|
Johann Jacob Paul Moldenhawer
Johann Jacob Paul Moldenhawer (11 February 1766 – 21 August 1827) was a German botanist who made a number of important discoveries in plant anatomy. He was born in Hamburg, the son of a minister, and started out studying theology and the classics. At some unknown point he became interested in plants, and in 1791 he published ''Tentamen in historiam plantarum Theophrasti'', on Theophrastus, and the following year he is recorded as "Extraordinary Professor of Botany and Fruit Tree Culture" (''außerordentlicher Professor für Botanik und Obstbau'') at the University of Kiel. He studied plant anatomy from 1795 until 1812, when he published ''Beyträge zur Anatomie der Pflanzen'' on his results. Immediately subsequently he concentrated on fruit tree culture. He died in Kiel. Moldenhawer's contributions center on the microscopic examination of plant tissues, for which he devised techniques to separate the cells from the middle lamella layer that separates them. He identified vascula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Botanist
Botany, also called , plant biology or phytology, is the science of plant life and a branch of biology. A botanist, plant scientist or phytologist is a scientist who specialises in this field. The term "botany" comes from the Ancient Greek word (''botanē'') meaning "pasture", " herbs" "grass", or " fodder"; is in turn derived from (), "to feed" or "to graze". Traditionally, botany has also included the study of fungi and algae by mycologists and phycologists respectively, with the study of these three groups of organisms remaining within the sphere of interest of the International Botanical Congress. Nowadays, botanists (in the strict sense) study approximately 410,000 species of land plants of which some 391,000 species are vascular plants (including approximately 369,000 species of flowering plants), and approximately 20,000 are bryophytes. Botany originated in prehistory as herbalism with the efforts of early humans to identify – and later cultivate – edible, med ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
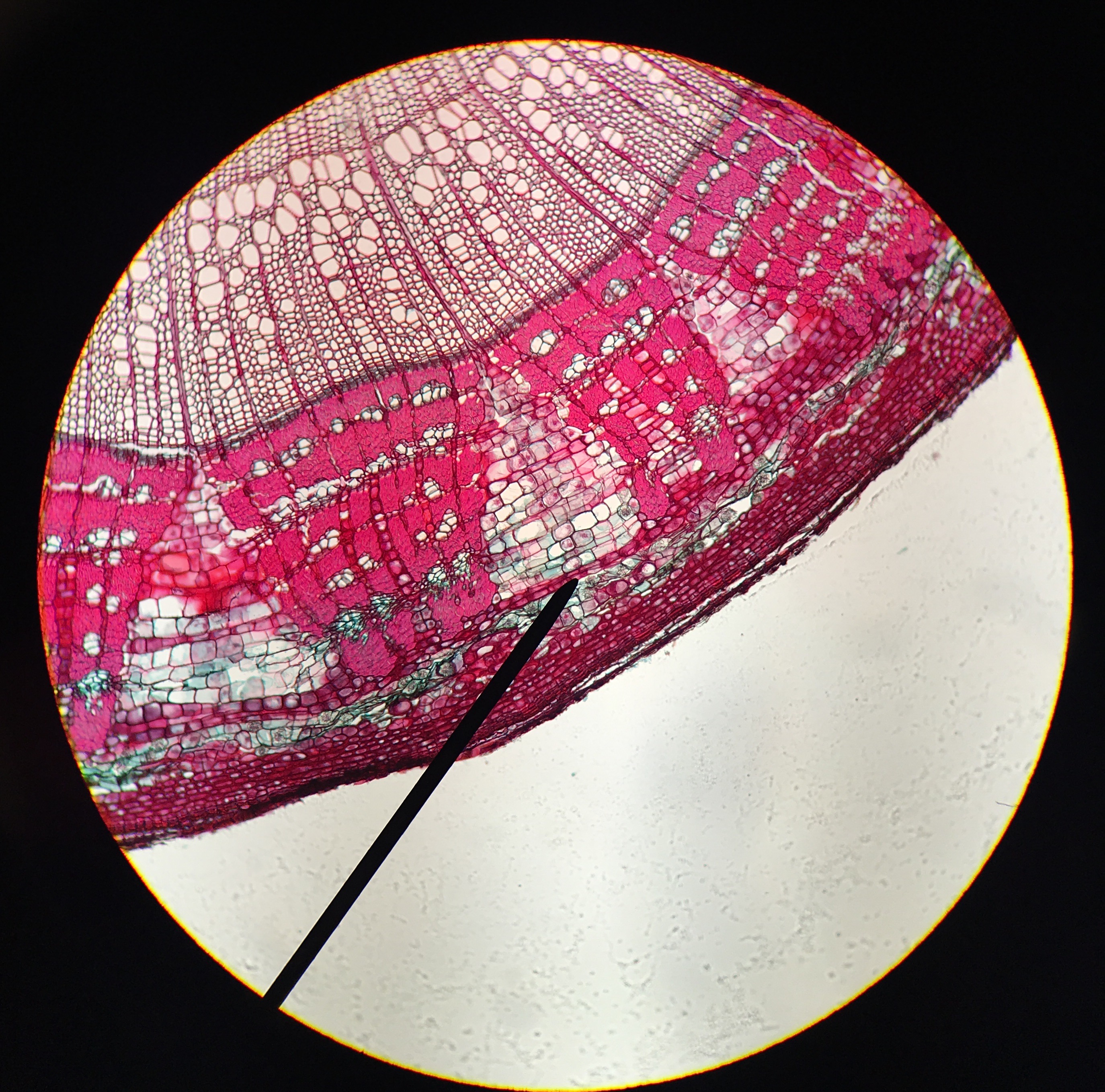
Tree Ring
Dendrochronology (or tree-ring dating) is the scientific method of dating tree rings (also called growth rings) to the exact year they were formed. As well as dating them, this can give data for dendroclimatology, the study of climate and atmospheric conditions during different periods in history from wood. Dendrochronology derives from Ancient Greek (), meaning "tree", (), meaning "time", and (), "the study of". Dendrochronology is useful for determining the precise age of samples, especially those that are too recent for radiocarbon dating, which always produces a range rather than an exact date. However, for a precise date of the death of the tree a full sample to the edge is needed, which most trimmed timber will not provide. It also gives data on the timing of events and rates of change in the environment (most prominently climate) and also in wood found in archaeology or works of art and architecture, such as old panel paintings. It is also used as a check in radiocarb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Kiel Alumni
A university () is an institution of higher (or tertiary) education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. Universities typically offer both undergraduate and postgraduate programs. In the United States, the designation is reserved for colleges that have a graduate school. The word ''university'' is derived from the Latin ''universitas magistrorum et scholarium'', which roughly means "community of teachers and scholars". The first universities were created in Europe by Catholic Church monks. The University of Bologna (''Università di Bologna''), founded in 1088, is the first university in the sense of: *Being a high degree-awarding institute. *Having independence from the ecclesiastic schools, although conducted by both clergy and non-clergy. *Using the word ''universitas'' (which was coined at its foundation). *Issuing secular and non-secular degrees: grammar, rhetoric, logic, theology, canon law, notarial law.Hunt Janin: "The university ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scientists From Hamburg
A scientist is a person who conducts scientific research to advance knowledge in an area of the natural sciences. In classical antiquity, there was no real ancient analog of a modern scientist. Instead, philosophers engaged in the philosophical study of nature called natural philosophy, a precursor of natural science. Though Thales (circa 624-545 BC) was arguably the first scientist for describing how cosmic events may be seen as natural, not necessarily caused by gods,Frank N. Magill''The Ancient World: Dictionary of World Biography'', Volume 1 Routledge, 2003 it was not until the 19th century that the term ''scientist'' came into regular use after it was coined by the theologian, philosopher, and historian of science William Whewell in 1833. In modern times, many scientists have advanced degrees in an area of science and pursue careers in various sectors of the economy such as academia, industry, government, and nonprofit environments.'''' History The roles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
18th-century German Botanists
The 18th century lasted from January 1, 1701 ( MDCCI) to December 31, 1800 ( MDCCC). During the 18th century, elements of Enlightenment thinking culminated in the American, French, and Haitian Revolutions. During the century, slave trading and human trafficking expanded across the shores of the Atlantic, while declining in Russia, China, and Korea. Revolutions began to challenge the legitimacy of monarchical and aristocratic power structures, including the structures and beliefs that supported slavery. The Industrial Revolution began during mid-century, leading to radical changes in human society and the environment. Western historians have occasionally defined the 18th century otherwise for the purposes of their work. For example, the "short" 18th century may be defined as 1715–1789, denoting the period of time between the death of Louis XIV of France and the start of the French Revolution, with an emphasis on directly interconnected events. To historians who expand t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1827 Deaths
Eighteen or 18 may refer to: * 18 (number), the natural number following 17 and preceding 19 * one of the years 18 BC, AD 18, 1918, 2018 Film, television and entertainment * ''18'' (film), a 1993 Taiwanese experimental film based on the short story ''God's Dice'' * ''Eighteen'' (film), a 2005 Canadian dramatic feature film * 18 (British Board of Film Classification), a film rating in the United Kingdom, also used in Ireland by the Irish Film Classification Office * 18 (''Dragon Ball''), a character in the ''Dragon Ball'' franchise * "Eighteen", a 2006 episode of the animated television series ''12 oz. Mouse'' Music Albums * ''18'' (Moby album), 2002 * ''18'' (Nana Kitade album), 2005 * '' 18...'', 2009 debut album by G.E.M. Songs * "18" (5 Seconds of Summer song), from their 2014 eponymous debut album * "18" (One Direction song), from their 2014 studio album ''Four'' * "18", by Anarbor from their 2013 studio album '' Burnout'' * "I'm Eighteen", by Alice Cooper commonl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1766 Births
Events January–March * January 1 – Charles Edward Stuart ("Bonnie Prince Charlie") becomes the new Stuart claimant to the throne of Great Britain, as King Charles III, and figurehead for Jacobitism. * January 14 – Christian VII becomes King of Denmark. * January 20 – Outside of the walls of the Thailand capital of Ayutthaya, tens of thousands of invaders from Burma (under the command of General Ne Myo Thihapate and General Maha Nawatra) are confronted by Thai defenders led by General Phya Taksin. The defenders are overwhelmed and the survivors take refuge inside Ayutthaya. The siege continues for 15 months before the Burmese attackers collapse the walls by digging tunnels and setting fire to debris. The city falls on April 9, 1767, and King Ekkathat is killed. * February 5 – An observer in Wilmington, North Carolina reports to the Edinburgh newspaper ''Caledonian Mercury'' that three ships have been seized by British men-of-war, on the ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moldenhawera
''Moldenhawera'' is a genus of flowering plants in the legume family, Fabaceae. It belongs to the subfamily Caesalpinioideae Caesalpinioideae is a botanical name at the rank of subfamily, placed in the large family Fabaceae or Leguminosae. Its name is formed from the generic name ''Caesalpinia''. It is known also as the peacock flower subfamily. The Caesalpinioideae .... References Caesalpinioideae Fabaceae genera {{Caesalpinioideae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Theory
In biology, cell theory is a scientific theory first formulated in the mid-nineteenth century, that living organisms are made up of Cell (biology), cells, that they are the basic structural/organizational unit of all organisms, and that all cells come from pre-existing cells. Cells are the basic unit of structure in all organisms and also the basic unit of reproduction. The three tenets of the cell theory are: # All living organisms are composed of one or more cells. # The cell is the basic unit of structure and organization in organisms. # Cells arise from pre-existing cells. The theory was once universally accepted, but now some biologists consider non-cellular life, non-cellular entities such as viruses living organisms, and thus disagree with the first tenet. As of 2021: "expert opinion remains divided roughly a third each between yes, no and don’t know". As there is no universally accepted definition of Life#Definition, life, discussion will continue. History With contin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stomata
In botany, a stoma (from Greek ''στόμα'', "mouth", plural "stomata"), also called a stomate (plural "stomates"), is a pore found in the epidermis of leaves, stems, and other organs, that controls the rate of gas exchange. The pore is bordered by a pair of specialized parenchyma cells known as guard cells that are responsible for regulating the size of the stomatal opening. The term is usually used collectively to refer to the entire stomatal complex, consisting of the paired guard cells and the pore itself, which is referred to as the stomatal aperture. Air, containing oxygen, which is used in respiration, and carbon dioxide, which is used in photosynthesis, passes through stomata by gaseous diffusion. Water vapour diffuses through the stomata into the atmosphere in a process called transpiration. Stomata are present in the sporophyte generation of all land plant groups except liverworts. In vascular plants the number, size and distribution of stomata varies widely. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambium (botany)
A cambium (plural cambia or cambiums), in plants, is a tissue layer that provides partially undifferentiated cells for plant growth. It is found in the area between xylem and phloem. A cambium can also be defined as a cellular plant tissue from which phloem, xylem, or cork grows by division, resulting (in woody plants) in secondary thickening. It forms parallel rows of cells, which result in secondary tissues. There are several distinct kinds of cambium found in plant stems and roots: * Cork cambium, a tissue found in many vascular plants as part of the periderm. * Unifacial cambium, which ultimately produces cells to the interior of its cylinder. * Vascular cambium, a lateral meristem in the vascular tissue of plants. Uses The cambium of many species of woody plants are edible; however, due to its vital role in the homeostasis and growth of woody plants, this may result in death of the plant if enough cambium is removed at once. The cambium can generally be eaten raw or cooke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
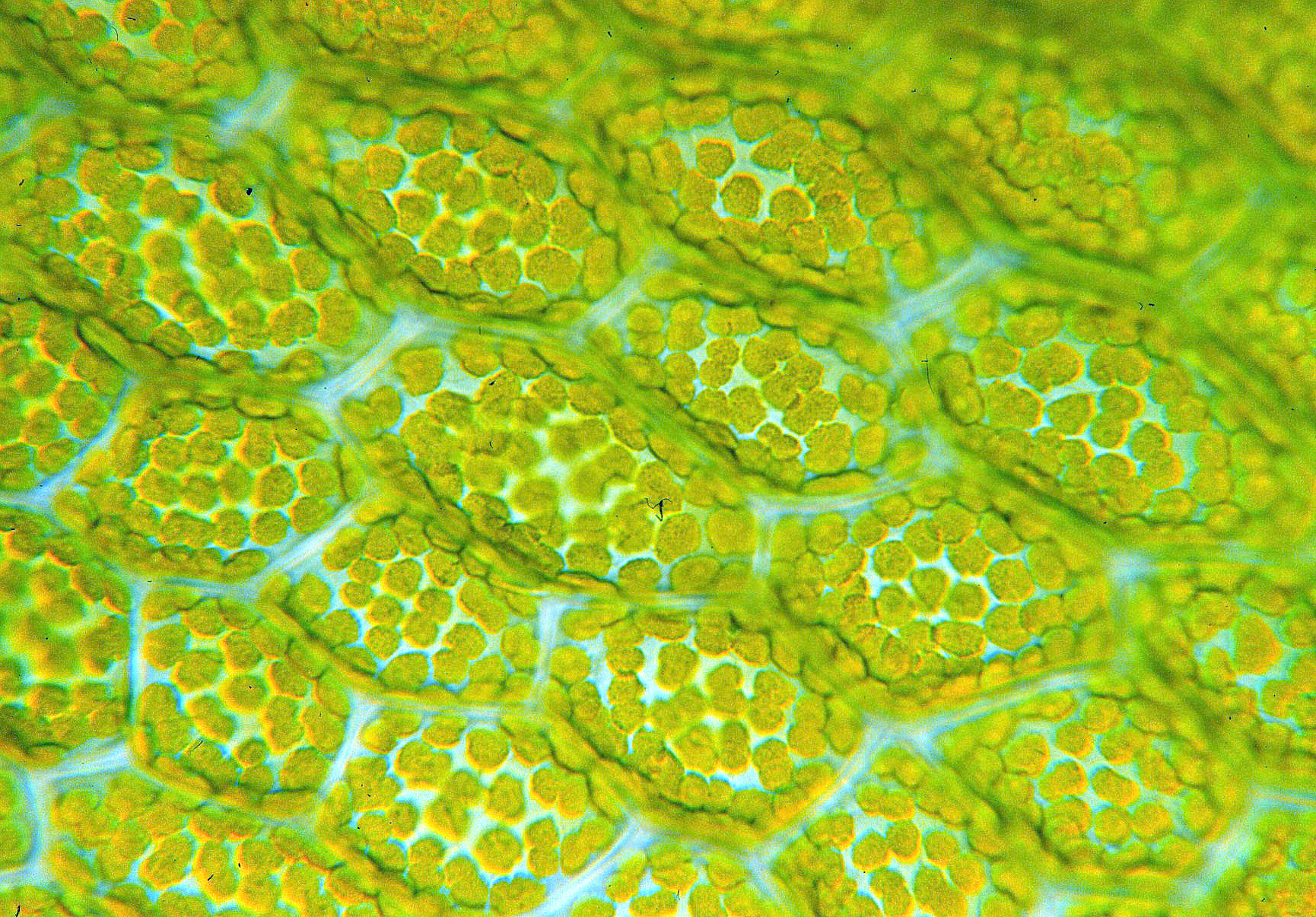
Plant Anatomy
Plant anatomy or phytotomy is the general term for the study of the internal structure of plants. Originally it included plant morphology, the description of the physical form and external structure of plants, but since the mid-20th century plant anatomy has been considered a separate field referring only to internal plant structure. Plant anatomy is now frequently investigated at the cellular level, and often involves the sectioning of tissues and microscopy. Structural divisions Some studies of plant anatomy use a systems approach, organized on the basis of the plant's activities, such as nutrient transport, flowering, pollination, embryogenesis or seed development. Others are more classically divided into the following structural categories: : Flower anatomy, including study of the Calyx, Corolla, Androecium, and Gynoecium : Leaf anatomy, including study of the Epidermis, stomata and Palisade cells : Stem anatomy, including Stem structure and vascular tissues, buds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |