|
John Johnston (fur Trader)
John Johnston (1762–1828) was a wealthy and successful British fur trader for the North West Company at Sault Ste. Marie when it was still Canadian territory before the War of 1812. He was a prominent citizen and leader in the Michigan Territory of the United States, although he never became a US citizen. He married '' Ozhaguscodaywayquay'' (Woman of the Green Glade), daughter of '' Waubojeeg'' (White Fisher), a prominent Ojibwe war chief and civil leader from what is now northern Wisconsin. The Johnstons were leaders in both the Euro-American and Ojibwa communities. Johnston's life was markedly disrupted by the War of 1812, as afterward the U.S. prohibited trading by Canadians in its territory. Early life fur trade Johnston was born in Belfast, Ireland to an upper-class Scots-Irish family.Robert Dale Parker, ''Jane J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belfast
Belfast ( , ; from ga, Béal Feirste , meaning 'mouth of the sand-bank ford') is the capital and largest city of Northern Ireland, standing on the banks of the River Lagan on the east coast. It is the 12th-largest city in the United Kingdom and the second-largest in Ireland. It had a population of 345,418 . By the early 19th century, Belfast was a major port. It played an important role in the Industrial Revolution in Ireland, briefly becoming the biggest linen-producer in the world, earning it the nickname "Linenopolis". By the time it was granted city status in 1888, it was a major centre of Irish linen production, tobacco-processing and rope-making. Shipbuilding was also a key industry; the Harland and Wolff shipyard, which built the , was the world's largest shipyard. Industrialisation, and the resulting inward migration, made Belfast one of Ireland's biggest cities. Following the partition of Ireland in 1921, Belfast became the seat of government for Northern Ireland ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Johnston House (Sault Ste
John Johnston House may refer to: * John Johnston House (Sault Ste. Marie, Michigan), listed on the National Register of Historic Places (NRHP) * John S. Johnston House, Missoula, Montana, listed on the NRHP in Missoula County, Montana * John Johnston House (Yanceyville, North Carolina), listed on the NRHP in Caswell County, North Carolina See also * John H. Johnston Cotton Gin Historic District, Levesque, Arkansas, listed on the National Register of Historic Places in Cross County, Arkansas * Johnston House (other) {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
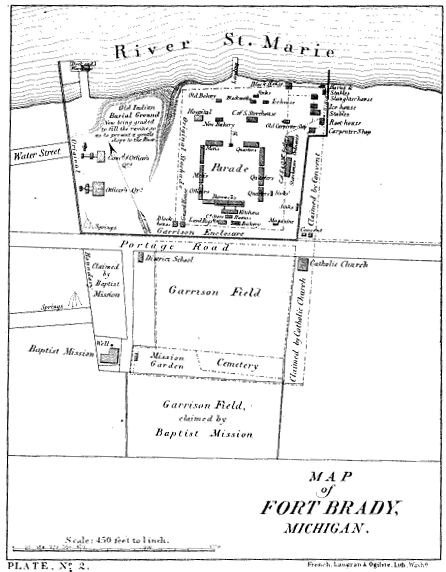
Fort Brady
Fort Brady was a frontier fort established in Sault Sainte Marie, Michigan to guard against British incursions from Canada. The original location of the fort, known as Old Fort Brady, was along the Saint Mary's River. Fort Brady was located at this site from 1822 until 1893, when it was moved to a new location on higher ground, known as New Fort Brady. The fort was located at the new site from 1893 until its close in 1944. The site of Old Fort Brady was designated a Michigan State Historic Site in 1956 and listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1971; New Fort Brady was designated a Michigan State Historic Site in 1970 and listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1972. Establishment of Fort Brady To enhance actual American control of the northwestern frontier against these incursions, especially in the wake of the War of 1812 against the British, the War Department decided to establish several forts along the Great Lakes. Despite several treaties w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hudson's Bay Company
The Hudson's Bay Company (HBC; french: Compagnie de la Baie d'Hudson) is a Canadian retail business group. A fur trading business for much of its existence, HBC now owns and operates retail stores in Canada. The company's namesake business division is Hudson's Bay, commonly referred to as The Bay ( in French). After incorporation by English royal charter in 1670, the company functioned as the ''de facto'' government in parts of North America for nearly 200 years until the HBC sold the land it owned (the entire Hudson Bay drainage basin, known as Rupert's Land) to Canada in 1869 as part of the Deed of Surrender, authorized by the Rupert's Land Act 1868. At its peak, the company controlled the fur trade throughout much of the English- and later British-controlled North America. By the mid-19th century, the company evolved into a mercantile business selling a wide variety of products from furs to fine homeware in a small number of sales shops (as opposed to trading posts) acros ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lewis Cass
Lewis Cass (October 9, 1782June 17, 1866) was an American military officer, politician, and statesman. He represented Michigan in the United States Senate and served in the Cabinets of two U.S. Presidents, Andrew Jackson and James Buchanan. He was also the 1848 Democratic presidential nominee. A slaveowner himself, he was a leading spokesman for the Doctrine of Popular Sovereignty, which held that the people in each territory should decide whether to permit slavery. Born in Exeter, New Hampshire, he attended Phillips Exeter Academy before establishing a legal practice in Zanesville, Ohio. After serving in the Ohio House of Representatives, he was appointed as a U.S. Marshal. Cass also joined the Freemasons and would eventually co-found the Grand Lodge of Michigan. He fought at the Battle of the Thames in the War of 1812 and was appointed to govern Michigan Territory in 1813. He negotiated treaties with Native Americans to open land for American settlement and led a survey e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cincinnati, Ohio
Cincinnati ( ) is a city in the U.S. state of Ohio and the county seat of Hamilton County. Settled in 1788, the city is located at the northern side of the confluence of the Licking and Ohio rivers, the latter of which marks the state line with Kentucky. The city is the economic and cultural hub of the Cincinnati metropolitan area. With an estimated population of 2,256,884, it is Ohio's largest metropolitan area and the nation's 30th-largest, and with a city population of 309,317, Cincinnati is the third-largest city in Ohio and 64th in the United States. Throughout much of the 19th century, it was among the top 10 U.S. cities by population, surpassed only by New Orleans and the older, established settlements of the United States eastern seaboard, as well as being the sixth-most populous city from 1840 until 1860. As a rivertown crossroads at the junction of the North, South, East, and West, Cincinnati developed with fewer immigrants and less influence from Europe than Ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Erie
Lake Erie ( "eerie") is the fourth largest lake by surface area of the five Great Lakes in North America and the eleventh-largest globally. It is the southernmost, shallowest, and smallest by volume of the Great Lakes and therefore also has the shortest average water residence time. At its deepest point Lake Erie is deep. Situated on the International Boundary between Canada and the United States, Lake Erie's northern shore is the Canadian province of Ontario, specifically the Ontario Peninsula, with the U.S. states of Michigan, Ohio, Pennsylvania, and New York on its western, southern, and eastern shores. These jurisdictions divide the surface area of the lake with water boundaries. The largest city on the lake is Cleveland, anchoring the third largest U.S. metro area in the Great Lakes region, after Greater Chicago and Metro Detroit. Other major cities along the lake shore include Buffalo, New York; Erie, Pennsylvania; and Toledo, Ohio. Situated below Lake Huron, Erie's p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oliver Hazard Perry
Oliver Hazard Perry (August 23, 1785 – August 23, 1819) was an American naval commander, born in South Kingstown, Rhode Island. The best-known and most prominent member of the Perry family naval dynasty, he was the son of Sarah Wallace Alexander and United States Navy Captain Christopher Raymond Perry, and older brother of Commodore Matthew C. Perry. Perry served in the West Indies during the Quasi War of 1798–1800 against France, in the Mediterranean during the Barbary Wars of 1801–1815, and in the Caribbean fighting piracy and the slave trade, but is most noted for his heroic role in the War of 1812 during the 1813 Battle of Lake Erie. During the war against Britain, Perry supervised the building of a fleet at Erie, Pennsylvania. He earned the title "Hero of Lake Erie" for leading American forces in a decisive naval victory at the Battle of Lake Erie, receiving a Congressional Gold Medal and the Thanks of Congress. Bloom, Page essay His leadership materially aid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michilimackinac
Michilimackinac ( ) is derived from an Ottawa Ojibwe name for present-day Mackinac Island and the region around the Straits of Mackinac between Lake Huron and Lake Michigan.. Early settlers of North America applied the term to the entire region along Lakes Huron, Michigan, and Superior. Today it is considered to be mostly within the boundaries of Michigan, in the United States. Michilimackinac was the original name for present day Mackinac Island and Mackinac County. History Woodland Period (1000 BCE–1650 CE) Pottery first appears during this period in the style of the Laurel complex. The people of the area engaged in long-distance trade, likely as part of the Hopewell tradition. The Anishinaabe and the French (1612–1763) The Straits of Mackinac linking Lakes Michigan and Huron was a strategic area controlling movement between the two lakes and much of the pays d'en haut. It was controlled by Algonquian Anishinaabe nations including the Ojibwa (called Chippewa in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jay Treaty
The Treaty of Amity, Commerce, and Navigation, Between His Britannic Majesty and the United States of America, commonly known as the Jay Treaty, and also as Jay's Treaty, was a 1794 treaty between the United States and Great Britain that averted war, resolved issues remaining since the Treaty of Paris of 1783 (which ended the American Revolutionary War), and facilitated ten years of peaceful trade between the United States and Britain in the midst of the French Revolutionary Wars, which began in 1792. The Treaty was designed by Alexander Hamilton and supported by President George Washington. It angered France and bitterly divided Americans. It inflamed the new growth of two opposing parties in every state, the pro-Treaty Federalists and the anti-Treaty Jeffersonian Republicans. The Treaty was negotiated by John Jay and gained many of the primary American goals. This included the withdrawal of British Army units from forts in the Northwest Territory that it had refused to relin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Métis
The Métis ( ; Canadian ) are Indigenous peoples who inhabit Canada's three Prairie Provinces, as well as parts of British Columbia, the Northwest Territories, and the Northern United States. They have a shared history and culture which derives from specific mixed European (primarily French) and Indigenous ancestry which became a distinct culture through ethnogenesis by the mid-18th century, during the early years of the North American fur trade. In Canada, the Métis, with a population of 624,220 as of 2021, are one of three major groups of Indigenous peoples that were legally recognized in the Constitution Act of 1982, the other two groups being the First Nations and Inuit. Smaller communities who self-identify as Métis exist in Canada and the United States, such as the Little Shell Tribe of Chippewa Indians of Montana. The United States recognizes the Little Shell Tribe as an Ojibwe Native American tribe. Alberta is the only Canadian province with a recognized Métis Nati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Native Americans In The United States
Native Americans, also known as American Indians, First Americans, Indigenous Americans, and other terms, are the Indigenous peoples of the mainland United States ( Indigenous peoples of Hawaii, Alaska and territories of the United States are generally known by other terms). There are 574 federally recognized tribes living within the US, about half of which are associated with Indian reservations. As defined by the United States Census, "Native Americans" are Indigenous tribes that are originally from the contiguous United States, along with Alaska Natives. Indigenous peoples of the United States who are not listed as American Indian or Alaska Native include Native Hawaiians, Samoan Americans, and the Chamorro people. The US Census groups these peoples as " Native Hawaiian and other Pacific Islanders". European colonization of the Americas, which began in 1492, resulted in a precipitous decline in Native American population because of new diseases, wars, ethni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.png)



.jpg)
