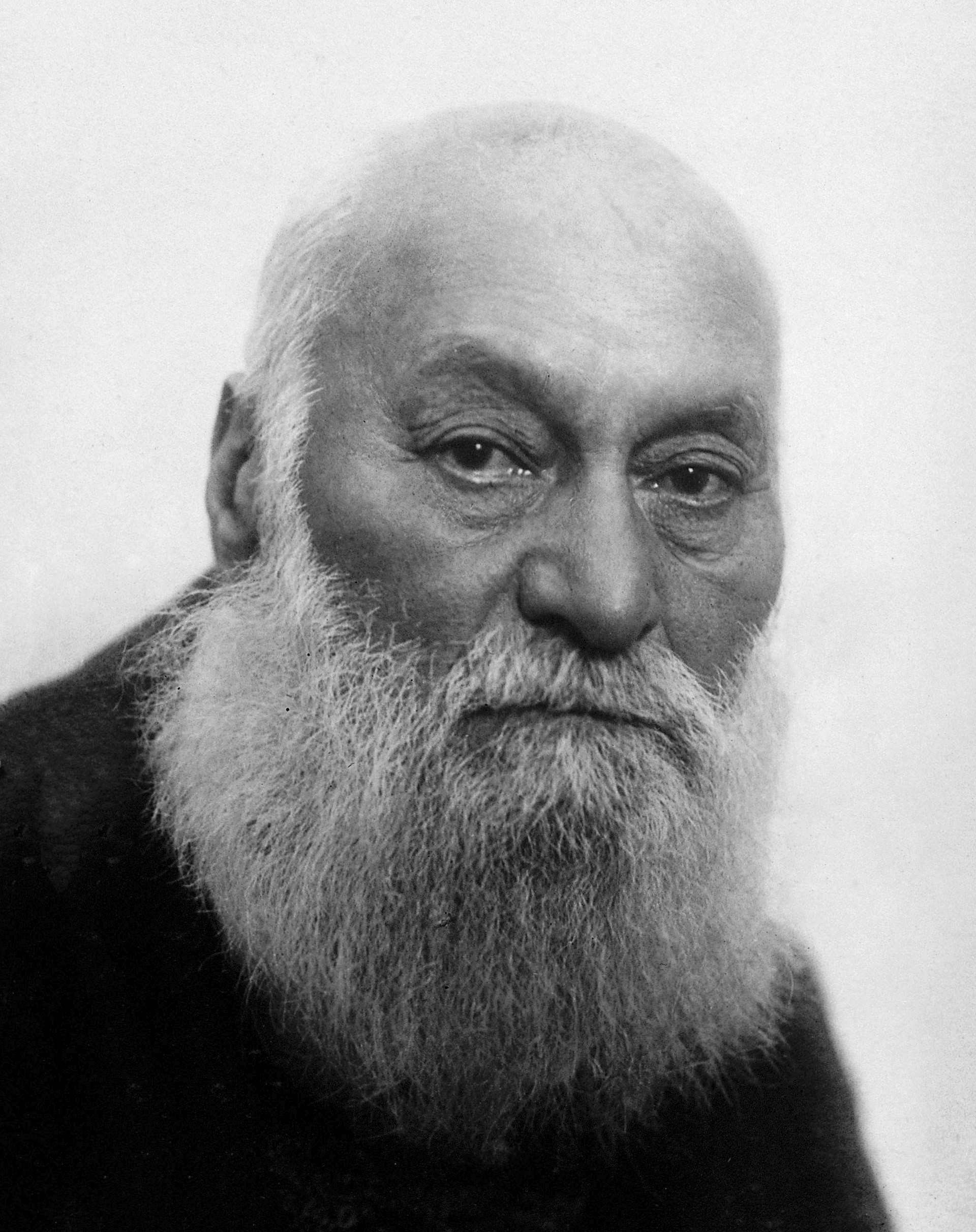|
Johannes Gad
Johannes Wilhelm Gad (30 June 1842 – 1926) was a German neurophysiologist who was a native of Posen. He was father-in-law to psychiatrist Oskar Kohnstamm (1871-1917). Life He was an assistant to Emil du Bois-Reymond (1818–1896) at the physiological institute at the University of Berlin, and later worked under Adolf Fick (1829–1901) at the University of Würzburg. In 1893–1894 he was a visiting lecturer of physiology at Western Reserve University in Cleveland, Ohio, and after returning to Germany, became departmental head at the physiological institute in Berlin. In 1895 he succeeded Ewald Hering (1834–1918) as manager of the department of physiology at the University of Prague. Gad is known from his work in experimental physiology. He performed numerous investigations involving electrophysiology, spinal cord functionality, the relationship between lactic acid to muscle contraction, et al. With Edward Flatau (1868–1932), he conducted experiments that were crit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johannes Gad
Johannes Wilhelm Gad (30 June 1842 – 1926) was a German neurophysiologist who was a native of Posen. He was father-in-law to psychiatrist Oskar Kohnstamm (1871-1917). Life He was an assistant to Emil du Bois-Reymond (1818–1896) at the physiological institute at the University of Berlin, and later worked under Adolf Fick (1829–1901) at the University of Würzburg. In 1893–1894 he was a visiting lecturer of physiology at Western Reserve University in Cleveland, Ohio, and after returning to Germany, became departmental head at the physiological institute in Berlin. In 1895 he succeeded Ewald Hering (1834–1918) as manager of the department of physiology at the University of Prague. Gad is known from his work in experimental physiology. He performed numerous investigations involving electrophysiology, spinal cord functionality, the relationship between lactic acid to muscle contraction, et al. With Edward Flatau (1868–1932), he conducted experiments that were crit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lactic Acid
Lactic acid is an organic acid. It has a molecular formula . It is white in the solid state and it is miscible with water. When in the dissolved state, it forms a colorless solution. Production includes both artificial synthesis as well as natural sources. Lactic acid is an alpha-hydroxy acid (AHA) due to the presence of a hydroxyl group adjacent to the carboxyl group. It is used as a synthetic intermediate in many organic synthesis industries and in various biochemical industries. The conjugate base of lactic acid is called lactate (or the lactate anion). The name of the derived acyl group is lactoyl. In solution, it can ionize by loss of a proton to produce the lactate ion . Compared to acetic acid, its p''K'' is 1 unit less, meaning lactic acid is ten times more acidic than acetic acid. This higher acidity is the consequence of the intramolecular hydrogen bonding between the α-hydroxyl and the carboxylate group. Lactic acid is chiral, consisting of two enantiomers. One ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1926 Deaths
Nineteen or 19 may refer to: * 19 (number), the natural number following 18 and preceding 20 * one of the years 19 BC, AD 19, 1919, 2019 Films * ''19'' (film), a 2001 Japanese film * ''Nineteen'' (film), a 1987 science fiction film Music * 19 (band), a Japanese pop music duo Albums * ''19'' (Adele album), 2008 * ''19'', a 2003 album by Alsou * ''19'', a 2006 album by Evan Yo * ''19'', a 2018 album by MHD * ''19'', one half of the double album ''63/19'' by Kool A.D. * ''Number Nineteen'', a 1971 album by American jazz pianist Mal Waldron * ''XIX'' (EP), a 2019 EP by 1the9 Songs * "19" (song), a 1985 song by British musician Paul Hardcastle. * "Nineteen", a song by Bad4Good from the 1992 album '' Refugee'' * "Nineteen", a song by Karma to Burn from the 2001 album ''Almost Heathen''. * "Nineteen" (song), a 2007 song by American singer Billy Ray Cyrus. * "Nineteen", a song by Tegan and Sara from the 2007 album '' The Con''. * "XIX" (song), a 2014 song by Slipkn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Neurologists
German(s) may refer to: * Germany (of or related to) **Germania (historical use) * Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language ** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law **Germanic peoples (Roman times) * German language **any of the Germanic languages * German cuisine, traditional foods of Germany People * German (given name) * German (surname) * Germán, a Spanish name Places * German (parish), Isle of Man * German, Albania, or Gërmej * German, Bulgaria * German, Iran * German, North Macedonia * German, New York, U.S. * Agios Germanos, Greece Other uses * German (mythology), a South Slavic mythological being * Germans (band), a Canadian rock band * "German" (song), a 2019 song by No Money Enterprise * ''The German'', a 2008 short film * "The Germans", an episode of ''Fawlty Towers'' * ''The German'', a nickname for Congolese rebel André Kisase Ngandu See also * Germanic (other) * Germa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Physiologists
German(s) may refer to: * Germany (of or related to) **Germania (historical use) * Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language ** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law **Germanic peoples (Roman times) * German language **any of the Germanic languages * German cuisine, traditional foods of Germany People * German (given name) * German (surname) * Germán, a Spanish name Places * German (parish), Isle of Man * German, Albania, or Gërmej * German, Bulgaria * German, Iran * German, North Macedonia * German, New York, U.S. * Agios Germanos, Greece Other uses * German (mythology), a South Slavic mythological being * Germans (band), a Canadian rock band * "German" (song), a 2019 song by No Money Enterprise * ''The German'', a 2008 short film * "The Germans", an episode of ''Fawlty Towers'' * ''The German'', a nickname for Congolese rebel André Kisase Ngandu See also * Germanic (other) * Germa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polish Wikipedia
The Polish Wikipedia ( pl, Polskojęzyczna Wikipedia) is the Polish-language edition of Wikipedia, a free online encyclopedia. Founded on September 26, 2001, it now has more than articles, making it the -largest Wikipedia edition overall."List of Wikipedias – Meta" Wikimedia.org. Retrieved November 7, 2015. It is also the second-largest edition in a , after the Russian Wikipedia. History [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sigmund Exner
Sigmund Exner (also ''Sigmund Exner'', ''Siegmund Exner-Ewarten'', ''Siegmund Exner Ritter von Ewarten''; 5 April 1846 – 5 February 1926) was an Austrian physiologist born in Vienna. Academic career He studied in Vienna under Ernst Wilhelm von Brücke (1819–1892), and in Heidelberg with Hermann von Helmholtz (1821–1894). In 1870 he received his degree, subsequently working as an assistant in the physiological institute at the University of Vienna. In 1891 he succeeded Ernst von Brücke as professor of physiology and director of the physiological institute. During his career, he received honorary doctorates from the Universities of Leipzig and Athens. Physiological research Sigmund Exner is known for his work in comparative physiology, and his studies of perception psychology from a physiological standpoint. He conducted important research on localization of behavioral functionality in the brain, in particular studies on the functional architecture of the visual cortex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alfred Goldscheider
Johannes Karl Eugen Alfred Goldscheider (4 August 1858 – 10 April 1935) was a German neurologist born into a Jewish family in Sommerfeld (today Lubsko, Poland). He studied medicine at Friedrich-Wilhelm Medical-Surgical Institute in Berlin (promotion 1881), and subsequently spent the next seven years as a military physician. During this period of time, he also served as an assistant to physiologist Emil du Bois-Reymond (1818-1896). He later became a professor at the University of Berlin. In Berlin, he served as directing physician at the ''Krankenhaus Moabit'' (from 1894) and at the ''Virchow-Krankenhaus'' (from 1906). In 1910 he succeeded Hermann Senator at the polyclinic. Research Goldscheider is best known for his work with the somatosensory system, in particular, research of the body's thermoreceptors in regards to localized "coolness" and "warmness" spots. He also performed research of localized tactile skin sensitivity that included tests involving "pain" and "tickle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Somatosensory System
In physiology, the somatosensory system is the network of neural structures in the brain and body that produce the perception of touch (haptic perception), as well as temperature (thermoception), body position (proprioception), and pain. It is a subset of the sensory nervous system, which also represents visual, auditory, olfactory, and gustatory stimuli. Somatosensation begins when mechano- and thermosensitive structures in the skin or internal organs sense physical stimuli such as pressure on the skin (see mechanotransduction, nociception). Activation of these structures, or receptors, leads to activation of peripheral sensory neurons that convey signals to the spinal cord as patterns of action potentials. Sensory information is then processed locally in the spinal cord to drive reflexes, and is also conveyed to the brain for conscious perception of touch and proprioception. Note, somatosensory information from the face and head enters the brain through periphera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean-François Heymans
Jean-François Heymans, also Jan Frans Heymans (25 December 1859, Gooik – 10 April 1932, Middelkerke) was a Belgian pharmacologist and physiologist. He was the father of physiologist Corneille Heymans, Corneille Jean François Heymans. He received his education at the Catholic University of Leuven (1834–1968), University of Leuven, where he earned doctorates in natural sciences (1884) and medicine (1887). From 1884 to 1887 he worked as a préparateur in the laboratory of physiology under Ernest Masoin. Afterwards, he travelled to Berlin, where he spent three years as an assistant to Emil Heinrich Du Bois-Reymond. In 1891 he was named professor of pharmacodynamics and general therapeutics at the University of Ghent. Here, he founded a laboratory for experimental pharmacology and therapeutics.Zeno.org Pagel: Biographical Dictionary outst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pharmacologist
Pharmacology is a branch of medicine, biology and pharmaceutical sciences concerned with drug or medication action, where a drug may be defined as any artificial, natural, or endogenous (from within the body) molecule which exerts a biochemical or physiological effect on the cell, tissue, organ, or organism (sometimes the word ''pharmacon'' is used as a term to encompass these endogenous and exogenous bioactive species). More specifically, it is the study of the interactions that occur between a living organism and chemicals that affect normal or abnormal biochemical function. If substances have medicinal properties, they are considered pharmaceuticals. The field encompasses drug composition and properties,functions,sources,synthesis and drug design, molecular and cellular mechanisms, organ/systems mechanisms, signal transduction/cellular communication, molecular diagnostics, interactions, chemical biology, therapy, and medical applications and antipathogenic capabilities. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Physiology
The human body is the structure of a human being. It is composed of many different types of cells that together create tissues and subsequently organ systems. They ensure homeostasis and the viability of the human body. It comprises a head, hair, neck, trunk (which includes the thorax and abdomen), arms and hands, legs and feet. The study of the human body involves anatomy, physiology, histology and embryology. The body varies anatomically in known ways. Physiology focuses on the systems and organs of the human body and their functions. Many systems and mechanisms interact in order to maintain homeostasis, with safe levels of substances such as sugar and oxygen in the blood. The body is studied by health professionals, physiologists, anatomists, and by artists to assist them in their work. Composition The human body is composed of elements including hydrogen, oxygen, carbon, calcium and phosphorus. These elements reside in trillions of cells and non-cellular com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |