|
John Katzenellenbogen
John Albert Katzenellenbogen (born May 10, 1944) is an American Professor of Chemistry at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. He studies the development of novel agents for the treatment of hormone-responsive and non-responsive breast and prostate cancers and the design of estrogens and antiestrogens that have a favorable balance of beneficial versus detrimental effects. Early life John Katzenellenbogen was born May 10, 1944, in Poughkeepsie, New York. His parents taught at Vassar College, his father a professor of Art History and his mother a pianist. In 1958, his family moved to Baltimore, Maryland, where his father became Head of the Department of Art History at Johns Hopkins University and his mother joined the faculty at Peabody Conservatory and Goucher College. Though he began playing the cello at age 10, his passion was for science. Katzenellenbogen attended Gilman School and held various summer jobs: in 1960, he worked at the Research Institute for Advanced St ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Illinois At Urbana–Champaign
The University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign (U of I, Illinois, University of Illinois, or UIUC) is a public land-grant research university in Illinois in the twin cities of Champaign and Urbana. It is the flagship institution of the University of Illinois system and was founded in 1867. Enrolling over 56,000 undergraduate and graduate students, the University of Illinois is one of the largest public universities by enrollment in the country. The University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign is a member of the Association of American Universities and is classified among "R1: Doctoral Universities – Very high research activity". In fiscal year 2019, research expenditures at Illinois totaled $652 million. The campus library system possesses the second-largest university library in the United States by holdings after Harvard University. The university also hosts the National Center for Supercomputing Applications and is home to the fastest supercomputer on a university campus. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Estrogen Receptor
Estrogen receptors (ERs) are a group of proteins found inside cells. They are receptors that are activated by the hormone estrogen ( 17β-estradiol). Two classes of ER exist: nuclear estrogen receptors (ERα and ERβ), which are members of the nuclear receptor family of intracellular receptors, and membrane estrogen receptors (mERs) (GPER (GPR30), ER-X, and Gq-mER), which are mostly G protein-coupled receptors. This article refers to the former (ER). Once activated by estrogen, the ER is able to translocate into the nucleus and bind to DNA to regulate the activity of different genes (i.e. it is a DNA-binding transcription factor). However, it also has additional functions independent of DNA binding. As hormone receptors for sex steroids (steroid hormone receptors), ERs, androgen receptors (ARs), and progesterone receptors (PRs) are important in sexual maturation and gestation. Proteomics There are two different forms of the estrogen receptor, usually referred to as α a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
People From Poughkeepsie, New York
A person ( : people) is a being that has certain capacities or attributes such as reason, morality, consciousness or self-consciousness, and being a part of a culturally established form of social relations such as kinship, ownership of property, or legal responsibility. The defining features of personhood and, consequently, what makes a person count as a person, differ widely among cultures and contexts. In addition to the question of personhood, of what makes a being count as a person to begin with, there are further questions about personal identity and self: both about what makes any particular person that particular person instead of another, and about what makes a person at one time the same person as they were or will be at another time despite any intervening changes. The plural form "people" is often used to refer to an entire nation or ethnic group (as in "a people"), and this was the original meaning of the word; it subsequently acquired its use as a plural form of per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
21st-century American Chemists
The 1st century was the century spanning AD 1 ( I) through AD 100 ( C) according to the Julian calendar. It is often written as the or to distinguish it from the 1st century BC (or BCE) which preceded it. The 1st century is considered part of the Classical era, epoch, or historical period. The 1st century also saw the appearance of Christianity. During this period, Europe, North Africa and the Near East fell under increasing domination by the Roman Empire, which continued expanding, most notably conquering Britain under the emperor Claudius ( AD 43). The reforms introduced by Augustus during his long reign stabilized the empire after the turmoil of the previous century's civil wars. Later in the century the Julio-Claudian dynasty, which had been founded by Augustus, came to an end with the suicide of Nero in AD 68. There followed the famous Year of Four Emperors, a brief period of civil war and instability, which was finally brought to an end by Vespasian, ninth Roman em ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Illinois Urbana-Champaign Faculty
A university () is an institution of higher (or tertiary) education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. Universities typically offer both undergraduate and postgraduate programs. In the United States, the designation is reserved for colleges that have a graduate school. The word ''university'' is derived from the Latin ''universitas magistrorum et scholarium'', which roughly means "community of teachers and scholars". The first universities were created in Europe by Catholic Church monks. The University of Bologna (''Università di Bologna''), founded in 1088, is the first university in the sense of: *Being a high degree-awarding institute. *Having independence from the ecclesiastic schools, although conducted by both clergy and non-clergy. *Using the word ''universitas'' (which was coined at its foundation). *Issuing secular and non-secular degrees: grammar, rhetoric, logic, theology, canon law, notarial law.Hunt Janin: "The university i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harvard Graduate School Of Arts And Sciences Alumni
Harvard University is a private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Founded in 1636 as Harvard College and named for its first benefactor, the Puritan clergyman John Harvard, it is the oldest institution of higher learning in the United States and one of the most prestigious and highly ranked universities in the world. The university is composed of ten academic faculties plus Harvard Radcliffe Institute. The Faculty of Arts and Sciences offers study in a wide range of undergraduate and graduate academic disciplines, and other faculties offer only graduate degrees, including professional degrees. Harvard has three main campuses: the Cambridge campus centered on Harvard Yard; an adjoining campus immediately across Charles River in the Allston neighborhood of Boston; and the medical campus in Boston's Longwood Medical Area. Harvard's endowment is valued at $50.9 billion, making it the wealthiest academic institution in the world. Endowment inco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Living People
Related categories * :Year of birth missing (living people) / :Year of birth unknown * :Date of birth missing (living people) / :Date of birth unknown * :Place of birth missing (living people) / :Place of birth unknown * :Year of death missing / :Year of death unknown * :Date of death missing / :Date of death unknown * :Place of death missing / :Place of death unknown * :Missing middle or first names See also * :Dead people * :Template:L, which generates this category or death years, and birth year and sort keys. : {{DEFAULTSORT:Living people 21st-century people People by status ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1944 Births
Events Below, the events of World War II have the "WWII" prefix. January * January 2 – WWII: ** Free France, Free French General Jean de Lattre de Tassigny is appointed to command First Army (France), French Army B, part of the Sixth United States Army Group in North Africa. ** Landing at Saidor: 13,000 US and Australian troops land on Papua New Guinea, in an attempt to cut off a Japanese retreat. * January 8 – WWII: Philippine Commonwealth troops enter the province of Ilocos Sur in northern Luzon and attack Japanese forces. * January 11 ** President of the United States Franklin D. Roosevelt proposes a Second Bill of Rights for social and economic security, in his State of the Union address. ** The Nazi German administration expands Kraków-Płaszów concentration camp into the larger standalone ''Konzentrationslager Plaszow bei Krakau'' in occupied Poland. * January 12 – WWII: Winston Churchill and Charles de Gaulle begin a 2-day conference in Marrakech ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Progesterone Receptor
The progesterone receptor (PR), also known as NR3C3 or nuclear receptor subfamily 3, group C, member 3, is a protein found inside cells. It is activated by the steroid hormone progesterone. In humans, PR is encoded by a single ''PGR'' gene residing on chromosome 11q22, it has two isoforms, PR-A and PR-B, that differ in their molecular weight. The PR-B is the positive regulator of the effects of progesterone, while PR-A serve to antagonize the effects of PR-B. Mechanism Progesterone is necessary to induce the progesterone receptors. When no binding hormone is present the carboxyl terminal inhibits transcription. Binding to a hormone induces a structural change that removes the inhibitory action. Progesterone antagonists prevent the structural reconfiguration. After progesterone binds to the receptor, restructuring with dimerization follows and the complex enters the nucleus and binds to DNA. There transcription takes place, resulting in formation of messenger RNA that is tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Androgen Receptor
The androgen receptor (AR), also known as NR3C4 (nuclear receptor subfamily 3, group C, member 4), is a type of nuclear receptor that is activated by binding any of the androgenic hormones, including testosterone and dihydrotestosterone in the cytoplasm and then translocating into the nucleus. The androgen receptor is most closely related to the progesterone receptor, and progestins in higher dosages can block the androgen receptor. The main function of the androgen receptor is as a DNA-binding transcription factor that regulates gene expression; however, the androgen receptor has other functions as well. Androgen-regulated genes are critical for the development and maintenance of the male sexual phenotype. Function Effect on development In some cell types, testosterone interacts directly with androgen receptors, whereas, in others, testosterone is converted by 5-alpha-reductase to dihydrotestosterone, an even more potent agonist for androgen receptor activation. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
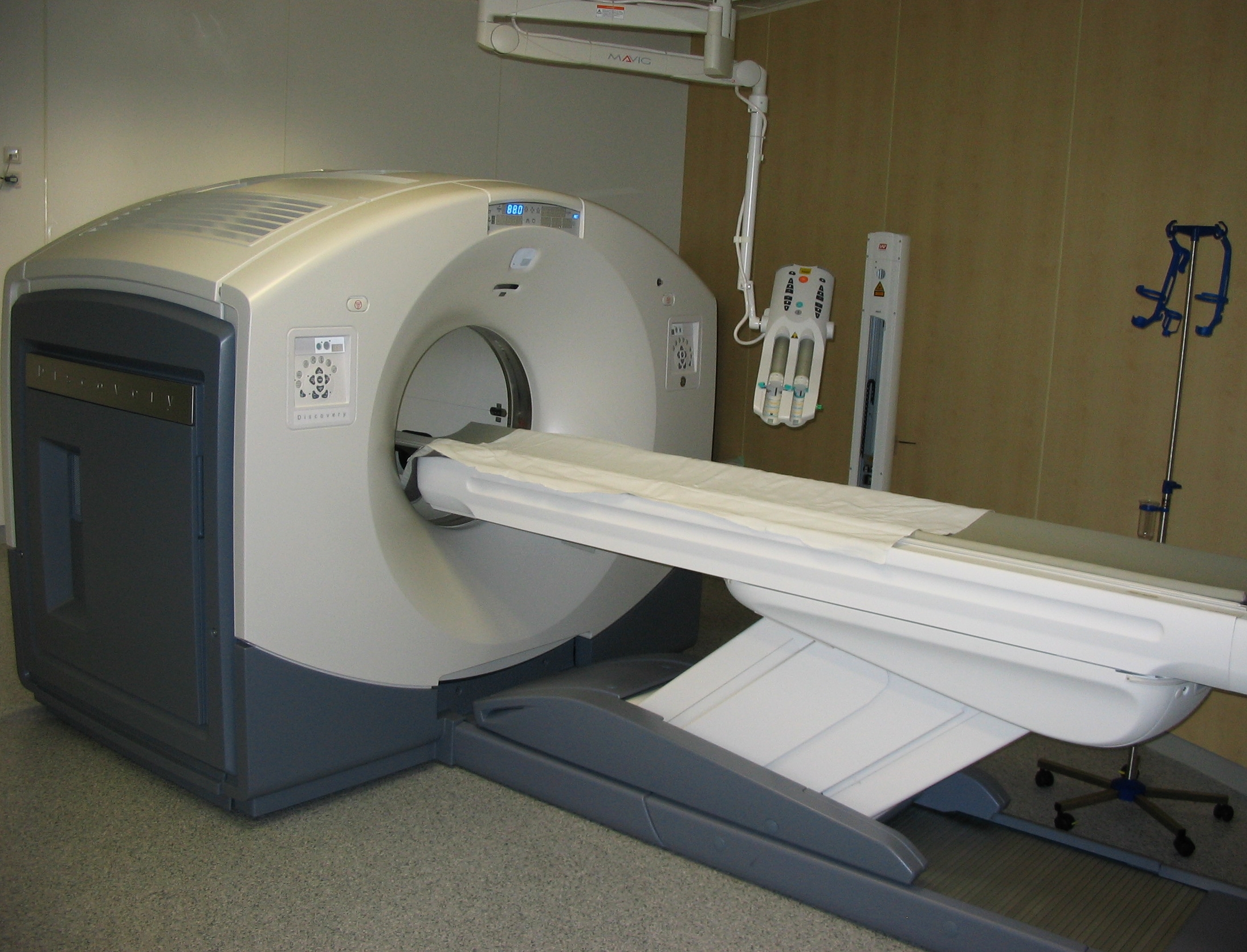
Positron Emission Tomography
Positron emission tomography (PET) is a functional imaging technique that uses radioactive substances known as radiotracers to visualize and measure changes in Metabolism, metabolic processes, and in other physiological activities including blood flow, regional chemical composition, and absorption. Different tracers are used for various imaging purposes, depending on the target process within the body. For example, 18F-FDG, -FDG is commonly used to detect cancer, Sodium fluoride#Medical imaging, NaF is widely used for detecting bone formation, and Isotopes of oxygen#Oxygen-15, oxygen-15 is sometimes used to measure blood flow. PET is a common medical imaging, imaging technique, a Scintigraphy#Process, medical scintillography technique used in nuclear medicine. A radiopharmaceutical, radiopharmaceutical — a radioisotope attached to a drug — is injected into the body as a radioactive tracer, tracer. When the radiopharmaceutical undergoes beta plus decay, a positron is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Affinity Label
Affinity labels are a class of enzyme inhibitors that covalently bind to their target causing its inactivation. The hallmark of an affinity label is the use of a targeting moiety to specifically and reversibly deliver a weakly reactive group to the enzyme that irreversibly binds to an amino acid residue. The targeting portion of the label often resembles the enzyme's natural substrate so that a similar mode of noncovalent binding is used prior to the covalent linkage. Their usefulness in medicine can be limited by the specificity of the first noncovalent binding step whereas indiscriminate action can be utilized for purposes such as affinity labeling - a technique for the validation of substrate-specific binding of compounds. These labels are not limited to enzymes but may also be designed to react with antibodies or ribozymes although this usage is less common. Although proteins such as hemoglobin do not have an active site, binding pockets can be exploited for their affinity and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_1938.jpg)