|
John Lloyd Stephens
John Lloyd Stephens (November 28, 1805October 13, 1852) was an American explorer, writer, and diplomat. Stephens was a pivotal figure in the rediscovery of Maya civilization throughout Middle America and in the planning of the Panama railroad. Early life John Lloyd Stephens was born November 28, 1805, in the township of Shrewsbury, New Jersey. He was the second son of Benjamin Stephens, a successful New Jersey merchant, and Clemence Lloyd, daughter of an eminent local judge. The following year the family moved to New York City. There Stephens received an education in the Classics at two privately tutored schools. At the age of 13 he enrolled at Columbia College, graduating at the top of his class four years later in 1822. After studying law with an attorney for a year, he attended the Litchfield Law School. He passed the bar exam after completing his course of study, and practiced in New York City. Stephens embarked on a journey through Europe in 1834, and went on to Egypt an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shrewsbury, New Jersey
Shrewsbury is a Borough (New Jersey), borough in Monmouth County, New Jersey, Monmouth County, New Jersey, United States. Centrally located in the Jersey Shore region in the New York Metropolitan area, the borough is an historic bedroom community of New York City. As of the 2010 United States Census, the borough's population was 3,809,DP-1 – Profile of General Population and Housing Characteristics: 2010 for Shrewsbury borough, Monmouth County, New Jersey , United States Census Bureau. Accessed August 1, 2012. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Von Humboldt
Friedrich Wilhelm Heinrich Alexander von Humboldt (14 September 17696 May 1859) was a German polymath, geographer, naturalist, explorer, and proponent of Romantic philosophy and science. He was the younger brother of the Prussian minister, philosopher, and linguist Wilhelm von Humboldt (1767–1835). Humboldt's quantitative work on botanical geography laid the foundation for the field of biogeography. Humboldt's advocacy of long-term systematic geophysical measurement laid the foundation for modern geomagnetic and meteorological monitoring. Between 1799 and 1804, Humboldt travelled extensively in the Americas, exploring and describing them for the first time from a modern Western scientific point of view. His description of the journey was written up and published in several volumes over 21 years. Humboldt was one of the first people to propose that the lands bordering the Atlantic Ocean were once joined (South America and Africa in particular). Humboldt resurrected the use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graham's Magazine
''Graham's Magazine'' was a nineteenth-century periodical based in Philadelphia established by George Rex Graham and published from 1840 to 1858. It was alternatively referred to as ''Graham's Lady's and Gentleman's Magazine'' (1841–1842, and July 1843 – June 1844), ''Graham's Magazine of Literature and Art'' (January 1844 – June 1844), ''Graham's American Monthly Magazine of Literature and Art'' (July 1848 – June 1856), and ''Graham's Illustrated Magazine of Literature, Romance, Art, and Fashion'' (July 1856 – 1858). The journal was founded after the merger of ''Burton's Gentleman's Magazine'' and ''Atkinson's Casket'' in 1840. Publishing short stories, critical reviews, and music as well as information on fashion, Graham intended the journal to reach all audiences including both men and women. He offered the high payment of $5 per page, successfully attracting some of the best-known writers of the day. It also became known for its engravings and artwork. ''Graham's'' m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edgar Allan Poe
Edgar Allan Poe (; Edgar Poe; January 19, 1809 – October 7, 1849) was an American writer, poet, editor, and literary critic. Poe is best known for his poetry and short stories, particularly his tales of mystery and the macabre. He is widely regarded as a central figure of Romanticism in the United States, and of American literature. Poe was one of the country's earliest practitioners of the short story, and considered to be the inventor of the detective fiction genre, as well as a significant contributor to the emerging genre of science fiction. Poe is the first well-known American writer to earn a living through writing alone, resulting in a financially difficult life and career. Poe was born in Boston, the second child of actors David and Elizabeth "Eliza" Poe. His father abandoned the family in 1810, and when his mother died the following year, Poe was taken in by John and Frances Allan of Richmond, Virginia. They never formally adopted him, but he was with them well ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yucatán (state)
Yucatán (, also , , ; yua, Yúukatan ), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Yucatán,; yua, link=no, Xóot' Noj Lu'umil Yúukatan. is one of the 31 states which comprise the federal entities of Mexico. It comprises 106 separate municipalities, and its capital city is Mérida. It is located on the northern part of the Yucatán Peninsula. It is bordered by the states of Campeche to the southwest and Quintana Roo to the southeast, with the Gulf of Mexico off its northern coast. Before the arrival of Spaniards in the Yucatán Peninsula, the name of this region was ''Mayab''. In the Yucatec Maya language, ''mayab'' means "flat", and is the source of the word "Maya" itself. The peninsula was a very important region for the Maya civilization, which reached the peak of its development here, where the Mayans founded the cities of Chichen Itza, Izamal, Motul, Mayapan, Ek' Balam and Ichcaanzihóo (also called Ti'ho), now Mérida. After the Spanish conquest of Yucatán (e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
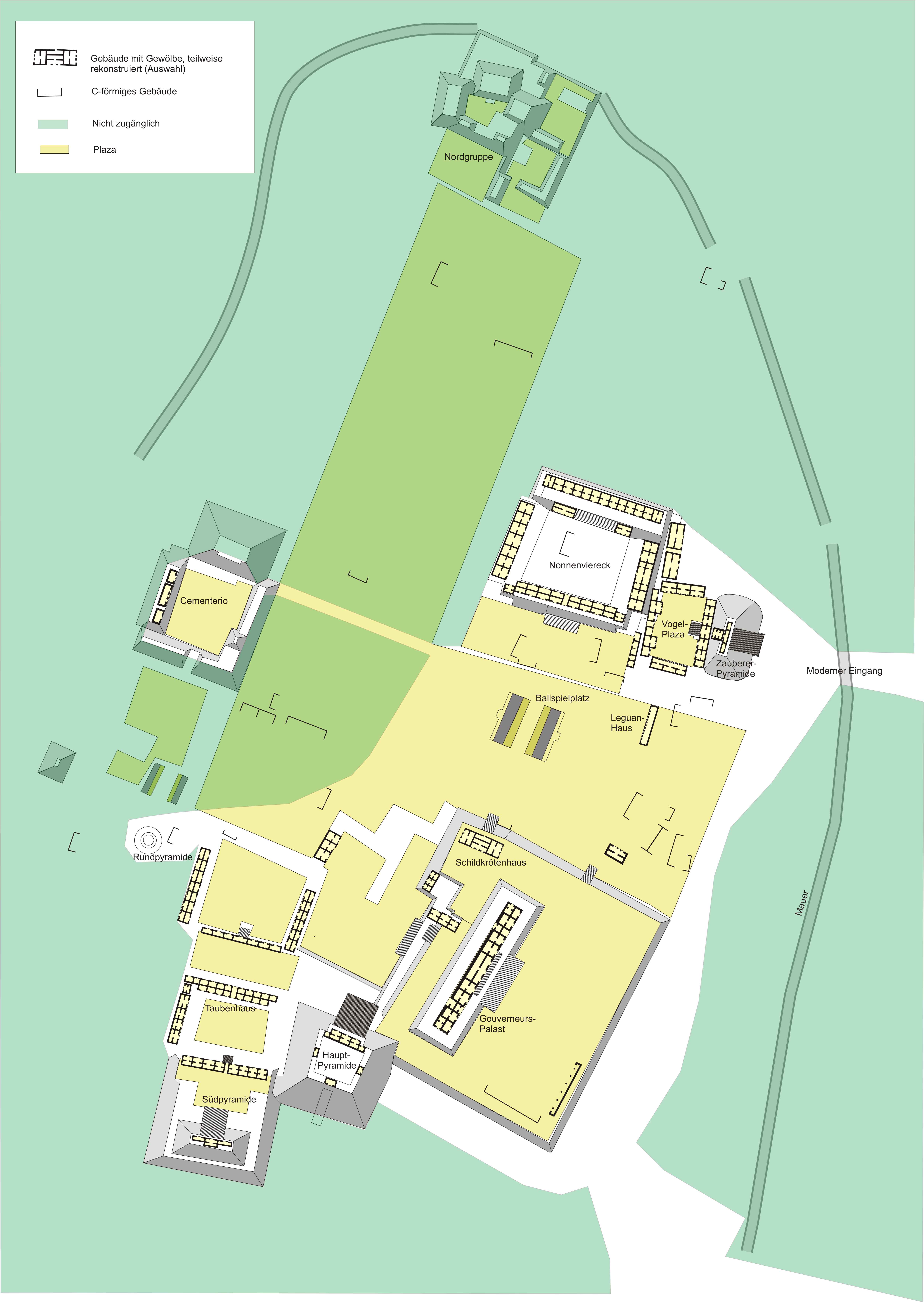
Uxmal
Uxmal (Yucatec Maya: ''Óoxmáal'' ) is an ancient Maya city of the classical period located in present-day Mexico. It is considered one of the most important archaeological sites of Maya culture, along with Palenque, Chichen Itza and Calakmul in Mexico, Caracol and Xunantunich in Belize, and Tikal in Guatemala. It is located in the Puuc region of the eastern Yucatán Peninsula, and is considered one of the Maya cities most representative of the region's dominant architectural style. It has been designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site in recognition of its significance. Uxmal is located 62 km south of Mérida, capital of Yucatán state in Mexico. Its buildings are noted for their size and decoration. Ancient roads called ''sacbes'' connect the buildings, and also were built to other cities in the area such as Chichén Itzá in modern-day Mexico, Caracol and Xunantunich in modern-day Belize, and Tikal in modern-day Guatemala. Its buildings are typical of the Puuc style, wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quiriguá
Quiriguá () is an ancient Maya archaeological site in the department of Izabal in south-eastern Guatemala. It is a medium-sized site covering approximately along the lower Motagua River, with the ceremonial center about from the north bank. During the Maya Classic Period (AD 200–900), Quiriguá was situated at the juncture of several important trade routes. The site was occupied by 200, construction on the acropolis had begun by about 550, and an explosion of grander construction started in the 8th century. All construction had halted by about 850, except for a brief period of reoccupation in the Early Postclassic (''c''. 900 – ''c''. 1200). Quiriguá shares its architectural and sculptural styles with the nearby Classic Period city of Copán, with whose history it is closely entwined. Quiriguá's rapid expansion in the 8th century was tied to king K'ak' Tiliw Chan Yopaat's military victory over Copán in 738. When the greatest king of Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palenque
Palenque (; Yucatec Maya language, Yucatec Maya: ), also anciently known in the Itza Language as Lakamhaʼ ("Big Water or Big Waters"), was a Maya city City-state, state in southern Mexico that perished in the 8th century. The Palenque ruins date from ca. 226 BC to ca. 799 AD. After its decline, it was overgrown by the Selva Lacandona, jungle of cedar, mahogany, and sapodilla trees, but has since been excavated and restored. It is located near the Usumacinta River in the Mexican state of Chiapas, about 130 km (81 mi) south of Ciudad del Carmen, above sea level. It averages a humid 26°C (79°F) with roughly of rain a year. Palenque is a medium-sized site, smaller than Tikal, Chichen Itza, or Copán, but it contains some of the finest architecture, sculpture, roof comb and bas-relief carvings that the Maya civilization, Mayas produced. Much of the history of Palenque has been reconstructed from reading the hieroglyphic inscriptions on the many monuments; historians now have a l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belize
Belize (; bzj, Bileez) is a Caribbean and Central American country on the northeastern coast of Central America. It is bordered by Mexico to the north, the Caribbean Sea to the east, and Guatemala to the west and south. It also shares a water boundary with Honduras to the southeast. It has an area of and a population of 441,471 (2022). Its mainland is about long and wide. It is the least populated and least densely populated country in Central America. Its population growth rate of 1.87% per year (2018 estimate) is the second-highest in the region and one of the highest in the Western Hemisphere. Its capital is Belmopan, and its largest city is the namesake city of Belize City. Belize is often thought of as a Caribbean country in Central America because it has a history similar to that of English-speaking Caribbean nations. Indeed, Belize’s institutions and official language reflect its history as a British colony. The Maya civilization spread into the area of Beli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Honduras
British Honduras was a British Crown colony on the east coast of Central America, south of Mexico, from 1783 to 1964, then a self-governing colony, renamed Belize in June 1973,CARICOM - Member Country Profile - BELIZE , . Accessed 23 June 2015. until September 1981, when it gained full independence as . British Honduras was the last continental possession of the United Kingdom in the . The colony grew out of the |
Copán
Copán is an archaeological site of the Maya civilization in the Copán Department of western Honduras, not far from the border with Guatemala. This ancient Maya city mirrors the beauty of the physical landscape in which it flourished—a fertile, well-watered mountain valley in western Honduras at an elevation of 600 meters (1,970 feet) above mean sea level. It was the capital city of a major Classic period kingdom from the 5th to 9th centuries AD. The city was in the extreme southeast of the Mesoamerican cultural region, on the frontier with the Isthmo-Colombian cultural region, and was almost surrounded by non-Maya peoples.. Copán was occupied for more than two thousand years, from the Early Preclassic period to the Postclassic. The city developed a distinctive sculptural style within the tradition of the lowland Maya, perhaps to emphasize the Maya ethnicity of the city's rulers. The city has a historical record that spans the greater part of the Classic period and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frederick Catherwood
Frederick Catherwood (27 February 1799 – 27 September 1854) was an English artist, architect and explorer, best remembered for his meticulously detailed drawings of the ruins of the Maya civilization. He explored Mesoamerica in the mid 19th century with writer John Lloyd Stephens. Their books, ''Incidents of Travel in Central America, Chiapas and Yucatán'' and ''Incidents of Travel in Yucatán'', were best sellers and introduced to the Western world the civilization of the ancient Maya. In 1837, Catherwood was elected into the National Academy of Design as an Honorary member. Mediterranean travels Catherwood, having made many trips to the Mediterranean between 1824 and 1832 to draw the monuments made by the Egyptians, Carthaginians, and Phoenicians, stated that the monuments in the Americas bear no architectural similarity to those in the Old World. Thus, they must have been made by the native people of the area. Catherwood made visits to Greece, Turkey, Egypt, and Pales ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |