|
John Clayton (minister)
John Clayton (1754–1843) was an English Independent minister. He became known for his conservative social views, after the Priestley Riots. Early life Clayton was born at Wood End Farm, Clayton, near Chorley, Lancashire, 5 October 1764, the only son of George Clayton, a bleacher; he had nine elder sisters. He was educated at Leyland grammar school, and was apprenticed to his brother-in-law, Boultbee, an apothecary in Manchester. At the end of four years he ran off, and made his way to the house of a married sister in London. Clayton was taken to hear the Rev. William Romaine preach, and a religious conversion followed. Clayton was then introduced to the Countess of Huntingdon, and sent by her to Trevecca College. He became a popular preacher, and was sent to take charge of a chapel at Tunbridge Wells. He also preached frequently in London. In 1777 he sought episcopal ordination, but difficulties arose, and reading Michaijah Towgood's ''Letters on Dissent'' made him a noncon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Independent (religion)
In Welsh and English church history, Independents advocated local congregational control of religious and church matters, without any wider geographical hierarchy, either ecclesiastical or political. They were particularly prominent during the Wars of the Three Kingdoms as well under the Commonwealth and Protectorate. The New Model Army became the champion of Independent religious views and its members helped carry out Pride's Purge in December 1648. Unlike their Presbyterian allies, Independents rejected any state role in religious practice, including the Church of England, and advocated freedom of religion for most non-Catholics. Their religious views led some to back radical political groups such as the Levellers, who supported concepts like Republicanism, universal suffrage and joint ownership of property. History At the outbreak of the First English Civil War in August 1642, the cause of Parliament was supported by an uneasy alliance between traditional members of the C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bunhill Fields
Bunhill Fields is a former burial ground in central London, in the London Borough of Islington, just north of the City of London. What remains is about in extent and the bulk of the site is a public garden maintained by the City of London Corporation. It was first in devoted use as a burial ground from 1665 until 1854, in which period approximately 123,000 interments were estimated to have taken place. Over 2,000 monuments remain, for the most part in concentrated blocks. It was a prototype of land-use protected, nondenominational grounds, and was particularly favoured by Nonconformist (Protestantism), nonconformists who passed their final years in the region. It contains the graves of many notable people, including John Bunyan (died 1688), author of ''The Pilgrim's Progress''; Daniel Defoe (died 1731), author of ''Robinson Crusoe''; William Blake (died 1827), artist, poet, and mystic; Susanna Wesley (died 1742), known as the "Mother of Methodism" through her education of sons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Dissenters
English Dissenters or English Separatists were Protestant Christians who separated from the Church of England in the 17th and 18th centuries. A dissenter (from the Latin ''dissentire'', "to disagree") is one who disagrees in opinion, belief and other matters. English Dissenters opposed state interference in religious matters, and founded their own churches, educational establishments and communities. Some emigrated to the New World, especially to the Thirteen Colonies and Canada. Brownists founded the Plymouth colony. English dissenters played a pivotal role in the spiritual development of the United States and greatly diversified the religious landscape. They originally agitated for a wide-reaching Protestant Reformation of the established Church of England, and they flourished briefly during the Protectorate under Oliver Cromwell. King James VI of Scotland, I of England and Ireland, had said "no bishop, no king", emphasising the role of the clergy in justifying royal legi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1843 Deaths
Events January–March * January ** Serial publication of Charles Dickens's novel ''Martin Chuzzlewit'' begins in London; in the July chapters, he lands his hero in the United States. ** Edgar Allan Poe's short story " The Tell-Tale Heart" is published in a Boston magazine. ** The Quaker magazine '' The Friend'' is first published in London. * January 3 – The ''Illustrated Treatise on the Maritime Kingdoms'' (海國圖志, ''Hǎiguó Túzhì'') compiled by Wei Yuan and others, the first significant Chinese work on the West, is published in China. * January 6 – Antarctic explorer James Clark Ross discovers Snow Hill Island. * January 20 – Honório Hermeto Carneiro Leão, Marquis of Paraná, becomes ''de facto'' first prime minister of the Empire of Brazil. * February – Shaikh Ali bin Khalifa Al-Khalifa captures the fort and town of Riffa after the rival branch of the family fails to gain control of the Riffa Fort and flees to Manama. Shaikh Mohamed bin Ahmed i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1754 Births
Events January–March * January 28 – Horace Walpole, in a letter to Horace Mann, coins the word ''serendipity''. * February 22 – Expecting an attack by Portuguese-speaking militias in the Viceroyalty of the Río de la Plata, the indigenous Guarani people residing in the Misiones Orientales stage an attack on a small Brazilian Portuguese settlement on the Rio Pardo in what is now the Brazilian state of Rio Grande do Sul. The attack by 300 Guarani soldiers from the missions at San Luis, San Lorenzo and San Juan Bautista is repelled with a loss of 30 Guarani and is the opening of the Guarani War * February 25 – Guatemalan Sergeant Major Melchor de Mencos y Varón departs the city of Santiago de los Caballeros de Guatemala with an infantry battalion to fight British pirates that are reportedly disembarking on the coasts of Petén (modern-day Belize), and sacking the nearby towns. * March 16 – Ten days after the death of British Prime Minister Henry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
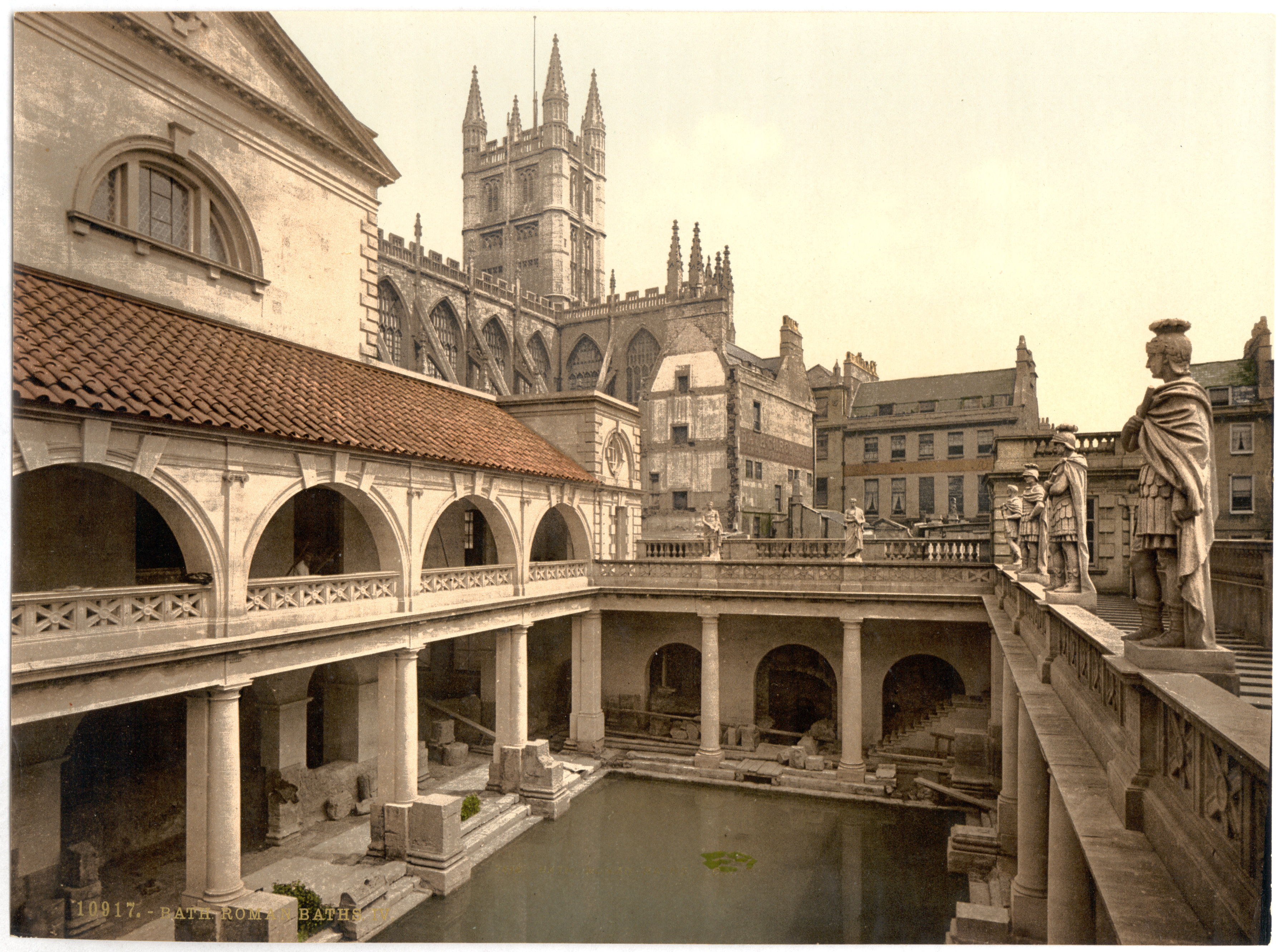
Bath, Somerset
Bath () is a city in the Bath and North East Somerset unitary area in the county of Somerset, England, known for and named after its Roman-built baths. At the 2021 Census, the population was 101,557. Bath is in the valley of the River Avon, west of London and southeast of Bristol. The city became a World Heritage Site in 1987, and was later added to the transnational World Heritage Site known as the "Great Spa Towns of Europe" in 2021. Bath is also the largest city and settlement in Somerset. The city became a spa with the Latin name ' ("the waters of Sulis") 60 AD when the Romans built baths and a temple in the valley of the River Avon, although hot springs were known even before then. Bath Abbey was founded in the 7th century and became a religious centre; the building was rebuilt in the 12th and 16th centuries. In the 17th century, claims were made for the curative properties of water from the springs, and Bath became popular as a spa town in the Georgian era. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shilling
The shilling is a historical coin, and the name of a unit of modern currencies formerly used in the United Kingdom, Australia, New Zealand, other British Commonwealth countries and Ireland, where they were generally equivalent to 12 pence or one-twentieth of a pound before being phased out during the 20th century. Currently the shilling is used as a currency in five east African countries: Kenya, Tanzania, Uganda, Somalia, as well as the ''de facto'' country of Somaliland. The East African Community additionally plans to introduce an East African shilling. History The word ''shilling'' comes from Old English "Scilling", a monetary term meaning twentieth of a pound, from the Proto-Germanic root skiljaną meaning 'to separate, split, divide', from (s)kelH- meaning 'to cut, split.' The word "Scilling" is mentioned in the earliest recorded Germanic law codes, those of Æthelberht of Kent. There is evidence that it may alternatively be an early borrowing of Phoenician ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lord Mansfield
William Murray, 1st Earl of Mansfield, PC, SL (2 March 170520 March 1793) was a British barrister, politician and judge noted for his reform of English law. Born to Scottish nobility, he was educated in Perth, Scotland, before moving to London at the age of 13 to take up a place at Westminster School. He was accepted into Christ Church, Oxford, in May 1723, and graduated four years later. Returning to London from Oxford, he was called to the Bar by Lincoln's Inn on 23 November 1730, and quickly gained a reputation as an excellent barrister. He became involved in politics in 1742, beginning with his election as a Member of Parliament for Boroughbridge, now in North Yorkshire, and appointment as Solicitor General. In the absence of a strong Attorney General, he became the main spokesman for the government in the House of Commons, and was noted for his "great powers of eloquence" and described as "beyond comparison the best speaker" in the House of Commons. With the promotion o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forgery
Forgery is a white-collar crime that generally refers to the false making or material alteration of a legal instrument with the specific intent to defraud anyone (other than themself). Tampering with a certain legal instrument may be forbidden by law in some jurisdictions but such an offense is not related to forgery unless the tampered legal instrument was actually used in the course of the crime to defraud another person or entity. Copies, studio replicas, and reproductions are not considered forgeries, though they may later become forgeries through knowing and willful misrepresentations. Forging money or currency is more often called counterfeiting. But consumer goods may also be ''counterfeits'' if they are not manufactured or produced by the designated manufacturer or producer given on the label or flagged by the trademark symbol. When the object forged is a record or document it is often called a false document. This usage of "forgery" does not derive from metalwork d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Flower (settler)
Richard Flower (1760–1829) was an English banker and brewer who was one of the pioneers of Albion, Illinois and promoted English immigration to the USA after the War of 1812. Early life Richard was the youngest son of George Flower (1715–1778), who had a stationery business in the City of London, and his wife Martha Fuller (1717-1805). She was the sister of two influential bankers: William Fuller, who became one of the richest men in England, and Richard Fuller, a long-serving Member of Parliament. His elder brother was Benjamin Flower. Career Initially destined for an agricultural career, Richard instead went into business in Hertford, becoming a brewer and a banker. In 1803 he was able to sell up and retire to his country estate of Marden Hill, where he farmed and also pursued his political interests. These included financial support for his brother Benjamin's radical publications and his own campaigns against what he considered unjust taxation. In 1817 he sold up and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benjamin Flower
Benjamin Flower (1755 – 17 February 1829) was an English radical journalist and political writer, and a vocal opponent of his country's involvement in the early stages of the Napoleonic Wars. Early life He was born in London, the son of a prosperous tradesman, George Flower, and Martha Fuller, sister of William Fuller. Richard Flower, who helped found Albion, Illinois and wrote on the English Settlement in the state, was his brother, and Richard's sons George Flower (cofounder of the Settlement) and Edward Fordham Flower therefore his nephews. His sister Mary married John Clayton. Attending several schools, from 1766 Flower was at the dissenting academy of John Collett Ryland, an associate of his father, in Northampton. Flower was given a legacy in 1778, when his father died, but lost the money in speculations. John Clayton took this badly, and blackened Flower's reputation, breaking also the family link. to a share in his father's business. Flower was in business in 178 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beulah Park, South Australia
Beulah Park is a suburb of Adelaide, South Australia in the City of Burnside. The suburb was established in 1941 when the name Beulah Park was transferred to a collection of land allotments. Clayton Wesley Uniting Church, on the north-east corner of Portrush Road and The Parade, Adelaide, The Parade, with its tall church spire, spire, is visible from Norwood, South Australia, Norwood down most of the length of The Parade from the west. This building was opened in May 1883, although an earlier building (still behind the present church, now the Lecture Hall) was built in 1856. Beulah Park Post Office opened around 1949 and closed in 1975. The Norwood Swim School is actually in Beulah Park, on the northern side of the Parade. References Further readingHistoric Self-Guided Walk: Beulah Park – includes much history of the suburb Suburbs of Adelaide {{adelaide-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)