|
John Ernest I, Duke Of Saxe-Weimar
Johann Ernst I, Duke of Saxe-Weimar (21 February 1594 in Altenburg – 6 December 1626 in Turz-Sankt Martin, Sankt Martin, Hungary), was a duke of Saxe-Weimar. Biography Born as the eldest son of Johann, Duke of Saxe-Weimar and Dorothea Maria of Anhalt, during his first years, Johann Ernst had a tutor and arms master, Matt of Johan. His father died on 18 July 1605, leaving the duchy under the governance of a regent. In 1608 he began his studies at the age of 14 at the University of Jena accompanied by his younger brothers, Wilhelm and Frederick. While at the university, his guardian appointed a companion and supervisor over the three princes, who later became Field Marshal Kaspar of Teutleben and the Preceptor Frederick Hortleder. In 1613-1614, Johann and his brothers, with his guardians, took a tour of France, Great Britain and the Netherlands as part of their studies. In 1615 Johann Ernst reached adulthood and took control of his duchy and the guardianship of his under-age youn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michiel Jansz
Michiel is a Dutch masculine given name equivalent to Michael and a Venetian surname. Given name * Michiel Andrieszoon (died 1684), Dutch pirate * Michiel Bartman (born 1967), Dutch rower * Michiel Borstlap (born 1966), Dutch pianist and composer * Michiel van den Bos (born 1975), Dutch video game composer * Michiel Josias Botha (born 1947), South African diamond cutter *Michiel Bothma (born 1973), South African golfer * Michiel Braam (born 1964), Dutch jazz pianist and composer * Michiel Carree (1657–1727), Dutch painter * Michiel Coignet (1549–1623), Flemish polymath *Michiel II Coignet (1618–1663), Flemish painter, son of the above *Michiel Coxie (1499–1592), Flemish painter * Michiel Driessen (born 1959), Dutch fencer *Michiel Dudok van Heel (1924–2003), Dutch Olympic sailor *Michiel Elijzen (born 1982), Dutch road bicycle racer *Michiel G. Eman (born 1961), Aruban Prime Minister *Michiel van der Gucht (1660–1725), Flemish engraver * Michiel Hazewinkel (born 194 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fruitbearing Society
The Fruitbearing Society (German Die Fruchtbringende Gesellschaft, lat. ''societas fructifera'') was a German literary society founded in 1617 in Weimar by German scholars and nobility. Its aim was to standardize vernacular German and promote it as both a scholarly and literary language, after the pattern of the Accademia della Crusca in Florence and similar groups already thriving in Italy, followed in later years also in France (1635) and Britain. It was also known as the Palmenorden ("Palm Order") because its emblem was the then-exotic ''fruitbearing'' coconut palm. (1576–1629), Hofmarschall at the court in Weimar, was the founding father of the society. As a young man he had travelled Italy and got inspired by the Italian language academies.''Teutleben, Caspar von'' at deutsche-biographie.de (in German) During the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allgemeine Deutsche Biographie
''Allgemeine Deutsche Biographie'' (ADB, german: Universal German Biography) is one of the most important and comprehensive biographical reference works in the German language. It was published by the Historical Commission of the Bavarian Academy of Sciences between 1875 and 1912 in 56 volumes, printed in Leipzig by Duncker & Humblot. The ADB contains biographies of about 26,500 people who died before 1900 and lived in the German language Sprachraum of their time, including people from the Netherlands before 1648. Its successor, the ''Neue Deutsche Biographie'', was started in 1953 and is planned to be finished in 2023. The index and full-text articles of ADB and NDB are freely available online via the website ''German Biography'' (''Deutsche Biographie ''Deutsche Biographie'' ( en, German Biography) is a German-language online biographical dictionary. It published thus far information about more than 730,000 individuals and families (2016).Historische Kommission bei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ernst Wülcker
Ernst Wülcker (24 August 1843, in Frankfurt am Main – 16 September 1895, in Weimar) was a German archivist and lexicographer. He was an older brother of philologist Richard Paul Wülker (1845–1910). He studied classical philology and Germanistics at the universities of Göttingen and Leipzig, and in 1870 was named secretary at the Frankfurt city archives. In 1875, he relocated to Weimar as first secretary of the private and city archives. In 1888 he was promoted to the archival council in Weimar.ADB:Wülcker, Ernst In: Allgemeine Deutsche Biographie (ADB). Band 44, Duncker & Humblot, Leipzig 1898, S. 559–562. Published works With |
Ernst Von Mansfeld
Peter Ernst, Graf von Mansfeld (german: Peter Ernst Graf von Mansfeld; c. 158029 November 1626), or simply Ernst von Mansfeld, was a German military commander who, despite being a Catholic, fought for the Protestants during the early years of the Thirty Years' War. He was one of the leading mercenary generals of the war. Biography Mansfeld was an illegitimate son of Count Peter Ernst von Mansfeld (1517–1604), a member of the comital House of Mansfeld and royal Spanish stadtholder. He was raised in the Catholic faith at his father's palace in Luxembourg. He gained his earliest military experiences during the Long War in Hungary, where his elder half-brother Charles (1543–1595), also a soldier of renown, held a high command in the imperial army. While his brother succumbed to an epidemic within short time, young Ernst stayed at the theatre of war for several years. In the War of the Jülich Succession he served under Archduke Leopold V of Austria, until that princ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lower Saxony
Lower Saxony (german: Niedersachsen ; nds, Neddersassen; stq, Läichsaksen) is a German state (') in northwestern Germany. It is the second-largest state by land area, with , and fourth-largest in population (8 million in 2021) among the 16 ' federated as the Federal Republic of Germany. In rural areas, Northern Low Saxon and Saterland Frisian language, Saterland Frisian are still spoken, albeit in declining numbers. Lower Saxony borders on (from north and clockwise) the North Sea, the states of Schleswig-Holstein, Hamburg, , Brandenburg, Saxony-Anhalt, Thuringia, Hesse and North Rhine-Westphalia, and the Netherlands. Furthermore, the Bremen (state), state of Bremen forms two enclaves within Lower Saxony, one being the city of Bremen, the other its seaport, Bremerhaven (which is a semi-enclave, as it has a coastline). Lower Saxony thus borders more neighbours than any other single '. The state's largest cities are state capital Hanover, Braunschweig (Brunswick), Lüneburg, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Westphalia
Westphalia (; german: Westfalen ; nds, Westfalen ) is a region of northwestern Germany and one of the three historic parts of the state of North Rhine-Westphalia. It has an area of and 7.9 million inhabitants. The territory of the region is almost identical with the historic Province of Westphalia, which was a part of the Kingdom of Prussia from 1815 to 1918 and the Free State of Prussia from 1918 to 1946. In 1946, Westphalia merged with North Rhine, another former part of Prussia, to form the newly created state of North Rhine-Westphalia. In 1947, the state with its two historic parts was joined by a third one: Lippe, a former principality and free state. The seventeen districts and nine independent cities of Westphalia and the single district of Lippe are members of the Westphalia-Lippe Regional Association (''Landschaftsverband Westfalen-Lippe''). Previous to the formation of Westphalia as a province of Prussia and later state part of North Rhine-Westphalia, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War was one of the longest and most destructive conflicts in European history, lasting from 1618 to 1648. Fought primarily in Central Europe, an estimated 4.5 to 8 million soldiers and civilians died as a result of battle, famine, and disease, while some areas of what is now modern Germany experienced population declines of over 50%. Related conflicts include the Eighty Years' War, the War of the Mantuan Succession, the Franco-Spanish War, and the Portuguese Restoration War. Until the 20th century, historians generally viewed it as a continuation of the religious struggle initiated by the 16th-century Reformation within the Holy Roman Empire. The 1555 Peace of Augsburg attempted to resolve this by dividing the Empire into Lutheran and Catholic states, but over the next 50 years the expansion of Protestantism beyond these boundaries destabilised the settlement. While most modern commentators accept differences over religion and Imperial authority were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cavalry
Historically, cavalry (from the French word ''cavalerie'', itself derived from "cheval" meaning "horse") are soldiers or warriors who Horses in warfare, fight mounted on horseback. Cavalry were the most mobile of the combat arms, operating as light cavalry in the roles of reconnaissance, Screening (tactical), screening, and skirmisher, skirmishing in many armies, or as heavy cavalry for decisive shock attacks in other armies. An individual soldier in the cavalry is known by a number of designations depending on era and tactics, such as cavalryman, Equestrianism, horseman, trooper (rank), trooper, cataphract, knight, hussar, uhlan, mamluk, cuirassier, lancer, dragoon, or horse archer. The designation of ''cavalry'' was not usually given to any Military animal, military forces that used other animals for mounts, such as Camel cavalry, camels or War elephant, elephants. Infantry who moved on horseback, but dismounted to fight on foot, were known in the early 17th to the early 18t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
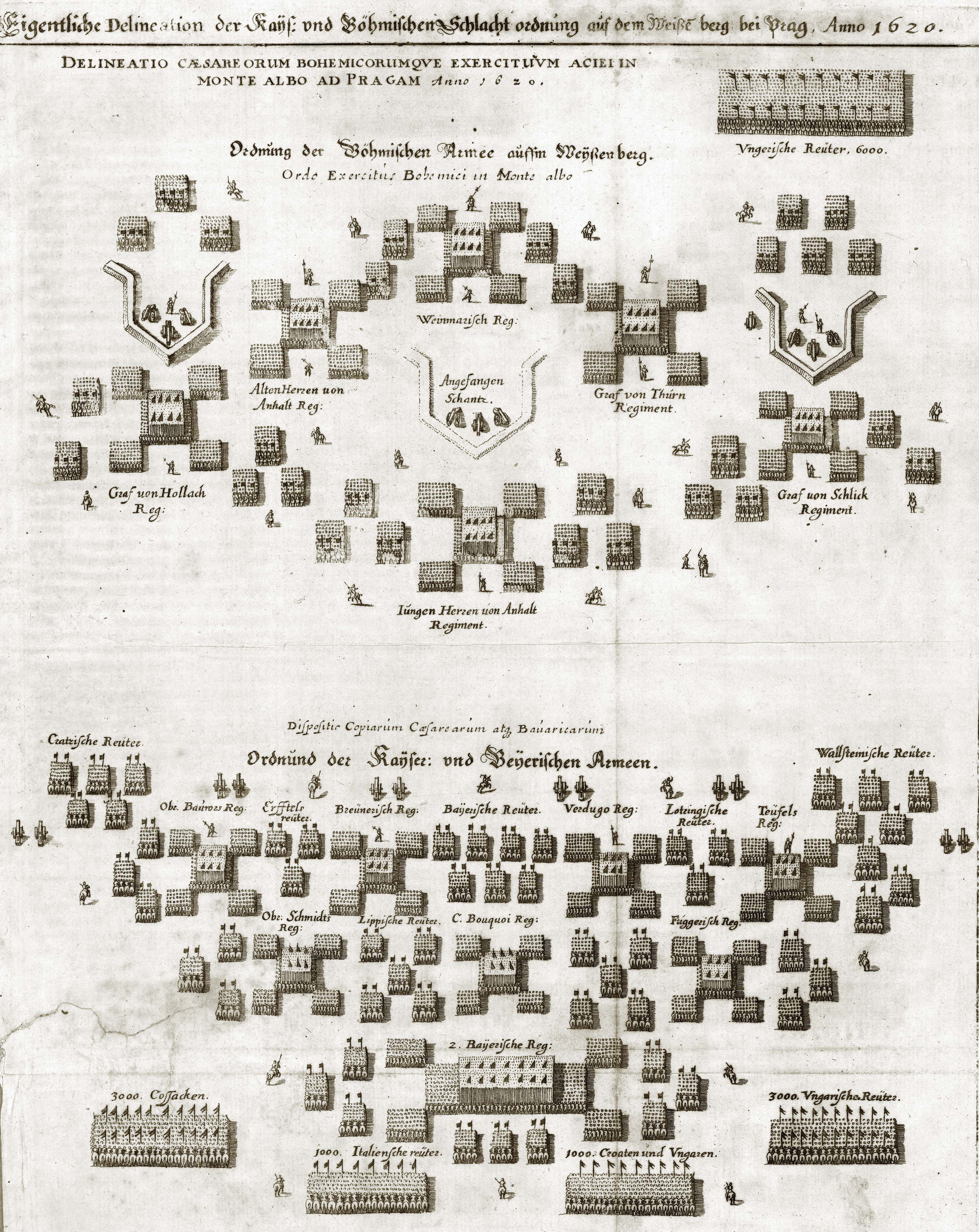
Battle Of White Mountain
), near Prague, Bohemian Confederation(present-day Czech Republic) , coordinates = , territory = , result = Imperial-Spanish victory , status = , combatants_header = , combatant1 = Catholic League , combatant2 = Bohemian Confederation Electoral Palatinate , commander1 = , commander2 = , strength1 = 23,00012 guns , strength2 = 21,00010 guns , casualties1 = 650 killed and wounded , casualties2 = 2,800 killed and wounded , map_type = Czech Republic Prague#Czech Republic , map_mark = Battle icon (crossed swords).svg , map_relief = , map_size = 300px , map_marksize = 30 , map_caption = , map_label = White Mountain The Battle of White Mountain ( cz, Bitva na Bílé hoře; german: Schlacht am Weißen Berg) was an important battle in the early stages of the Thirty Years' War. It led to the defeat of the Bohemian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frederick V, Elector Palatine
Frederick V (german: link=no, Friedrich; 26 August 1596 – 29 November 1632) was the Elector Palatine of the Rhine in the Holy Roman Empire from 1610 to 1623, and reigned as King of Bohemia from 1619 to 1620. He was forced to abdicate both roles, and the brevity of his reign in Bohemia earned him the derisive sobriquet "the Winter King" ( Czech: ''Zimní král''; German: ''Winterkönig''). Frederick was born at the hunting lodge (german: Jagdschloss) in Deinschwang, Palatinate (present-day Lauterhofen, Germany). He was the son of Frederick IV and of Louise Juliana of Orange-Nassau, the daughter of William the Silent and Charlotte de Bourbon-Montpensier. An intellectual, a mystic, and a Calvinist, he succeeded his father as Prince-Elector of the Rhenish Palatinate in 1610. He was responsible for the construction of the famous '' Hortus Palatinus'' gardens in Heidelberg. In 1618 the largely Protestant Czech nobility of Bohemia rebelled against their Catholic King Ferdi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |