|
Johanne Paradis
Johanne Catherine Paradis is a language scientist and expert on bilingual language development. She is Professor of Linguistics and Adjunct Professor of Communication Sciences and Disorders at the University of Alberta, where she directs the Language Acquisition Lab and the Child English Second Language (CHESL) Center. Paradis is the Editor in Chief of the ''Journal of Child Language'' and has served on the editorial board of the '' Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research''. She co-authored (with Fred Genesee and Martha Crago) the book ''Dual Language Development & Disorders: A Handbook on Bilingualism & Second Language Learning''. Additionally, she served as editor of the volume ''Input and Experience in Bilingual Development'' and co-editor of ''The Acquisition of French in Different Contexts: Focus on Functional Categories''. Paradis was awarded the 2017 Faculty of Arts Research Excellence Award by the University of Alberta in recognition of her outstanding contrib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Alberta
The University of Alberta, also known as U of A or UAlberta, is a public research university located in Edmonton, Alberta, Canada. It was founded in 1908 by Alexander Cameron Rutherford,"A Gentleman of Strathcona – Alexander Cameron Rutherford", Douglas R. Babcock, 1989, The University of Calgary Press, 2500 University Drive NW, Calgary, Alberta, Canada, the first premier of Alberta, and Henry Marshall Tory,"Henry Marshall Tory, A Biography", originally published 1954, current edition January 1992, E.A. Corbett, Toronto: Ryerson Press, the university's first president. It was enabled through the Post-secondary Learning Act''.'' The university is considered a "comprehensive academic and research university" (CARU), which means that it offers a range of academic and professional programs that generally lead to undergraduate and graduate level credentials. The university comprises four campuses in Edmonton, an Augustana Campus in Camrose, and a staff centre in downtown Cal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Postdoctoral Researcher
A postdoctoral fellow, postdoctoral researcher, or simply postdoc, is a person professionally conducting research after the completion of their doctoral studies (typically a PhD). The ultimate goal of a postdoctoral research position is to pursue additional research, training, or teaching in order to have better skills to pursue a career in academia, research, or any other field. Postdocs often, but not always, have a temporary academic appointment, sometimes in preparation for an academic faculty position. They continue their studies or carry out research and further increase expertise in a specialist subject, including integrating a team and acquiring novel skills and research methods. Postdoctoral research is often considered essential while advancing the scholarly mission of the host institution; it is expected to produce relevant publications in peer-reviewed academic journals or conferences. In some countries, postdoctoral research may lead to further formal qualificati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Women Linguists
A woman is an adult female human. Prior to adulthood, a female human is referred to as a girl (a female child or adolescent). The plural ''women'' is sometimes used in certain phrases such as "women's rights" to denote female humans regardless of age. Typically, women inherit a pair of X chromosomes, one from each parent, and are capable of pregnancy and giving birth from puberty until menopause. More generally, sex differentiation of the female fetus is governed by the lack of a present, or functioning, SRY-gene on either one of the respective sex chromosomes. Female anatomy is distinguished from male anatomy by the female reproductive system, which includes the ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, vagina, and vulva. A fully developed woman generally has a wider pelvis, broader hips, and larger breasts than an adult man. Women have significantly less facial and other body hair, have a higher body fat composition, and are on average shorter and less muscular than men. Thro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canadian Women Psychologists
Canadians (french: Canadiens) are people identified with the country of Canada. This connection may be residential, legal, historical or cultural. For most Canadians, many (or all) of these connections exist and are collectively the source of their being ''Canadian''. Canada is a multilingual and multicultural society home to people of groups of many different ethnic, religious, and national origins, with the majority of the population made up of Old World immigrants and their descendants. Following the initial period of French and then the much larger British colonization, different waves (or peaks) of immigration and settlement of non-indigenous peoples took place over the course of nearly two centuries and continue today. Elements of Indigenous, French, British, and more recent immigrant customs, languages, and religions have combined to form the culture of Canada, and thus a Canadian identity. Canada has also been strongly influenced by its linguistic, geographic, and e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Living People
Related categories * :Year of birth missing (living people) / :Year of birth unknown * :Date of birth missing (living people) / :Date of birth unknown * :Place of birth missing (living people) / :Place of birth unknown * :Year of death missing / :Year of death unknown * :Date of death missing / :Date of death unknown * :Place of death missing / :Place of death unknown * :Missing middle or first names See also * :Dead people * :Template:L, which generates this category or death years, and birth year and sort keys. : {{DEFAULTSORT:Living people 21st-century people People by status ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Year Of Birth Missing (living People)
A year or annus is the orbital period of a planetary body, for example, the Earth, moving in its orbit around the Sun. Due to the Earth's axial tilt, the course of a year sees the passing of the seasons, marked by change in weather, the hours of daylight, and, consequently, vegetation and soil fertility. In temperate and subpolar regions around the planet, four seasons are generally recognized: spring, summer, autumn and winter. In tropical and subtropical regions, several geographical sectors do not present defined seasons; but in the seasonal tropics, the annual wet and dry seasons are recognized and tracked. A calendar year is an approximation of the number of days of the Earth's orbital period, as counted in a given calendar. The Gregorian calendar, or modern calendar, presents its calendar year to be either a common year of 365 days or a leap year of 366 days, as do the Julian calendars. For the Gregorian calendar, the average length of the calendar year (the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multilingualism
Multilingualism is the use of more than one language, either by an individual speaker or by a group of speakers. It is believed that multilingual speakers outnumber monolingual speakers in the world's population. More than half of all Europeans claim to speak at least one language other than their mother tongue; but many read and write in one language. Multilingualism is advantageous for people wanting to participate in trade, globalization and cultural openness. Owing to the ease of access to information facilitated by the Internet, individuals' exposure to multiple languages has become increasingly possible. People who speak several languages are also called polyglots. Multilingual speakers have acquired and maintained at least one language during childhood, the so-called first language (L1). The first language (sometimes also referred to as the mother tongue) is usually acquired without formal education, by mechanisms about which scholars disagree. Children acquirin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monolingualism
Monoglottism (Greek μόνος ''monos'', "alone, solitary", + γλῶττα , "tongue, language") or, more commonly, monolingualism or unilingualism, is the condition of being able to speak only a single language, as opposed to multilingualism. In a different context, "unilingualism" may refer to a language policy which enforces an official or national language over others. Being monolingual or unilingual is also said of a text, dictionary, or conversation written or conducted in only one language, and of an entity in which a single language is either used or officially recognized (in particular when being compared with bilingual or multilingual entities or in the presence of individuals speaking different languages). Note that mono''glottism'' can only refer to lacking the ''ability'' to speak several languages. Multilingual speakers outnumber monolingual speakers in the world's population. Suzzane Romaine pointed out, in her 1995 book ''Bilingualism'', that it would be weir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grammaticality Judgment Task
An acceptability judgment task, also called acceptability rating task, is a common method in empirical linguistics to gather information about the internal grammar of speakers of a language. Acceptability and grammaticality The goal of acceptability rating studies is to gather insights into the mental grammars of participants. As the grammaticality of a linguistic construction is an abstract construct that cannot be accessed directly, this type of tasks is usually not called grammaticality, but acceptability judgment. This can be compared to intelligence. Intelligence is an abstract construct that cannot be measured directly. What can be measured are the outcomes of specific test items. The result of one item, however, is not very telling. Instead, IQ tests consist of several items building a score. Similarly, in acceptability rating studies, grammatical constructions are measured through several items, i.e., sentences to be rated. This is also done to ensure that participants do no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morphology (linguistics)
In linguistics, morphology () is the study of words, how they are formed, and their relationship to other words in the same language. It analyzes the structure of words and parts of words such as stems, root words, prefixes, and suffixes. Morphology also looks at parts of speech, intonation and stress, and the ways context can change a word's pronunciation and meaning. Morphology differs from morphological typology, which is the classification of languages based on their use of words, and lexicology, which is the study of words and how they make up a language's vocabulary. While words, along with clitics, are generally accepted as being the smallest units of syntax, in most languages, if not all, many words can be related to other words by rules that collectively describe the grammar for that language. For example, English speakers recognize that the words ''dog'' and ''dogs'' are closely related, differentiated only by the plurality morpheme "-s", only found bound to noun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
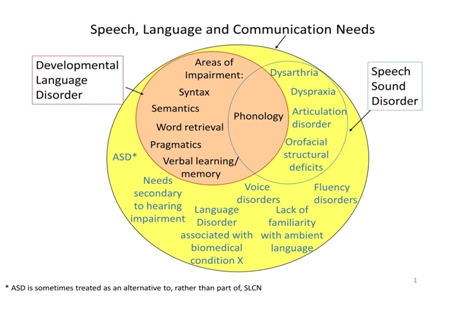
Developmental Language Disorder
Developmental language disorder (DLD) is identified when a child has problems with language development that continue into school age and beyond. The language problems have a significant impact on everyday social interactions or educational progress, and occur in the absence of autism spectrum disorder, intellectual disability or a known biomedical condition. The most obvious problems are difficulties in using words and sentences to express meanings, but for many children, understanding of language (receptive language) is also a challenge. This may not be evident unless the child is given a formal assessment. Classification Terminology The term developmental language disorder (DLD) was endorsed in a consensus study involving a panel of experts (CATALISE Consortium) in 2017. The study was conducted in response to concerns that a wide range of terminology was used in this area, with the consequence that there was poor communication, lack of public recognition, and in some cases childr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Specific Language Impairment
Specific language impairment (SLI) (the term developmental language disorder is preferred by some) is diagnosed when a child's language does not develop normally and the difficulties cannot be accounted for by generally slow development, physical abnormality of the speech apparatus, autism spectrum disorder, apraxia, acquired brain damage or hearing loss. Twin studies have shown that it is under genetic influence. Although language impairment can result from a single-gene mutation, this is unusual. More commonly SLI results from the combined influence of multiple genetic variants, each of which is found in the general population, as well as environmental influences. Classification Specific language impairment (SLI) is diagnosed when a child has delayed or disordered language development for no apparent reason. Usually the first indication of SLI is that the child is later than usual in starting to speak and subsequently is delayed in putting words together to form sentences. S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)