|
John Freeborn
John Connell Freeborn, (1 December 1919 – 28 August 2010) was a fighter pilot and flying ace in the Royal Air Force (RAF) during the Second World War. In 1939, he shot down another RAF fighter in a friendly-fire incident that marked the first death of an RAF fighter pilot in the war, as well as the first aircraft shotdown by a Supermarine Spitfire. The following year, he flew more operational hours than any other RAF pilot during the Battle of Britain. Early life Freeborn was born in Middleton in West Yorkshire. His father Harold was a branch manager with the Yorkshire Penny Bank (now Yorkshire Bank), and he was something of a disciplinarian at home. Freeborn remembered that his mother Jean (née Connell) was a stern woman, saying 'I never saw her smile'. He had five siblings, two sisters and three brothers. They moved to Headingley when Freeborn was still an infant. He later attended Leeds Grammar School and, although a bright and confident pupil, his dislike of petty aut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middleton, West Yorkshire
Middleton is a largely residential suburb of Leeds in West Yorkshire, England and historically a village in the West Riding of Yorkshire. It is situated on a hill south of Leeds city centre and north north-west of London. It sits in the Middleton Park ward of Leeds City Council and Leeds Central parliamentary constituency. The population of Middleton Park ward - which includes Belle Isle - was 26,228 at the 2011 Census. Middleton was occupied before the Norman Conquest and recorded in the ''Domesday Book'' of 1086 as ''Mildetone''. It developed as a manorial estate and its owners began to exploit the coal seams that outcropped within its boundaries. At the start of the Industrial Revolution a wooden wagonway was built to link the coal pits to Leeds. The colliery agent, John Blenkinsop designed an iron railway and its first steam-powered locomotive which was built by Matthew Murray in Holbeck. The coal mines on which the local economy was based lasted until 1968 and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acting Pilot Officer
Acting pilot officer (A/Plt Off) is the lowest commissioned grade in the Royal Air Force. Acting pilot officer is not an actual military rank, therefore acting pilot officers are regraded to pilot officer instead of receiving a promotion. Unlike other RAF ranks which officers may hold in an acting capacity, acting pilot officer is maintained as a separate grade. The grade normally denotes an officer who has recently been commissioned and joined as a non-graduate direct entrant. Although acting pilot officer has a NATO ranking code of OF(D), neither the British Army, Royal Marines nor Royal Navy has an exactly equivalent rank. As acting pilot officers are junior to second lieutenants in the British Army or the Royal Marines and to Royal Navy midshipmen, the rank is the most junior commissioned rank in the British Armed Forces. On a University Air Squadron, students can apply for the position of acting pilot officer in order to undertake a senior student or flight commander r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
JG 51
''Jagdgeschwader'' 51 (JG 51) was a German fighter wing during World War II. JG 51's pilots won more awards than any other fighter wing of the Luftwaffe, and operated in all major theatres of war. Its members included Anton Hafner, Heinz Bär, Karl-Gottfried Nordmann, and Günther Schack. World War II Formed in August 1939 and commanded by Theo Osterkamp, JG 51 was based in the early months of the war in the West, fighting in the Battle of France and the Battle of Britain. From late June 1940 to mid July 1940, JG 51 was the only fighter Geschwader engaged continuously against the RAF. During the battle JG 51 lost 68 pilots, the highest casualty rate of the Luftwaffe fighter units engaged. From 12 July 1940 until November 1940, Stab JG 51 was located at Saint-Inglevert Airfield in Saint-Inglevert, France. Major Werner Mölders became the unit's commander in July 1940 and led the unit during the invasion of the Soviet Union in June 1941. During Operation Barbarossa, JG 51 wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bf 109
The Messerschmitt Bf 109 is a German World War II fighter aircraft that was, along with the Focke-Wulf Fw 190, the backbone of the Luftwaffe's fighter force. The Bf 109 first saw operational service in 1937 during the Spanish Civil War and was still in service at the end of World War II in 1945. It was one of the most advanced fighters when it first appeared, with an all-metal monocoque construction, a closed canopy, and retractable landing gear. It was powered by a liquid-cooled, inverted-V12 aero engine. It was called the Me 109 by Allied aircrew and some German aces, even though this was not the official German designation. It was designed by Willy Messerschmitt and Robert Lusser who worked at Bayerische Flugzeugwerke during the early to mid-1930s. It was conceived as an interceptor, although later models were developed to fulfill multiple tasks, serving as bomber escort, fighter-bomber, day-, night-, all-weather fighter, ground-attack aircraft, and reconnaissance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
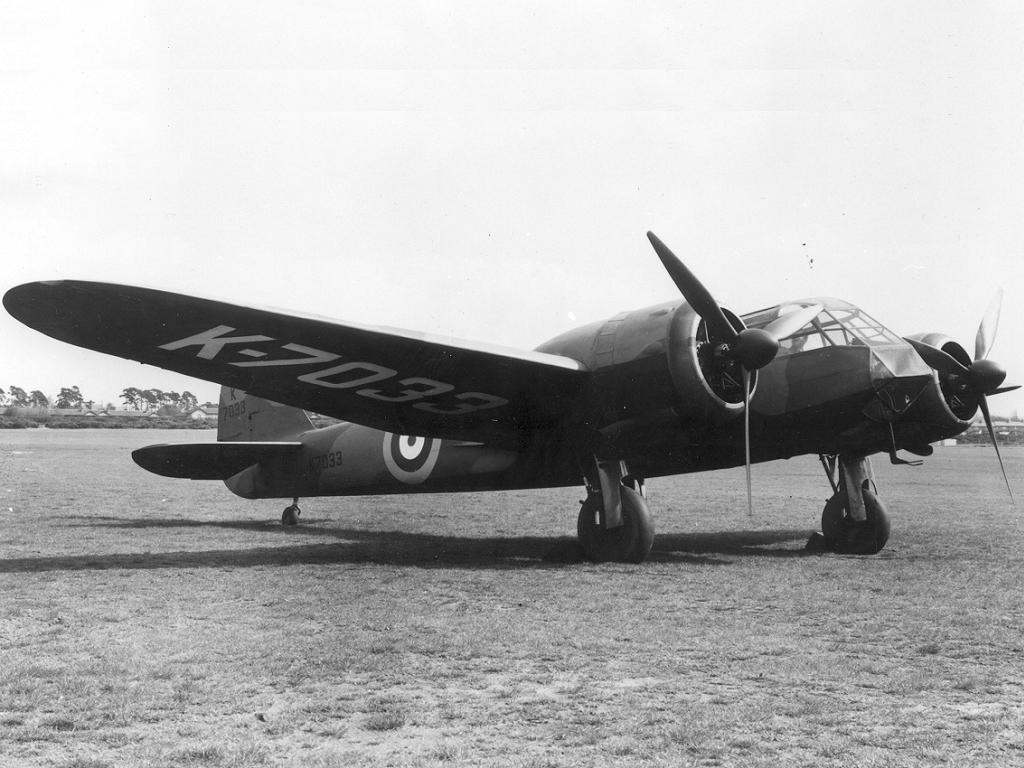
Bristol Blenheim
The Bristol Blenheim is a British light bomber aircraft designed and built by the Bristol Aeroplane Company (Bristol) which was used extensively in the first two years of the Second World War, with examples still being used as trainers until the end of the war. Development began with the ''Type 142'', a civil airliner, in response to a challenge from Lord Rothermere to produce the fastest commercial aircraft in Europe. The ''Type 142'' first flew in April 1935, and the Air Ministry, impressed by its performance, ordered a modified design as the ''Type 142M'' for the Royal Air Force (RAF) as a bomber. Deliveries of the newly named Blenheim to RAF squadrons commenced on 10 March 1937. In service the Type 142M became the Blenheim Mk.I which would be developed into the longer Type 149, designated the Blenheim Mk.IV, except in Canada where Fairchild Canada built the Type 149 under licence as the Bolingbroke. The Type 160 Bisley was also developed from the Blenheim, but was already o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Junkers Ju 88
The Junkers Ju 88 is a German World War II ''Luftwaffe'' twin-engined multirole combat aircraft. Junkers Aircraft and Motor Works (JFM) designed the plane in the mid-1930s as a so-called ''Schnellbomber'' ("fast bomber") that would be too fast for fighters of its era to intercept. It suffered from technical problems during its development and early operational periods but became one of the most versatile combat aircraft of the war. Like a number of other ''Luftwaffe'' bombers, it served as a bomber, dive bomber, night fighter, torpedo bomber, reconnaissance aircraft, heavy fighter and at the end of the war, as a flying bomb. Despite a protracted development, it became one of the ''Luftwaffe''s most important aircraft. The assembly line ran constantly from 1936 to 1945 and more than 15,000 Ju 88s were built in dozens of variants, more than any other twin-engine German aircraft of the period. Throughout production the basic structure of the aircraft remained unchanged.Angelucci a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Expeditionary Force (World War II)
The British Expeditionary Force (BEF) was the name of the contingent of the British Army sent to France in 1939 after Britain and France declared war on Nazi Germany on 3 September, beginning the Second World War. The BEF existed from 2 September 1939 when the BEF GHQ was formed until 31 May 1940, when GHQ closed down and its troops reverted to the command of Home Forces. During the 1930s, the British government had planned to deter war by abolishing the Ten Year Rule and rearming from the very low level of readiness of the early 1930s. The bulk of the extra money went to the Royal Navy and the Royal Air Force but plans were made to re-equip a small number of Army and Territorial Army divisions for service overseas. General Lord Gort was appointed to the command of the BEF on 3 September 1939 and the BEF began moving to France on 4 September 1939. The BEF assembled along the Belgian–French border. The BEF took their post to the left of the French First Army under the com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dunkirk Evacuation
The Dunkirk evacuation, codenamed Operation Dynamo and also known as the Miracle of Dunkirk, or just Dunkirk, was the evacuation of more than 338,000 Allied soldiers during the Second World War from the beaches and harbour of Dunkirk, in the north of France, between 26 May and 4 June 1940. The operation commenced after large numbers of Belgian, British, and French troops were cut off and surrounded by German troops during the six-week Battle of France. In a speech to the House of Commons, British Prime Minister Winston Churchill called this "a colossal military disaster", saying "the whole root and core and brain of the British Army" had been stranded at Dunkirk and seemed about to perish or be captured. In his "We shall fight on the beaches" speech on 4 June, he hailed their rescue as a "miracle of deliverance". After Germany invaded Poland in September 1939, France and the British Empire declared war on Germany and imposed an economic blockade. The British Expeditionary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patrick Hastings
Sir Patrick Gardiner Hastings (17 March 1880 – 26 February 1952) was an English barrister and politician noted for his long and highly successful career as a barrister and his short stint as Attorney General. He was educated at Charterhouse School until 1896, when his family moved to continental Europe. There he learnt to shoot and ride horses, allowing him to join the Suffolk Imperial Yeomanry after the outbreak of the Second Boer War. After demobilisation he worked briefly as an apprentice to an engineer in Wales before moving to London to become a barrister. Hastings joined the Middle Temple as a student on 4 November 1901, and after two years of saving money for the call to the bar he finally qualified as a barrister on 15 June 1904. Hastings first rose to prominence as a result of the Case of the Hooded Man in 1912, and became noted for his skill at cross-examinations. After his success in '' Gruban v Booth'' in 1917, his practice steadily grew, and in 1919 he bec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Court Martial
A court-martial or court martial (plural ''courts-martial'' or ''courts martial'', as "martial" is a postpositive adjective) is a military court or a trial conducted in such a court. A court-martial is empowered to determine the guilt of members of the armed forces subject to military law, and, if the defendant is found guilty, to decide upon punishment. In addition, courts-martial may be used to try prisoners of war for war crimes. The Geneva Conventions require that POWs who are on trial for war crimes be subject to the same procedures as would be the holding military's own forces. Finally, courts-martial can be convened for other purposes, such as dealing with violations of martial law, and can involve civilian defendants. Most navies have a standard court-martial which convenes whenever a ship is lost; this does not presume that the captain is suspected of wrongdoing, but merely that the circumstances surrounding the loss of the ship be made part of the official record. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sailor Malan
Adolph Gysbert Malan, (3 October 1910 – 17 September 1963), better known as Sailor Malan, was a South African fighter pilot and flying ace in the Royal Air Force (RAF) who led No. 74 Squadron RAF during the Battle of Britain. He finished his fighter career in 1941 with twenty-seven destroyed, seven shared destroyed and two unconfirmed, three probables and sixteen damaged. At the time he was the RAF's leading ace, and one of the highest scoring pilots to have served wholly with Fighter Command during the Second World War. After the war, Malan became leader of the Torch Commando, a liberal anti-authoritarian organization that opposed the introduction of the apartheid system. Early life Malan was born on 3 October 1910 to an Afrikaner family of Huguenot descent in Wellington, Western Cape, then part of the Cape Colony. He joined the South African Training Ship ''General Botha'' in 1924 or 1925 as a naval cadet (cadet number 168) at the age of 14, and on 5 January 1928 engaged ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hawker Hurricane
The Hawker Hurricane is a British single-seat fighter aircraft of the 1930s–40s which was designed and predominantly built by Hawker Aircraft Ltd. for service with the Royal Air Force (RAF). It was overshadowed in the public consciousness by the Supermarine Spitfire during the Battle of Britain in 1940, but the Hurricane inflicted 60 percent of the losses sustained by the Luftwaffe in the campaign, and fought in all the major theatres of the Second World War. The Hurricane originated from discussions between RAF officials and aircraft designer Sir Sydney Camm about a proposed monoplane derivative of the Hawker Fury biplane in the early 1930s. Despite an institutional preference for biplanes and lack of interest by the Air Ministry, Hawker refined their monoplane proposal, incorporating several innovations which became critical to wartime fighter aircraft, including retractable landing gear and the more powerful Rolls-Royce Merlin engine. The Air Ministry ordered Hawker's ''Int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)