|
John Askin
John Askin (1739–1815) was an Irish fur trader, merchant, and colonial official. He was instrumental in the establishment of British rule in Upper Canada. Early years He was born in Aughnacloy, Ireland in 1739; his ancestors are believed to have originally lived in Scotland with the surname Erskine. Career He came to North America with the British Army in 1758. After the British took over New France, he entered the fur trade and operated a trading post at Fort Michilimackinac. In 1781, he formed a partnership with Robert Hamilton’s son Alexander and Richard Cartwright; Askin was based in Detroit. From 1786 to 1789, he was part of a group of trading companies known as the Miamis Company. He was also involved in a shipping business and land speculation; he was one of the partners involved in the Cuyahoga Purchase along the south shore of Lake Erie. In 1789, he was named justice of the peace at Detroit. When Detroit was turned over to the Americans in 1796, he became a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brackets
A bracket is either of two tall fore- or back-facing punctuation marks commonly used to isolate a segment of text or data from its surroundings. Typically deployed in symmetric pairs, an individual bracket may be identified as a 'left' or 'right' bracket or, alternatively, an "opening bracket" or "closing bracket", respectively, depending on the Writing system#Directionality, directionality of the context. Specific forms of the mark include parentheses (also called "rounded brackets"), square brackets, curly brackets (also called 'braces'), and angle brackets (also called 'chevrons'), as well as various less common pairs of symbols. As well as signifying the overall class of punctuation, the word "bracket" is commonly used to refer to a specific form of bracket, which varies from region to region. In most English-speaking countries, an unqualified word "bracket" refers to the parenthesis (round bracket); in the United States, the square bracket. Glossary of mathematical sym ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territories, nine Minor Outlying Islands, and 326 Indian reservations. The United States is also in free association with three Pacific Island sovereign states: the Federated States of Micronesia, the Marshall Islands, and the Republic of Palau. It is the world's third-largest country by both land and total area. It shares land borders with Canada to its north and with Mexico to its south and has maritime borders with the Bahamas, Cuba, Russia, and other nations. With a population of over 333 million, it is the most populous country in the Americas and the third most populous in the world. The national capital of the United States is Washington, D.C. and its most populous city and principal financial center is New York City. Paleo-Americ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marcel Trudel
Marcel Trudel (May 29, 1917 – January 11, 2011) was a Canadian historian, university professor (1947–1982) and author who published more than 40 books on the history of New France. He brought academic rigour to an area that had been marked by nationalistic and religious biases. His work was part of the marked changes to Quebec society during the Quiet Revolution. Trudel's work has been honoured with major awards, including the Governor General's Literary Award for French Non-Fiction in 1966, and a second nomination for the award in 1987. Early life and education Marcel Trudel was born in Saint-Narcisse-de-Champlain, Quebec, northeast of Trois-Rivières, the son of Hermyle Trudel and Antoinette Cossette, the ninth of eleven children. Orphaned at the age of five, he was adopted by a local couple in his extended family, Théodore Baril and Mary Trépanier. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Askin Jr
John is a common English name and surname: * John (given name) * John (surname) John may also refer to: New Testament Works * Gospel of John, a title often shortened to John * First Epistle of John, often shortened to 1 John * Second Epistle of John, often shortened to 2 John * Third Epistle of John, often shortened to 3 John People * John the Baptist (died c. AD 30), regarded as a prophet and the forerunner of Jesus Christ * John the Apostle (lived c. AD 30), one of the twelve apostles of Jesus * John the Evangelist, assigned author of the Fourth Gospel, once identified with the Apostle * John of Patmos, also known as John the Divine or John the Revelator, the author of the Book of Revelation, once identified with the Apostle * John the Presbyter, a figure either identified with or distinguished from the Apostle, the Evangelist and John of Patmos Other people with the given name Religious figures * John, father of Andrew the Apostle and Saint Peter * Pope Joh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monette (slave)
Monette, also known as Manette (fl. 1760s), was a Native American enslaved woman of John Askin. She gave birth to three children who were educated and married into prominent families of the Great Lakes regions of present-day Michigan and Ontario, Canada. Her son was John Askin Jr. Daughter Catherine married Captain William Robertson, who operated one of Askin's boats, and was married a second time to Robert Hamilton, founder of Queenston, Ontario. Daughter Madeline was married to Dr. Robert Richardson, the surgeon of the Queen's Rangers stationed at Fort George. Enslaved to John Askin Monette was purchased from René Bourassa by John Askin for 50 pounds. The sale took place before 1762 at the Straits of Mackinac, a trading center. One of Monette and Askin's son-in-law states in a letter that his Native American mother-in-law was a Pawaneese slave who was captured in war. She was described as a Panis, enslaved people for Seneca people and other warring tribes affiliated with the Fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Slavery In Michigan
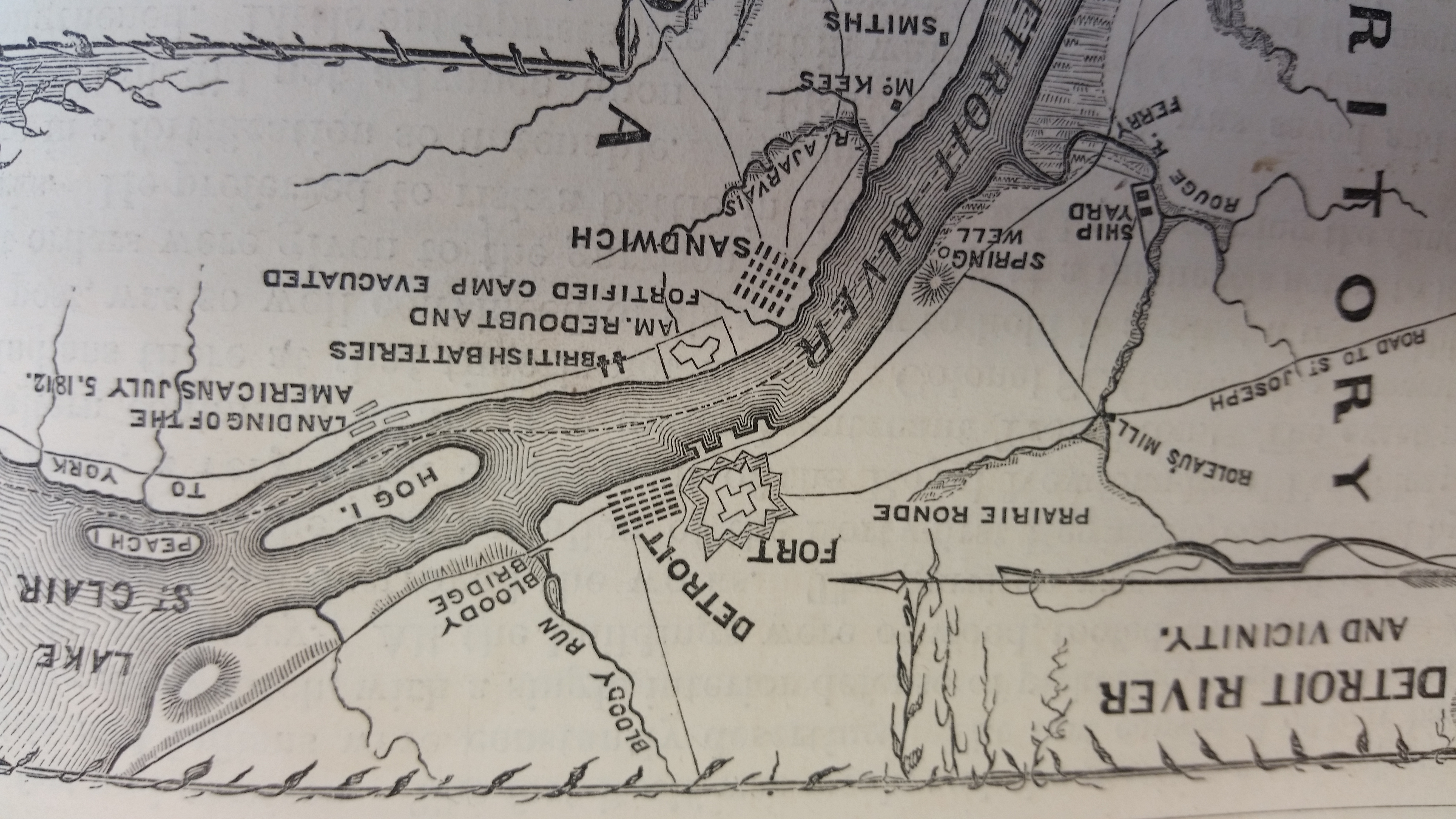
The History of slavery in Michigan includes the pro-slavery and anti-slavery efforts of the state's residents prior to the ratification of the Thirteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution in 1865. Slavery Slavery in Michigan began centuries ago with the French when they began to trade with indigenous people in the 16th century. Detroit was founded at the beginning of the 18th century, at which point the number of enslaved people began to be recorded. While the records are incomplete and therefore under-report the numbers, historian Marcel Trudel counted 523 Native American and 127 Black enslaved people, for a total of 650 people, from the 18th and early 19th century Detroit. The average life-span for enslaved Native Americans was 17.2 years, for Blacks, the average life span was 25.2 years. About 10% of early Detroit's population was made up of indentured servants, who worked for five to seven years paying off the cost of their transportation to the New World or debts. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Durand
James Durand (1775 – 22 March 1833) was a businessman and political figure in Upper Canada. He was born in Abergavenny, Wales in 1775 and came to Upper Canada in 1802 to deal with delinquent accounts on behalf of a group of London merchants. Having seized the Bridgewater Works at Chippawa, Durand purchased the operation from his employers. He also established a trading depot near Long Point. In 1810, he sold the operation at Chippawa due to a downturn in the produce market. He served in the Lincoln Militia during the War of 1812. In 1815, he became the representative for West York in the 6th Parliament of Upper Canada in a by-election after Abraham Markle joined the Americans. Durand criticized the introduction of martial law during the war. With John Willson, he drafted the ''Common Schools Act of 1816'', which introduced public support of elementary schools. He also helped establish the Gore District with Hamilton as the district town. In 1817, he was elected in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hamilton, Ontario
Hamilton is a port city in the Canadian province of Ontario. Hamilton has a population of 569,353, and its census metropolitan area, which includes Burlington and Grimsby, has a population of 785,184. The city is approximately southwest of Toronto in the Greater Toronto and Hamilton Area (GTHA). Conceived by George Hamilton when he purchased the Durand farm shortly after the War of 1812, the town of Hamilton became the centre of a densely populated and industrialized region at the west end of Lake Ontario known as the Golden Horseshoe. On January 1, 2001, the current boundaries of Hamilton were created through the amalgamation of the original city with other municipalities of the Regional Municipality of Hamilton–Wentworth. Residents of the city are known as Hamiltonians. Traditionally, the local economy has been led by the steel and heavy manufacturing industries. During the 2010s, a shift toward the service sector occurred, such as health and sciences. Hamilton is ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elijah Brush
Elijah Brush (May 10, 1773 – December 14, 1813) was a lawyer and politician from Detroit, Michigan. Early life Elijah Brush was born in Bennington, Vermont in 1773, the son of Colonel Nathaniel Brush and Samantha Parker (d. 1789). Brush graduated from Dartmouth College and came to Detroit in 1798. Career Following Detroit's hand-over to American control, John Askin, a British subject, moved across the Detroit River to Canada, leaving behind his farm, "Private Claim #1," which was immediately adjacent to Detroit. Public service Elijah Brush was elected a trustee in 1803, appointed Lieutenant Colonel of the Territorial Militia in 1805, and appointed as mayor of the town of Detroit after Solomon Sibley's resignation in 1806. Brush also served as Treasurer of the Michigan Territory from 1806 to 1813, and from 1811 to 1814 served as United States Attorney. In 1807, Brush was the counsel in the first case to test the right to hold slaves in Michigan, ''Denison v. Tucker''. D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Robertson (Western Quebec And Upper Canada)
William Robertson (ca 1760 – December 3, 1806) was a businessman and political figure in Upper Canada. He was born at Monymusk, near Aberdeen in Scotland around 1760 and settled in Detroit (then part of Quebec) in 1782. By 1788, he was an important merchant in the fur trade in the area and he was appointed to the district court and land board of the Hesse District of Upper Canada. Robertson resigned from his position as judge because he felt he was not qualified. In July 1792, he was appointed to the Executive Council and Legislative Council of Upper Canada. He resigned both offices in November, possibly because he believed that his business interests kept him too occupied. He had close business ties to Robert Hamilton, who had married his brother Samuel's widow, Catherine Askin, in 1785. He also held a number of contracts to supply garrisons in Upper Canada. Robertson moved to Montreal in 1797. After the death of his first wife in 1800, he returned to Great Britain and in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Randal
Robert Randal ( – May 2, 1834) was a businessman and political figure in Upper Canada and the United States. He was born in the United States and convicted of attempting to bribe members of the United States Congress in order to buy the lower Michigan peninsula. He bought mills and acres of land in Upper Canada. However, his businesses were unsuccessful and sold to British creditors. He was arrested in Montreal and he was sued for unpaid debts. He hired G. D'Arcy Boulton as his lawyer to protect his properties, but the delay in court proceedings put him in debt with the lawyers, causing more of his properties to be sold to pay his debts. Randal was elected to the Legislative Assembly of Upper Canada in 1820 to represent the 4th Riding of Lincoln. He successfully brought a petition from the Upper Canadian legislature to the British Parliament in London asking for civil rights for American loyalists who moved to Upper Canada. Reformers used his biography to campaign against the po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ebenezer Allen (1868–1931), Australian businessman and politician
{{hndis, Allen, Ebenezer ...
Ebenezer Allen may refer to: * Ebenezer Allen (Vermont politician) (1743–1806) * Ebenezer Allen (Texas politician) (1804–1863) * Eben Allen Ebenezer "Eben" Allen (15 November 1868 – 20 May 1931) was an Australian businessman and politician who was a member of the Legislative Assembly of Western Australia from 1911 to 1917, representing the seat of West Perth. Allen was born in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_(14730340946).jpg)
.jpg)