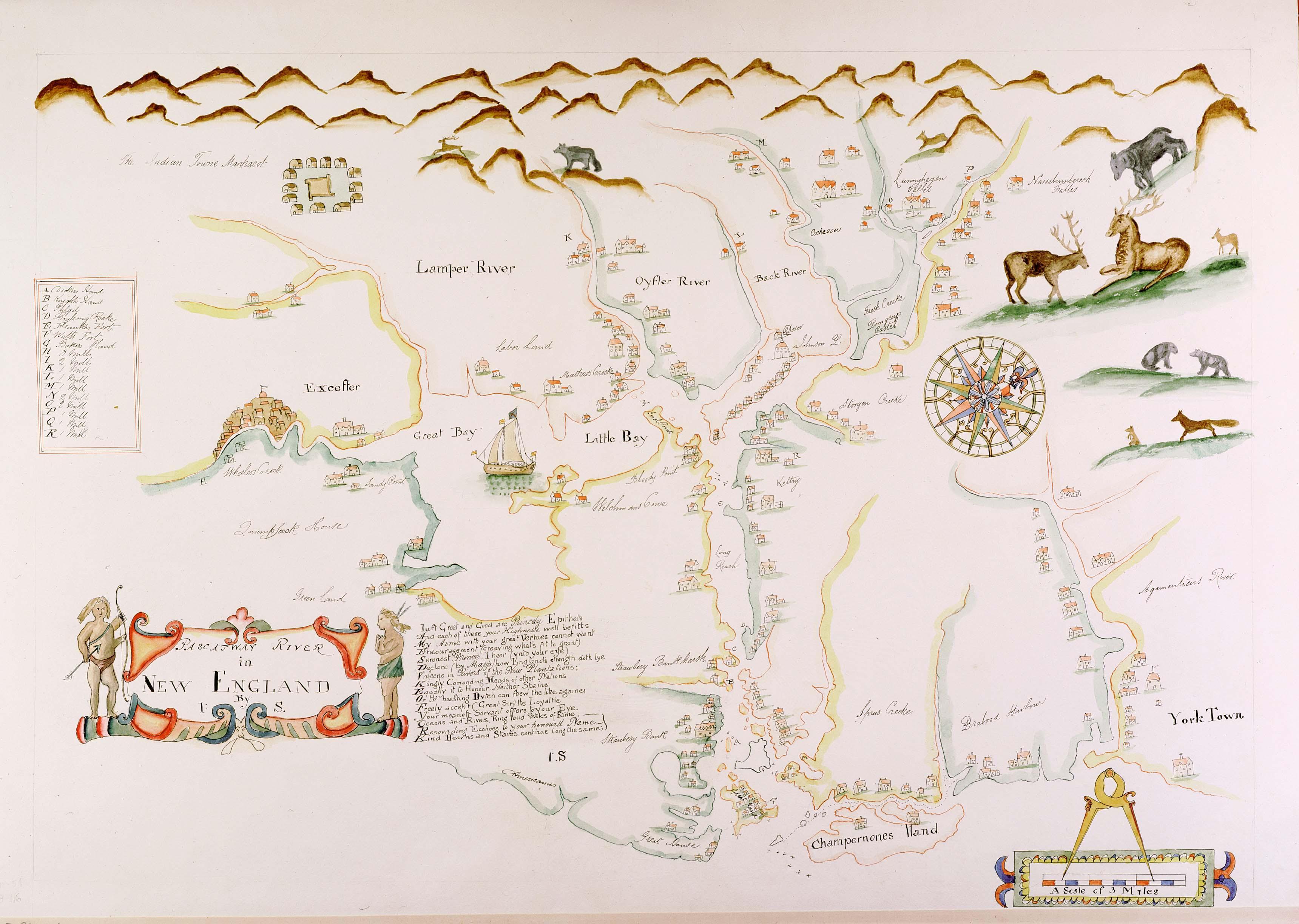
Piscataqua River
The Piscataqua River (Abenaki: ''Pskehtekwis'') is a tidal river forming the boundary of the U.S. states of New Hampshire and Maine from its origin at the confluence of the Salmon Falls River and Cochecho River. The drainage basin of the river is approximately , including the subwatersheds of the Great Works River and the five rivers flowing into Great Bay: the Bellamy, Oyster, Lamprey, Squamscott, and Winnicut. The river runs southeastward, with New Hampshire to the south and west and Maine to the north and east, and empties into the Gulf of Maine east of Portsmouth, New Hampshire. The last before the sea are known as Portsmouth Harbor and have a tidal current of around . The cities/towns of Portsmouth, New Castle, Newington, Kittery and Eliot have developed around the harbor. History Named by the area's original Abenaki inhabitants, the word ''Piscataqua'' is believed to be a combination of ''peske'' (branch) with ''tegwe'' (a river with a strong current, possibl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kennebec River
The Kennebec River (Abenaki language, Abenaki: ''Kinəpékʷihtəkʷ'') is a U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map , accessed June 30, 2011 river within the U.S. state of Maine. It rises in Moosehead Lake in west-central Maine. The East and West Outlets join at Indian Pond and the river flows southward. Harris Station Dam, the largest hydroelectric dam in the state, was constructed near that confluence. The river is joined at The Forks, Maine, The Forks by its tributary the Dead River (Kennebec River), Dead River, also called the West Branch. It continues south past the cities of Madison, Maine, Madison, Skowhegan, Maine, Skowhegan, Waterville, Maine, Waterville, and the state capital Augusta, Maine, Augusta. At Richmond, Maine, Richmond, it flows into Merrymeeting Bay, a freshwater tidal bay into which also flow the Androscoggin River and five smaller rivers. The Kennebec runs past the shipbuilding center of Bath, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Merrimack River
The Merrimack River (or Merrimac River, an occasional earlier spelling) is a river in the northeastern United States. It rises at the confluence of the Pemigewasset and Winnipesaukee rivers in Franklin, New Hampshire, flows southward into Massachusetts, and then flows northeast until it empties into the Gulf of Maine at Newburyport. From Pawtucket Falls in Lowell, Massachusetts, onward, the Massachusetts–New Hampshire border is roughly calculated as the line three miles north of the river. The Merrimack is an important regional focus in both New Hampshire and Massachusetts. The central-southern part of New Hampshire and most of northeast Massachusetts is known as the Merrimack Valley. Several U.S. naval ships have been named and USS ''Merrimac'' in honor of this river. The river is perhaps best known for the early American literary classic ''A Week on the Concord and Merrimack Rivers'' by Henry David Thoreau. Etymology and spelling The etymology of the name of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plymouth Council For New England
The Council for New England was a 17th-century English joint stock company that was granted a royal charter to found colonial settlements along the coast of North America. The Council was established in November of 1620, and was disbanded (although with no apparent changes in land titles) in 1635. It provided for the establishment of the Plymouth Colony, the State of New Hampshire, the Massachusetts Bay Colony, the New Haven Colony, and the eventual State of Maine. It was largely the creation of Sir Ferdinand Gorges. Some of the persons involved had previously received a charter in 1606 as the Plymouth Company and had founded the short-lived Popham Colony within the territory of northern Virginia (actually in present-day Maine in the United States). The company had fallen into disuse following the abandonment of the 1607 colony. The Council was re-established after, with support from Gorges, (1) Captain John Smith had completed a thorough survey of the Atlantic side of New Englan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Land Patent
A land patent is a form of letters patent assigning official ownership of a particular tract of land that has gone through various legally-prescribed processes like surveying and documentation, followed by the letter's signing, sealing, and publishing in public records, made by a sovereign entity. It is the highest evidence of right, title, and interest to a defined area. It is usually granted by a central, federal, or state government to an individual, partnership, trust, or private company. The land patent is not to be confused with a land grant. Patented lands may be lands that had been granted by a sovereign authority in return for services rendered or accompanying a title or otherwise bestowed ''gratis'', or they may be lands privately purchased by a government, individual, or legal entity from their prior owners. "Patent" is both a process and a term. As a process, it is somewhat parallel to gaining a patent for intellectual property, including the steps of uniquely def ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferdinando Gorges
Sir Ferdinando Gorges ( – 24 May 1647) was a naval and military commander and governor of the important port of Plymouth in England. He was involved in Essex's Rebellion against the Queen, but escaped punishment by testifying against the main conspirators. His early involvement in English trade with and settlement of North America as well as his efforts in founding the Province of Maine in 1622 earned him the title of the "Father of English Colonization in North America," even though Gorges himself never set foot in the New World. Origins Ferdinando Gorges was born between 1565 and 1568, probably in Clerkenwell, in Middlesex where the family maintained their London town house, but possibly at the family's manor of Wraxall, in Somerset. He was the second son of Edward Gorges of Wraxall, by his wife Cicely Lygon. The circumstances of his father's death aged 31 suggested to Baxter (Gorges's first biographer) that Ferdinando was born at about the time of his father's death on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia ( ; ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is one of the three Maritime provinces and one of the four Atlantic provinces. Nova Scotia is Latin for "New Scotland". Most of the population are native English-speakers, and the province's population is 969,383 according to the 2021 Census. It is the most populous of Canada's Atlantic provinces. It is the country's second-most densely populated province and second-smallest province by area, both after Prince Edward Island. Its area of includes Cape Breton Island and 3,800 other coastal islands. The Nova Scotia peninsula is connected to the rest of North America by the Isthmus of Chignecto, on which the province's land border with New Brunswick is located. The province borders the Bay of Fundy and Gulf of Maine to the west and the Atlantic Ocean to the south and east, and is separated from Prince Edward Island and the island of Newfoundland by the Northumberland and Cabot straits, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Alexander, Earl Of Stirling
William Alexander, 1st Earl of Stirling (c. 1567 in Menstrie, Clackmannanshire12 February 1640) was a Scottish courtier and poet who was involved in the Scottish colonisation of Charles Fort, later Port-Royal, Nova Scotia in 1629 and Long Island, New York. His literary works include ''Aurora'' (1604), ''The Monarchick Tragedies'' (1604) and ''Doomes-Day'' (1614, 1637). Biography Early life William Alexander was the son of Alexander of Menstrie and Marion, daughter of an Allan Couttie. He was born at Menstrie Castle, near Stirling. The family was old and claimed to be descended from Somerled, Lord of the Isles, through John of Islay. Because his father died in 1580, and William was entrusted to the care of his great-uncle James in Stirling, he was probably educated at Stirling grammar school. There is a tradition that he was at the University of Glasgow; and, according to his friend the poet William Drummond of Hawthornden, he was a student at Leiden University. As a young man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |