|
John, Duke Of Brunswick-Lüneburg
John ( – 13 December 1277), a member of the House of Welf, was Duke of Brunswick-Lüneburg from 1252 until his death. He initially reigned jointly with his brother, Albert the Tall, until the partition of the duchy in 1269, when John became the first ruler of the newly created Principality of Lüneburg. Life John's father, Otto the Child, was the first Duke of Brunswick-Lüneburg, having received the Welf allodial possessions in Saxony from the hands of Emperor Frederick II. After his death in 1252, John ruled the duchy jointly with his elder brother Albert. As the brothers could not agree who should govern the duchy, in 1267 they decided to divide their possession. In 1269 John received the right to choose his part. He chose the northern Lüneburg estates with the city of Hanover, forming the Principality of Lüneburg. Albert received the southern estates of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel with further lands around Calenberg and Göttingen. John thus founded the Old Line of L� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duchy Of Brunswick-Lüneburg
The Duchy of Brunswick-Lüneburg (german: Herzogtum Braunschweig und Lüneburg), or more properly the Duchy of Brunswick and Lüneburg, was a historical duchy that existed from the late Middle Ages to the Late Modern era within the Holy Roman Empire, until the year of its dissolution. The duchy was located in what is now northwestern Germany. Its name came from the two largest cities in the territory: Brunswick and Lüneburg. The dukedom emerged in 1235 from the allodial lands of the House of Welf in Saxony and was granted as an imperial fief to Otto the Child, a grandson of Henry the Lion. The duchy was divided several times during the High Middle Ages amongst various lines of the House of Welf, but each ruler was styled "Duke of Brunswick-Lüneburg" in addition to his own particular title. By 1692, the territories had consolidated to two: the Electorate of Brunswick-Lüneburg (commonly known as Electorate of Hanover) and the Principality of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uelzen
Uelzen (; officially the ''Hanseatic Town of Uelzen'', German: ''Hansestadt Uelzen'', , Low German ''Ülz’n'') is a town in northeast Lower Saxony, Germany, and capital of the county of Uelzen. It is part of the Hamburg Metropolitan Region, a Hanseatic town and an independent municipality. Uelzen is characterised by timber-framed architecture and also has some striking examples of North German brick Gothic. The county town earned pan-regional fame when Friedensreich Hundertwasser was selected to redesign the station: the final work of the celebrated Viennese artist and architect was ceremonially opened in 2000 as the Hundertwasser Station, Uelzen, and has since been a popular tourist magnet. The Polabian name for Uelzen is (spelled ''Wiltzaus'' in older German reference material), possibly derived from or (< Slavic *) 'alder'. Geography Locat ...
|
Walsrode
Walsrode (; nds, Wasra) is a town in the district of Heidekreis, in Lower Saxony, Germany. The former municipality Bomlitz was merged into Walsrode in January 2020. History Middle Ages 986 Foundation of Walsrode Abbey by Count Walo. The first recorded mention of the town is dated May 7, 986. 1383 The dukes of Brunswick and Lüneburg grant Walsrode a town charter. 1479 First recorded instance of Walsrode's coat of arms. At the end of the 15th century the sculptor Hans Brüggemann, creator of the renowned Bordesholm Altar of Schleswig Cathedral, is born in the town. Early modern times 1626 Extensive destruction in the town by the troops of Count Tilly during the Thirty Years' War. 1757 The town is totally destroyed by a catastrophic fire. 1811 During the Napoleonic era, Walsrode becomes a border town between France and the Kingdom of Westphalia. 1814 Walsrode is incorporated in the Kingdom of Hanover. 1866 Annexation of Walsrode by Prussia. 1890 Railroad first extends ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John II, Count Of Oldenburg
John II, Count of Oldenburg (german: Johann II. Graf von Oldenburg; died c. 1314 or 1316) was Count of Oldenburg from 1275 until around 1301. He was the son of Christian III, Count of Oldenburg. His mother was either Hedwig von Oldenburg in Wildeshausen or Jutta of Bentheim. Marriages and issue John married twice. His first marriage was to Elisabeth, the daughter of John, Duke of Brunswick and Lunenburg and Liutgard von Holstein-Itzehoe. His second marriage was to Countess Hedwig of Diepholz. John had five children: * Christian IV, Count of Oldenburg * John III, Count of Oldenburg, married Mechtild (Matilda) of Bronckhorst * Conrad I, Count of Oldenburg * Maurice of Oldenburg (killed in action in 1368 near Blexen), Dean (Domdechant) of Bremen Cathedral, Diocesan Administrator of the Archdiocese of Bremen The Prince-Archbishopric of Bremen (german: Fürsterzbistum Bremen) — not to be confused with the modern Archdiocese of Hamburg, founded in 1994 — was an ecclesi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry I, Prince Of Mecklenburg-Güstrow
Henry I (died 8 October 1291) was a Prince of Mecklenburg-Werle and Mecklenburg-Güstrow. Biography He was the son of Prince Nicholas I of Mecklenburg-Werle and his wife Princess Jutta of Anhalt the daughter of Prince Henry I of Anhalt and his wife Princess Irmgard of Thuringia. Henry and his brother John ruled Mecklenburg-Werle jointly following the death of their father on 10 May 1277. Henry and his brother ruled jointly until 1283 when Henry founded the principality of Mecklenburg-Güstrow while John took up residence in the principality of Mecklenburg-Parchim which he ruled jointly with Prince Pribislaw II. Henry's reign in Güstrow came to an end on 8 October 1291 after he was murdered near Saal by his two sons Henry and Nicholas both of whom succeeded him. Marriages and children Henry was married twice; firstly in 1262 to Rikissa Birgersdotter (died 1288), with the following children: * Henry II of Werle (died 1308) married Beatrix of Pomerania (died 1315–16), dau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis II, Duke Of Bavaria
Louis the Strict (german: Ludwig der Strenge) (13 April 1229 – 2 February 1294) was Duke of Upper Bavaria and Count Palatine of the Rhine from 1253. He is known as Louis II or Louis VI following an alternative numbering. Born in Heidelberg, he was a son of Otto II Wittelsbach, Duke of Bavaria and Agnes of the Palatinate. Biography In 1246, the young Louis supported his brother-in-law King Conrad IV of Germany against the usurpation of Heinrich Raspe. In 1251, Louis was at war again against the bishop of Regensburg. Louis succeeded his father Otto as Duke of Bavaria in 1253. When the Wittelsbach country was divided in 1255 among Otto's sons, Louis received the Palatinate and Upper Bavaria, while his brother duke Henry XIII of Bavaria received Lower Bavaria. This partition was against the law and therefore caused the anger of the bishops in Bavaria who later allied themselves with king Ottokar II of Bohemia in 1257. During the German interregnum, after King William's death ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
House Of Wittelsbach
The House of Wittelsbach () is a German dynasty, with branches that have ruled over territories including Bavaria, the Palatinate, Holland and Zeeland, Sweden (with Finland), Denmark, Norway, Hungary (with Romania), Bohemia, the Electorate of Cologne and other prince-bishoprics, and Greece. Their ancestral lands of the Palatinate and Bavaria were Prince-electorates, and the family had three of its members elected emperors and kings of the Holy Roman Empire. They ruled over the Kingdom of Bavaria which was created in 1805 and continued to exist until 1918. The House of Windsor, the reigning royal house of the British monarchy, are descendants of Sophia of Hanover, a Wittelsbach Princess of the Palatinate by birth and Electress of Hanover by marriage, who had inherited the succession rights of the House of Stuart and passed them on to the House of Hanover. History When Otto I, Count of Scheyern, died in 1072, his third son Otto II, Count of Scheyern, acquired the castl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gerhard I, Count Of Holstein-Itzehoe
Gerhard I, Count of Holstein-Itzehoe (1232 – 21 December 1290) was the only count of Holstein-Itzehoe. Life He was the second son of Count Adolf IV of Holstein and Heilwig of Lippe. When his father retired to a monastery in 1238, he ruled the Holstein jointly with his elder brother John I, initially under the guardianship of their brother-in-law the Duke Abel of Schleswig. When they came of age, the brothers took up government and continue their joint rule. In 1255, they concluded a trade agreement with Lübeck. When their father died in 1261, John and Gerhard divided Holstein. Gerhard took Holstein-Itzehoe, consisting of the districts of Stormarn, Plön and Schaumburg, with his residence in Itzehoe. John received Holstein-Kiel, consisting of the districts Kiel, Wagria and East Holstein, with his seat in Kiel. John later won Rendsburg back from Denmark and traded it with Gerhard for Segeberg. Gerhard founded several villages, in order to develop Holstein and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden and the North and Central European Plain. The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and from 10°E to 30°E longitude. A marginal sea of the Atlantic, with limited water exchange between the two water bodies, the Baltic Sea drains through the Danish Straits into the Kattegat by way of the Øresund, Great Belt and Little Belt. It includes the Gulf of Bothnia, the Bay of Bothnia, the Gulf of Finland, the Gulf of Riga and the Bay of Gdańsk. The " Baltic Proper" is bordered on its northern edge, at latitude 60°N, by Åland and the Gulf of Bothnia, on its northeastern edge by the Gulf of Finland, on its eastern edge by the Gulf of Riga, and in the west by the Swedish part of the southern Scandinavian Peninsula. The Baltic Sea is connected by artificial waterways to the White Sea via the White Sea–Baltic Canal and to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lübeck
Lübeck (; Low German also ), officially the Hanseatic City of Lübeck (german: Hansestadt Lübeck), is a city in Northern Germany. With around 217,000 inhabitants, Lübeck is the second-largest city on the German Baltic coast and in the state of Schleswig-Holstein, after its capital of Kiel, and is the 35th-largest city in Germany. The city lies in Holstein, northeast of Hamburg, on the mouth of the River Trave, which flows into the Bay of Lübeck in the borough of Travemünde, and on the Trave's tributary Wakenitz. The city is part of the Hamburg Metropolitan Region, and is the southwesternmost city on the Baltic, as well as the closest point of access to the Baltic from Hamburg. The port of Lübeck is the second-largest German Baltic port after the port of Rostock. The city lies in the Northern Low Saxon dialect area of Low German. Lübeck is famous for having been the cradle and the ''de facto'' capital of the Hanseatic League. Its city centre is Germany's most extens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
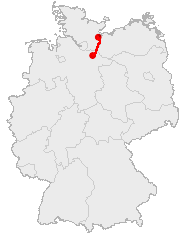
Old Salt Route
The Old Salt Route was a medieval trade route in Northern Germany, one of the ancient network of salt roads which were used primarily for the transport of salt and other staples. In Germany it was referred to as ''Alte Salzstraße''. Salt was very valuable at that time; it was sometimes referred to as "white gold." The vast majority of the salt transported on the road was produced from brine near Lüneburg, a city in the northern central part of the country and then transported to Lübeck, a major seaport on Germany's Baltic Sea coast. History Historians generally recognize the Old Salt Route as part of a much longer path, which functioned as an important connection between the northern and southern reaches of the country. One of the oldest documents that confirms Lüneburg and its role in refining and transporting salt dates from 956 A.D. According to that document, King Otto I the Great granted the St. Michaelis Monastery in Lüneburg the customs revenue from the saltworks ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
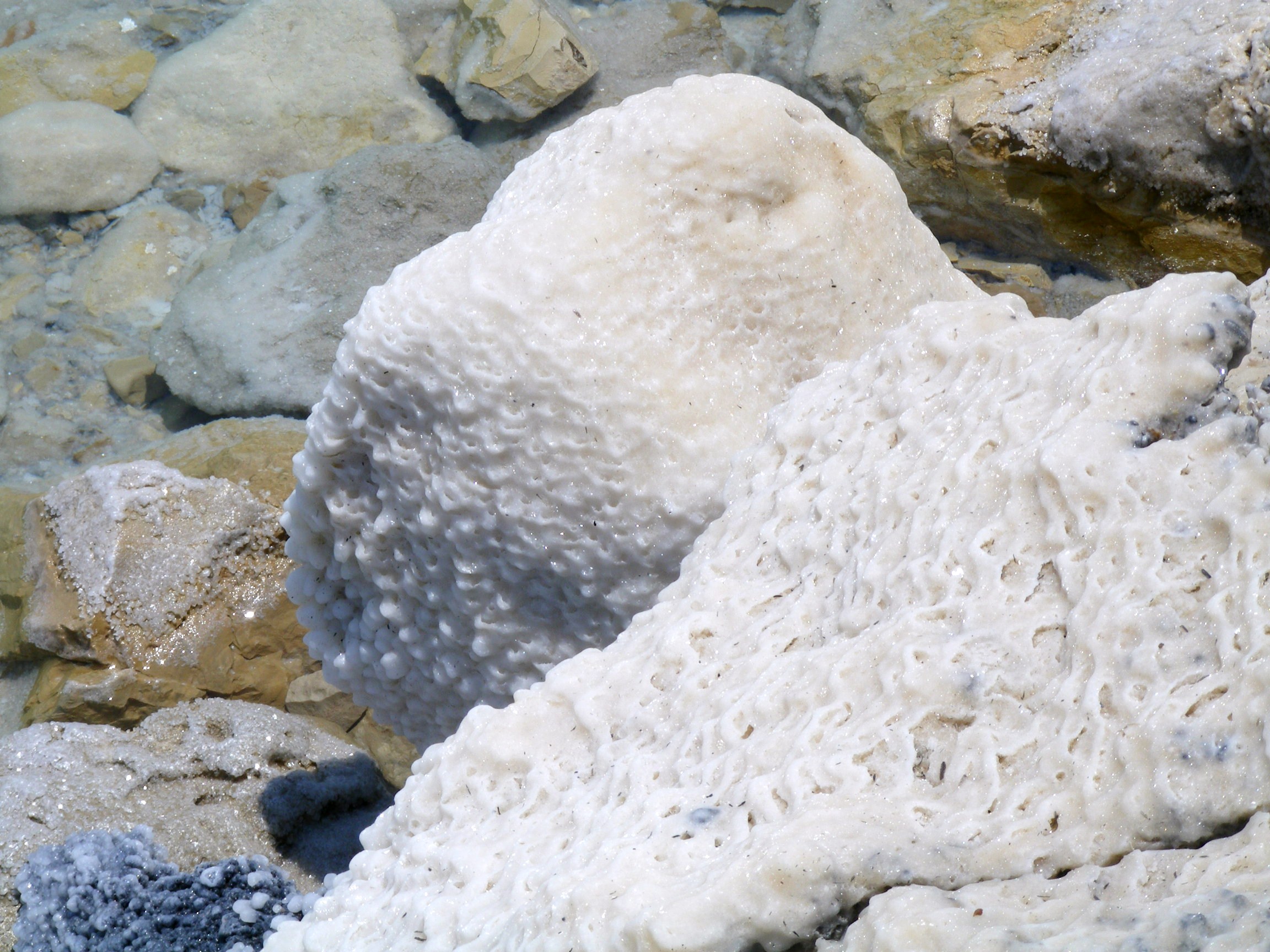
Salt
Salt is a mineral composed primarily of sodium chloride (NaCl), a chemical compound belonging to the larger class of salts; salt in the form of a natural crystalline mineral is known as rock salt or halite. Salt is present in vast quantities in seawater. The open ocean has about of solids per liter of sea water, a salinity of 3.5%. Salt is essential for life in general, and saltiness is one of the basic human tastes. Salt is one of the oldest and most ubiquitous food seasonings, and is known to uniformly improve the taste perception of food, including otherwise unpalatable food. Salting, brining, and pickling are also ancient and important methods of food preservation. Some of the earliest evidence of salt processing dates to around 6,000 BC, when people living in the area of present-day Romania boiled spring water to extract salts; a salt-works in China dates to approximately the same period. Salt was also prized by the ancient Hebrews, Greeks, Romans, By ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.png)
.jpg)